Contents
MariaDB Install
|
1 |
# dnf -y install mariadb-server |
MariaDBl Version Check
|
1 2 |
# mariadb -V mariadb Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.11.11-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapper |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# systemctl start mariadb # systemctl enable --now mariadb Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/mysql.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service'. Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service'. Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service'. |
Use the "mariadb_secure_installation" command to set the root user password and set some basic policies
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 |
# mariadb-secure-installation NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none): OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] y Enabled successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Change the root password? [Y/n] y New password: Re-enter new password: Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] y ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB! |
When accessing MariaDB after that
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# mariadb -u root -p Enter password: (Enter the new password set above) Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 13 Server version: 10.11.11-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> |
WordPress
1. Create database for WordPress
As an example, assume database [wp_db] database user [wp_user] password [?Y123456y]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
# mariadb -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 14 Server version: 10.11.11-MariaDB MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> create database wp_db; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> create user 'wp_user'@'localhost' identified by '?Y123456y'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on wp_db.* to 'wp_user'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> exit Bye |
2.Wordpress Install
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz # tar xvf latest.tar.gz |
3.Edit WordPress configuration file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
# cd wordpress/ # cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php # vi wp-config.php // ** Database settings - You can get this info from your web host ** // /** The name of the database for WordPress */^ define('DB_NAME', 'wp_db'); /** Database username */ define('DB_USER', 'wp_user'); /** Database password */ define('DB_PASSWORD', '?Y123456y'); Add the following to the last line If you do not do this, you will be asked for FTP connection information when you add the plugin. define('FS_METHOD', 'direct'); |
4.Moving Files
①Move the expanded contents under /var/www/html/[FQDN]
|
1 2 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # mv wordpress/* . |
After confirming that the files have been moved, delete the wordpress directory and downloaded latest.tar.gz
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # rm -R -f wordpress # rm latest.tar.gz |
Make apache the owner of the wordpress directory.
|
1 |
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/[FQDN] |
5.Starting wordpress installation
You can use your browser to go to http://[FQDN]/wp-admin/install.php
If successful, the following WordPress installation information input screen will be output.
"Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress."When displayed
Install php library-related software if not already installed.
|
1 2 3 |
# dnf install php-mysqlnd # systemctl restart mysqld # systemctl restart httpd |
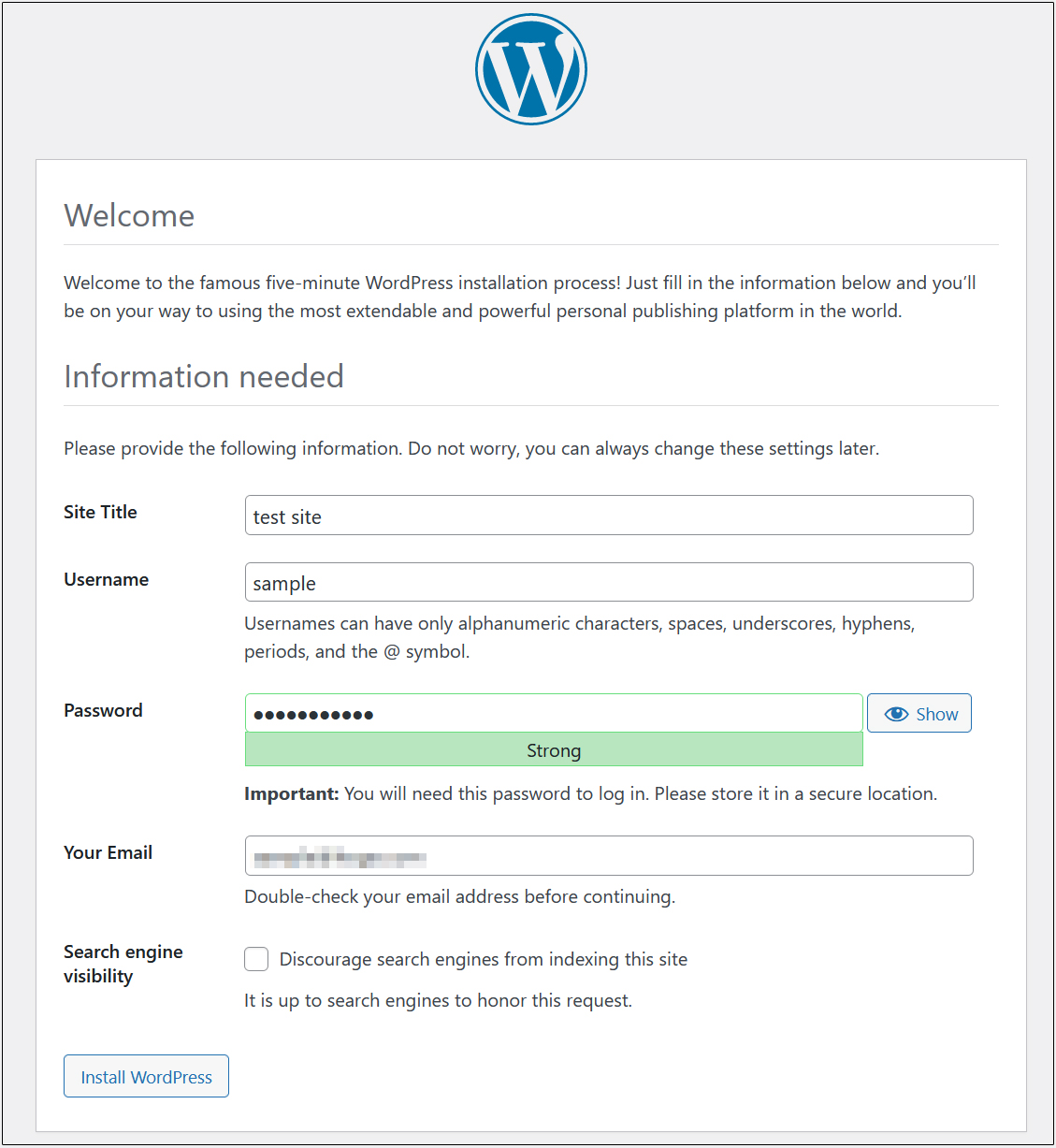
On the following input screen
Site Title Any name
Username Any name
Password Any password
Your Email Administrator's email address
Enter the information and click "Install WordPress". Remember to enter your "username" and "password" as they are required to access the WordPress administration screen.
Click on "Login"
User Name : The user name you have just set
Password : User's password you have just set
and click "Login".