Contents
1.Disable SELinux
First, disable selinux. selinux is a feature that improves auditing and security in Linux, but when it is enabled, it restricts the behavior of services and settings to a great extent. For this reason, selinux is basically disabled in most cases.
If you build a server while looking at a website and it does not work as expected, it may be due to the fact that selinux is enabled. So, don't forget to disable it after installation.
You can disable it by doing the following (In this page, the general user name is "jimy" and the host name is "Lepard")
After logging in as a general user, we will proceed with the known method of changing the permissions to the root user.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Lepard login: jimy Password: [jimy@Lepard ~]$ su - [root@Lepard ~]# getenforce ← Check the SELinux function. Enforcing ← SELinux enabled [root@Lepard ~]# setenforce 0 ← Disable the SELinux feature. [root@Lepard ~]# getenforce ← Review the SELinux feature. Permissive ← SELinux function is disabled |
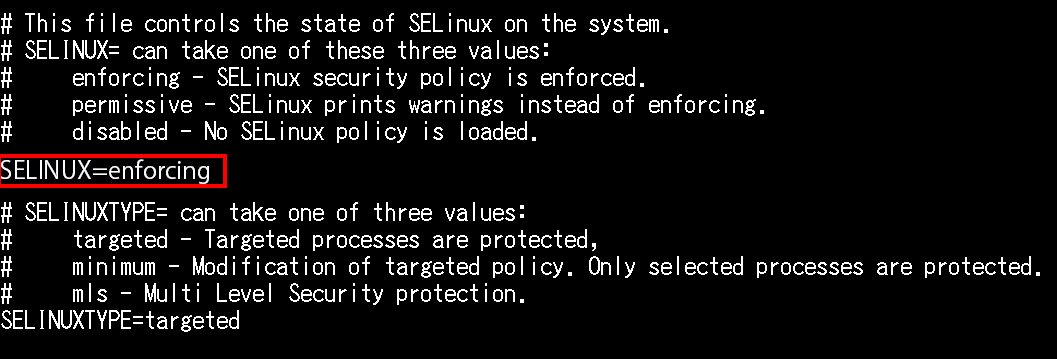
Reboot the server and seinux will be enabled again. To permanently disable selinux, modify the /etc/sysconfig/selinux file.
|
1 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux |
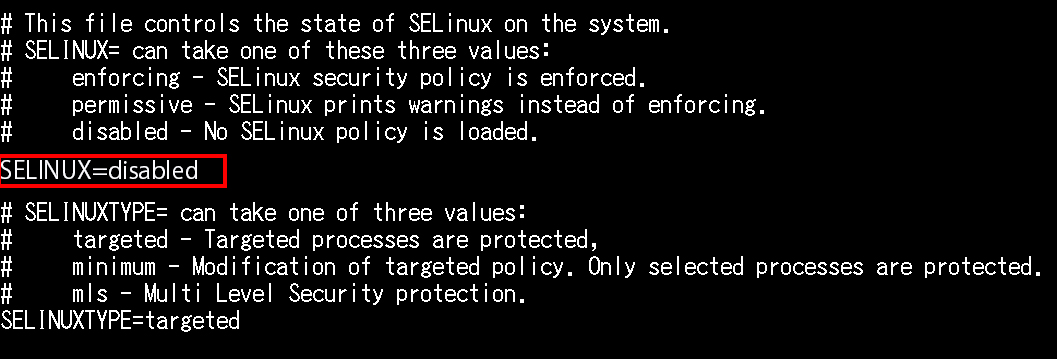
Change "SELINUX=enforcing" to "SELINUX=disabled"
After change
2.Setting up a remote connection using SSH
SSH is a service to connect to a server remotely, and is basically running right after the OS installation, but the default settings are somewhat insecure.
In this section, we will configure the settings to change the default settings and increase the security of the ssh connection.
2.1 Change the configuration file of SSH service.
Modify the configuration file to change the settings of the SSH service.
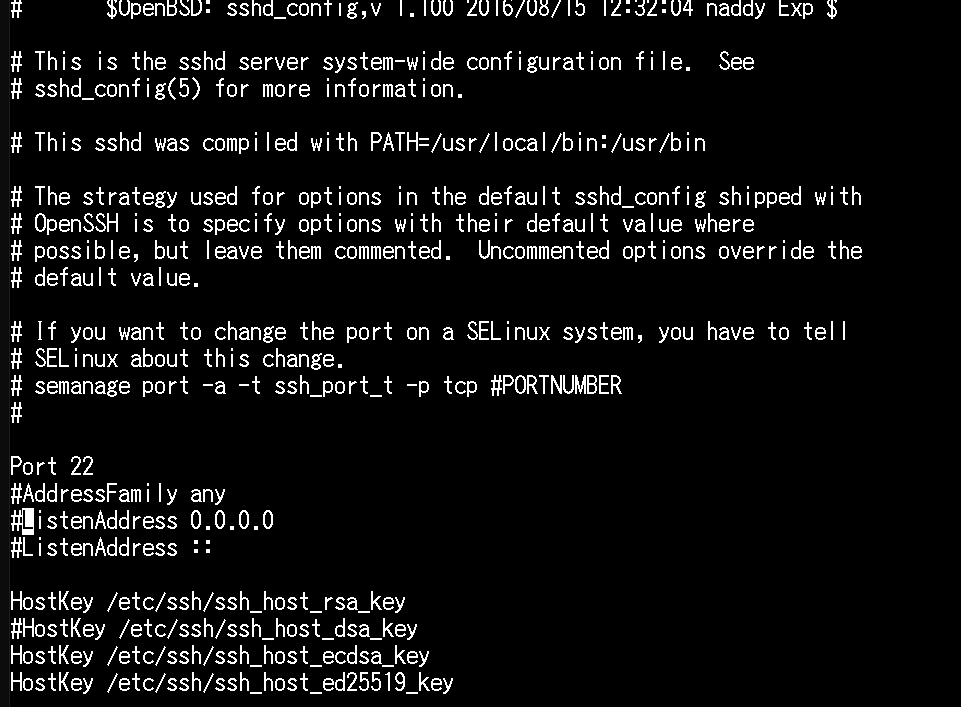
The configuration file for the SSH service is "/etc/ssh/sshd_config".
When you open it with the vi editor, you will see a screen like the following.
Restart SSH
|
1 |
# systemctl restart sshd.service |
3.How to set up a firewall (firewalld)
In Rocky Linux, the firewall is set to firewalld by default, which is enabled during OS installation.
To briefly explain firewalld, when setting up a communication control policy, communication permission/blocking rules are applied to predefined zones, and the zones are assigned to each NIC (network adapter).
3.1 How to use the firewall-cmd command to control "firewalld".
1)About Zones
Nine zones are provided by default.
| zone | Communication Permission Service | Description. |
| block | None All external connections are blocked | Setting cannot be changed Return "CIMP Pohibited" when blocked, return communication is also allowed when communicating from inside |
| dmz | ssh | Zones defined for dmz |
| drop | None All external communications are blocked | Cannot change settings Internal communication can be sent, but return communication from the outside is blocked, resulting in all communication not being possible. |
| external | ssh | Zone defined for use in connection with external networks, such as routers with IP masquerade enabled. |
| home | dhcpv6-client ipp-client mdns samba-client ssh | Zones defined for use at home, etc. |
| internal | dhcpv6-client ipp-client mdns samba-client | Zone defined for use in the internal network. |
| public | dhcpv6-client ssh | Zones defined for use in public places. |
| trusted | Allow all communication | Setting cannot be changed |
| work | dhcpv6-client ipp-client ssh | Zones defined for use in work areas such as the workplace. |
2)Command to check the status and settings of firewalld
①Check firewalld operation status
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd --state |
If "firewalld" is running, "running" will be displayed; if it is not running, "not running" will be displayed.
or
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since 金 2016-08-26 15:13:37 JST; 26min ago Main PID: 735 (firewalld) CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service mq735 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid If the system is stopped The message "Active: inactive (dead)" shows that firewalld is stopped. |
➁Show default zone settings
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# firewall-cmd --list-all public (default, active) interfaces: eno16777736 eno33554984 sources: services: dhcpv6-client ssh ports: masquerade: no forward-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: |
➂Show the settings for the specified zone.
The following example shows how to display the settings for the "dmz" zone
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
# firewall-cmd --zone=dmz --list-all dmz interfaces: sources: services: ssh ports: masquerade: no forward-ports: icmp-blocks: |
④About the "--permanent" option
In order to prevent the settings from being lost when the server is restarted or the "firewalld" service is restarted, the "--permanent" option must be used.
To prevent the settings from being lost when the server is restarted or the "firewalld" service is restarted, the "--permanent" option must be used to configure the settings. In this case, if the "--permanent" option is specified, the settings will not be reflected in "firewalld" as they are, so it is necessary to reflect the settings using "fiewall-cmd --reload".
As an example, to use the HTTP service permanently without being initialized even if the system is rebooted
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
⑤Adding and removing services to and from a zone
To add an already defined service to the zone, use "--add-service" to specify the serviceす
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd [--permanent] --zone=Zone name --add-service=Service Name |
If you want to add a service to the zone permanently, you need to configure it with the "--permanent" option.
Configuration example for adding a temporary service
|
1 2 3 |
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http success # firewall-cmd --reload |
Configuration example for permanently adding a service
Example of adding the "http" service to the "public" zone with the "--permanent" option
|
1 2 3 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http success # firewall-cmd --reload |
⑥service deletion
Use "--remove-service" to remove a service configured for a zone
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd [--permanent] --zone=Zone name --remove-service=Service Name |
Remove the "http" service from the "public" zone as an example
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-service=http success # firewall-cmd --reload success |
⑦Add or remove ports to a zone
To add a communication that has not been added as a service to the zone, add it by specifying the port number and protocol
Adding a port
Use "--add-port" to add a port to the zone
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd [--permanent] --zone=Zone name --add-port=Port number/protocol |
Added rules for port number 10022 and protocol TCP in the "public" zone.
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=10022/tcp success # firewall-cmd --reload success |
Use "--remove-port" to remove a port from a zone
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd [--permanent]--zone=Zone name --remove-port=Port number/protocol |
Delete the "10022/tcp" rule in the "public" zone that we just added
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-port=10022/tcp success # firewall-cmd --reload success |
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3333/tcp success # firewall-cmd --reload success |
Since firewalld is controlled by systemd, use the systemctl command to start and stop it.
Start firewalld
|
1 |
# systemctl start firewalld |
|
1 |
# systemctl stop firewalld |
If you check the operation status of the firewall (firewalld)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# systemctl status firewalld firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled) Active: active (running) since 月 2014-09-** 06:01:06 JST; 5min ago Main PID: 567 (firewalld) [abbreviation] WARNING: AllowZoneDrifting is enabled.> |
Back up "firewalld.conf".
|
1 |
# cp -p /etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf /etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf.original_bk |
|
1 2 3 |
# vi /etc/firewalld/firewalld.conf Change the last line to AllowZoneDrifting=no |
|
1 |
# systemctl restart firewalld |
4.Install the missing package
Starting with RHEL 8, yum has been changed to dnf by default. You can still use yum.
Install "Base" and "Other Development" with groupinstall.
※※ Caution.※※
Note that if you do yum -y update first, you will get an error installing Base.
In other words, do not set the kernel version to the latest version first.
|
1 |
# dnf -y groupinstall "Base" "Additional Development" |
5.Services to be stopped for security measures
Stop the following services that you think are unnecessary.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
# systemctl stop atd.service # systemctl disable atd.service # systemctl stop auditd.service # systemctl disable auditd.service # systemctl stop kdump.service # systemctl disable kdump.service # systemctl stop lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl disable lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl stop mdmonitor.service # systemctl disable mdmonitor.service # systemctl stop rngd.service # systemctl disable rngd.service # systemctl stop smartd.service # systemctl disable smartd.service # systemctl stop tuned.service # systemctl disable tuned.service # systemctl stop dm-event.socket # systemctl disable dm-event.socket |

