Contents
Nagios Server, open-source integrated monitoring software
Nagios is an open-source monitoring solution that runs on Linux.
Nagios was developed by Ethan Galstad and first released in 1999. Subsequently, the project was enhanced as an open-source project by several contributors.
Nagios is designed to periodically check critical parameters of networks, applications, or servers. These parameters include microprocessor load, number of running processes, log files, disk and memory usage, as well as many other services such as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), and POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3).
To run Nagois, you need PHP, a database such as MySQL, and a web server such as Apache or Nginx. This time, we will proceed assuming all of these are already configured.
1.Nagios Installation
|
1 |
# zypper -n install nagios |
2. Creating Nagios Web Users
Create a user account to access the Nagios Web dashboard. This user account is used for authentication.
The default user name is nagiosadmin, defined as the preferred user name within the /etc/nagios/cgi.cfg file.
|
1 2 3 4 |
# htpasswd -c /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin New password: [password] Re-type new password: [again password] Adding password for user nagiosadmin |
Set ownership and permissions
|
1 2 |
# chown wwwrun:wwwrun /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users # chmod 640 /etc/nagios/htpasswd.users |
Restart Apache
|
1 |
# systemctl restart apache2 |
Open the HTTP service port in the firewall.
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
Create the necessary directories and set ownership.
|
1 2 |
# mkdir /var/lib/nagios/rw/ # chown -R nagios:nagios /var/lib/nagios/rw/ |
Editing Nagios Systemd Services
Add Type=forking to [Service]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
# vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios.service 1 [Unit] 2 Description=Network Monitor Nagios 3 After=syslog.target network.target 4 5 [Service] 6 # for details of the additional system hardening configuration please see 7 # https://en.opensuse.org/openSUSE:Security_Features#Systemd_hardening_effor t 8 ProtectSystem=full 9 ProtectHome=true 10 ProtectHostname=true 11 ProtectKernelTunables=true 12 ProtectKernelModules=true 13 ProtectControlGroups=true 14 RestrictRealtime=true 15 # end of system hardening 16 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg 17 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nagios -d /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg 18 ExecStopPost=/usr/bin/rm -f /var/spool/nagios/nagios.cmd 19 ExecReload=/usr/sbin/nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg 20 ExecReload=kill -HUP $MAINPI 21 Type=forking ←Additional 22 [Install] 23 WantedBy=multi-user.target 24 Alias=monitoring_daemon.service |
Start and Enable Nagios Services
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl start nagios # systemctl enable nagios --now Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/monitoring_daemon.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios.service'. Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nagios.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios.service'. |
Restart the system
|
1 |
# shutdown -r now |
Verify that the service is running
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
# systemctl status nagios ● nagios.service - Network Monitor Nagios Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2025-10-09 21:00:20 JST; 2s ago Invocation: f228ddb94b3c48b1aff332fca95c2bd3 Process: 2346 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 2348 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nagios -d /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 2349 (nagios) Tasks: 8 (limit: 9397) CPU: 88ms CGroup: /system.slice/nagios.service tq2349 /usr/sbin/nagios -d /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg tq2351 /usr/sbin/nagios --worker /var/lib/nagios/rw/nagios.qh tq2352 /usr/sbin/nagios --worker /var/lib/nagios/rw/nagios.qh tq2353 /usr/sbin/nagios --worker /var/lib/nagios/rw/nagios.qh tq2354 /usr/sbin/nagios --worker /var/lib/nagios/rw/nagios.qh tq2355 /usr/sbin/nagios -d /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg tq2356 /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ping -H 127.0.0.1 -w 3000.0,80% -c 5000.0,100% -p 5 mq2357 /usr/bin/ping -4 -n -U -w 30 -c 5 127.0.0.1 Oct 09 21:00:20 Lepard nagios[2349]: qh: Socket '/var/lib/nagios/rw/nagios.qh' successfully initialized Oct 09 21:00:20 Lepard nagios[2349]: qh: core query handler registered Oct 09 21:00:20 Lepard nagios[2349]: qh: echo service query handler registered Oct 09 21:00:20 Lepard nagios[2349]: qh: help for the query handler registered |
3. Access the Nagios Web Interface
Access http://[IP_Address]/nagios/ in any browser. Enter nagiosadmin for [Username] and the password you specified when creating the user above for [Password], then click [Sign in].
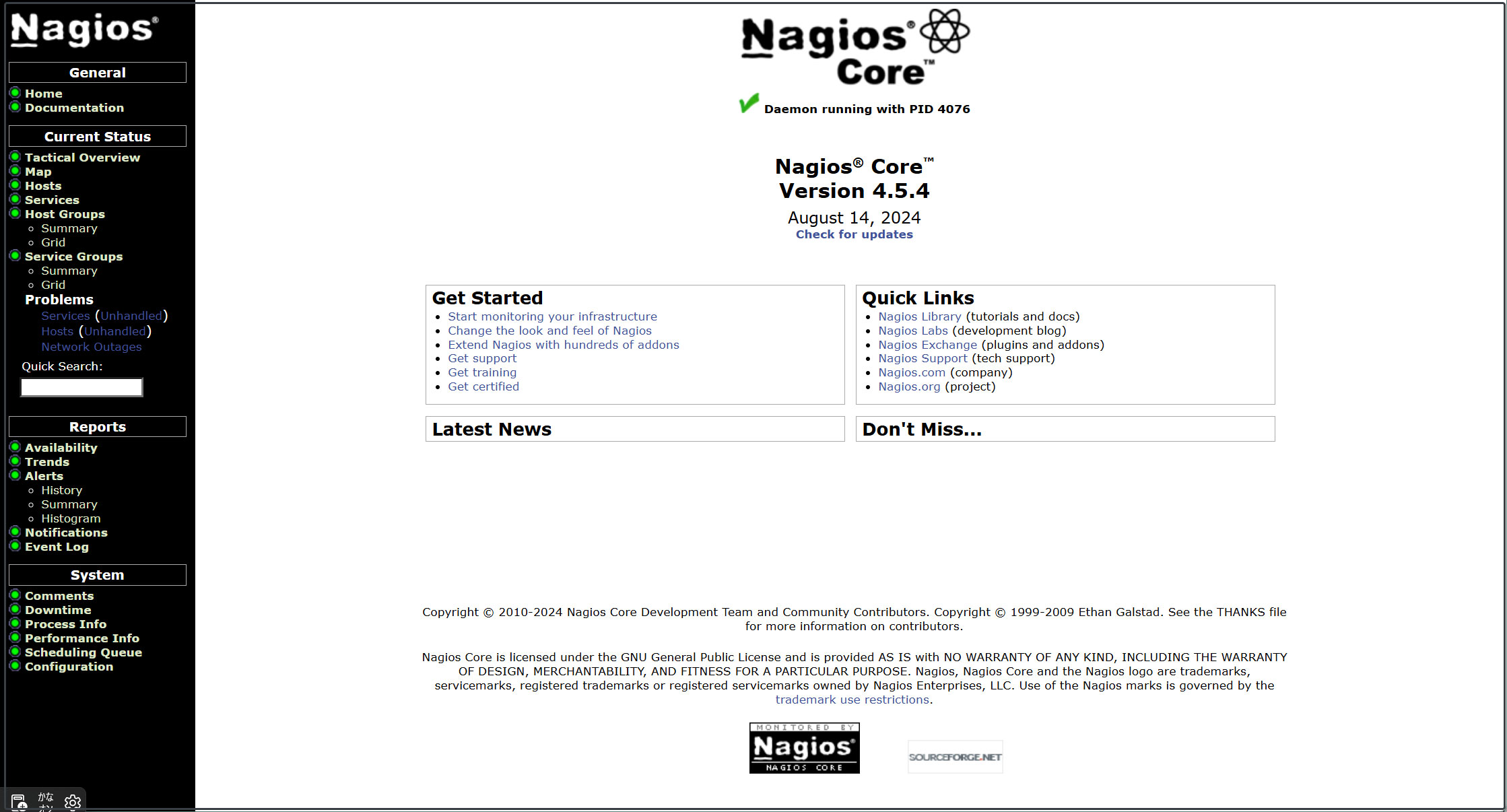
After successfully logging in, the following dashboard will be displayed.
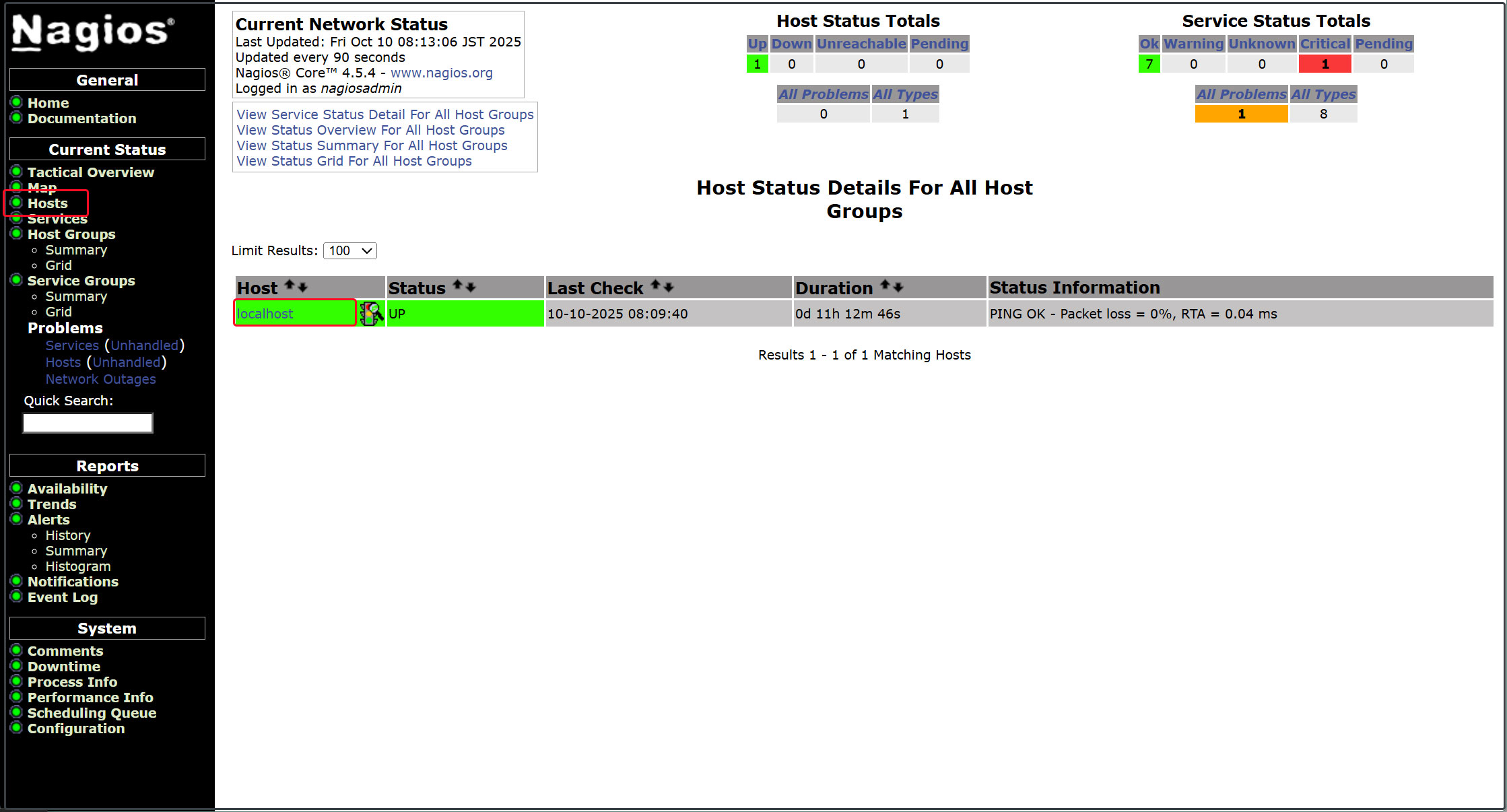
Display host availability
Click [Hosts] in the left menu
Click [Tactical Overview] in the left menu to view monitoring data.
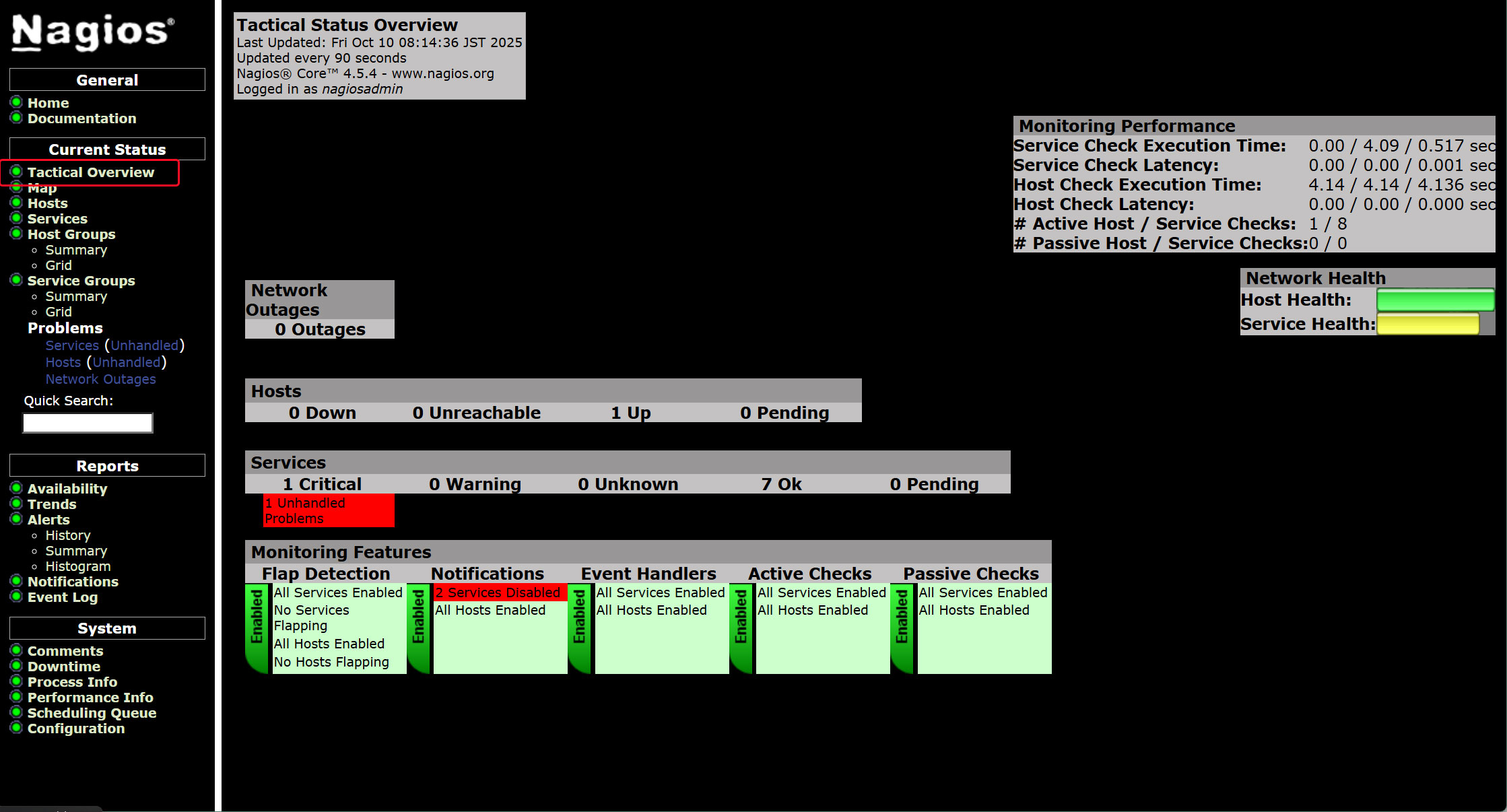
Click [Current Status] [Services] in the left menu.
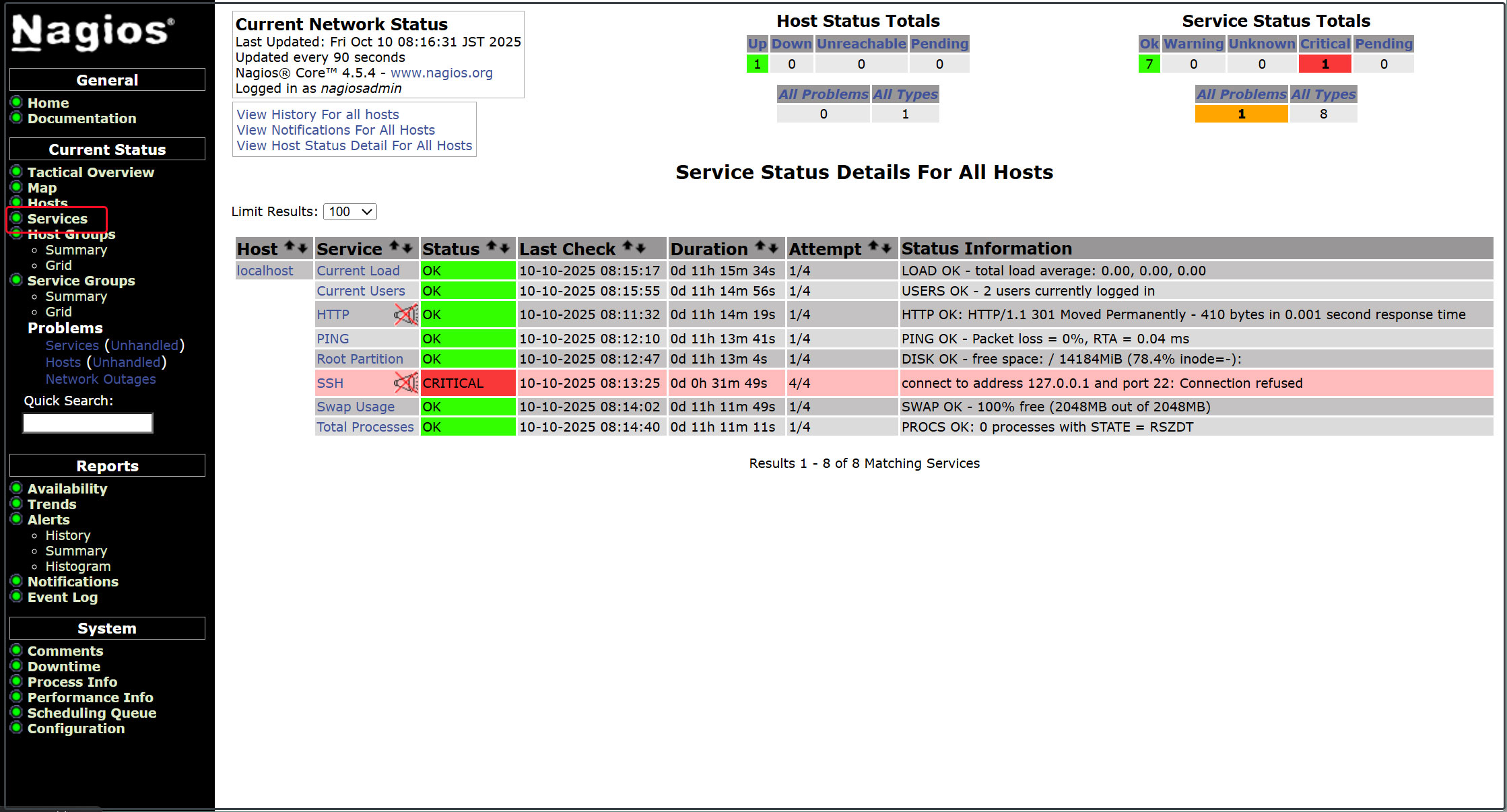
4. Configuring the Nagios Agent
What is required to monitor agents
Nagios plugins for data collection
NRPE Agent to execute the plugins
4.1 Nagios plugins
Nagios plugins are located in the /usr/lib/nagios/plugins directory. To list all plugins available on the system, list this directory.
|
1 |
# ls /usr/lib/nagios/plugins |
The following nagios-plugins are available:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
check_breeze check_icmp check_ntp check_smtp check_by_ssh check_ide_smart check_ntp_peer check_spop check_clamd check_ifoperstatus check_ntp_time check_ssh check_cluster check_ifstatus check_nwstat check_ssmtp check_dhcp check_imap check_oracle check_swap check_dig check_ircd check_overcr check_tcp check_disk check_jabber check_ping check_time check_disk_smb check_load check_pop check_udp check_dns check_log check_procs check_ups check_dummy check_mailq check_procs_perf check_users check_file_age check_mrtg check_real check_wave check_flexlm check_mrtgtraf check_rpc negate check_ftp check_nntp check_rta_multi urlize check_host check_nntps check_sensors utils.pm check_http check_nt check_simap utils.sh |
4.2 Installing the Nagios NRPE Agent
|
1 |
# zypper -n install nrpe |
Version Check
|
1 2 3 |
# nrpe -V NRPE - Nagios Remote Plugin Executor Version: 4.1.1 |
Start the service and enable it
|
1 2 3 |
# systemctl enable --now nrpe.service Created symlink '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nrpe.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/nrpe.service'. |
Check the status of the NRPE agent
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
# systemctl status nrpe ● nrpe.service - Nagios Remote Plugin Executor Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nrpe.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2025-10-10 08:51:52 JST; 2s ago Invocation: a633bdbd19284878977d0a3404dd7864 Docs: http://www.nagios.org/documentation Main PID: 5695 (nrpe) Tasks: 1 (limit: 9397) CPU: 46ms CGroup: /system.slice/nrpe.service mq5695 /usr/sbin/nrpe -c /etc/nrpe.cfg -f Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard systemd[1]: Started Nagios Remote Plugin Executor. Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard nrpe[5695]: Starting up daemon Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard nrpe[5695]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 5666. Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard nrpe[5695]: socket: Address family not supported by protocol Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard nrpe[5695]: Listening for connections on port 5666 Oct 10 08:51:52 Lepard nrpe[5695]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,::1 |
socket: Address family not supported by protocol
The message "IPv6 related" appears, but since we are not using IPv6 this time, we will ignore it and proceed.
Open the NRPE port on the firewall
NRPE uses TCP port 5666 by default. If a firewall is in operation, open this port to allow external checks from the Nagios monitoring server.
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-port=5666/tcp # firewall-cmd --reload |
Verify that port 5666/tcp is listening.
|
1 2 3 |
# ss -altnp | grep 5666 LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* users:(("nrpe",pid=5695,fd=4)) |
5. Add Monitoring Host
Add the following server as a host and configure it as a target for simple ping-based availability monitoring.
OS : Ubuntu24.04
IP address : 192.168.11.85
5.1 Editing Configuration Files
|
1 2 3 |
# vi /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg Line 51 cfg_dir=/etc/nagios/servers Unlock comments |
5.2 Directory Creation
|
1 2 3 |
# mkdir /etc/nagios/servers # chgrp nagios /etc/nagios/servers # chmod 750 /etc/nagios/servers |
5.3 Create New Definition File
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# vi /etc/nagios/servers/korodes.cfg define host { use linux-server host_name korodes alias korodes address 192.168.11.85 } define service { use generic-service host_name korodes service_description PING check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60% } |
5.4 Nagios Server Restart
|
1 |
# systemctl restart nagios.service |
Log in to the Nagios server (http://[server IP address]/nagios) and view Hosts to see that the host has been added.
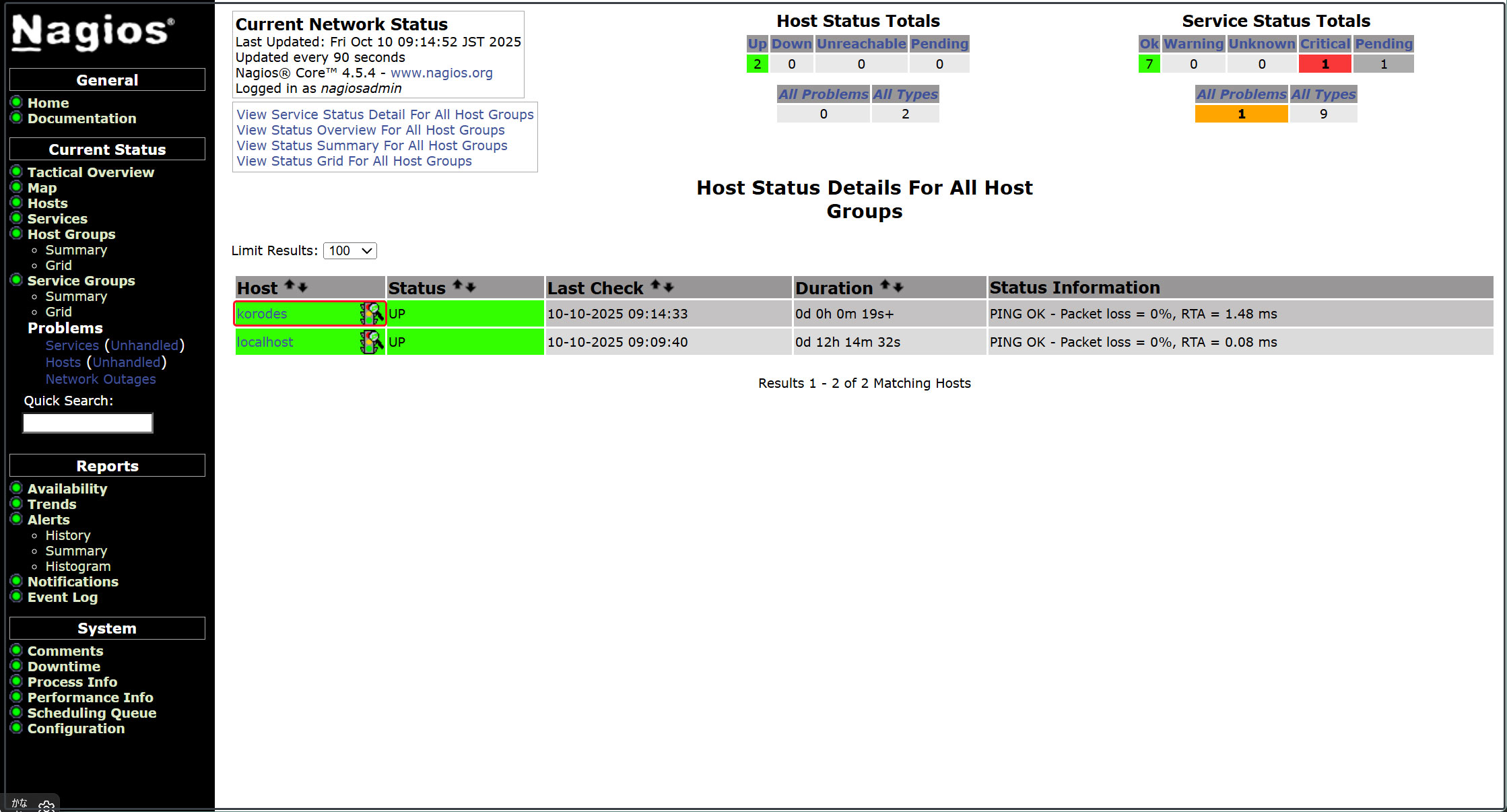
6. Add Monitoring Service
Add the monitoring service to the host added above.
OS : Ubuntu24.04
IP address : 192.168.11.85
6.1 Settings on the monitored server
6.1.1 Install the agent on the monitored host
Install nrpe and representative service plugins from EPEL
|
1 |
# apt install nagios-nrpe-server |
6.1.2 Editing Configuration Files
# vi /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
Line 106: Add hosts to allow connections (specify Nagios server)
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,::1,192.168.11.83
Line 122: Allow command arguments
dont_blame_nrpe=1
Lines 300-304: Commented out and added
# command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users -w 5 -c 10
# command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -r -w .15,.10,.05 -c .30,.25,.20
# command[check_hda1]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
# command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
# command[check_total_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 150 -c 200
command[check_by_ssh]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_by_ssh $ARG1$
command[check_dhcp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_dhcp $ARG1$
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk $ARG1$
command[check_file_age]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_file_age $ARG1$
command[check_ftp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ftp $ARG1$
command[check_http]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_http $ARG1$
command[check_imap]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_imap $ARG1$
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load $ARG1$
command[check_log]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_log $ARG1$
command[check_mysql]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_mysql $ARG1$
command[check_ntp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ntp $ARG1$
command[check_ntp_peer]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ntp_peer $ARG1$
command[check_ntp_time]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ntp_time $ARG1$
command[check_ping]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ping $ARG1$
command[check_pop]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_pop $ARG1$
command[check_spop]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_spop $ARG1$
command[check_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs $ARG1$
command[check_smtp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_smtp $ARG1$
command[check_ssmtp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ssmtp $ARG1$
command[check_ssh]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ssh $ARG1$
command[check_swap]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_swap $ARG1$
command[check_tcp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_tcp $ARG1$
command[check_udp]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_udp $ARG1$
command[check_ups]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ups $ARG1$
command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users $ARG1$
6.1.3 Enable and start the NRPE server
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
# systemctl enable --now nagios-nrpe-server # systemctl start nagios-nrpe-server # /etc/init.d/nagios-nrpe-server status ● nagios-nrpe-server.service - Nagios Remote Plugin Executor Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios-nrpe-server.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2025-10-10 13:34:03 JST; 40s ago Docs: http://www.nagios.org/documentation Main PID: 11474 (nrpe) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4548) Memory: 736.0K (peak: 864.0K) CPU: 11ms CGroup: /system.slice/nagios-nrpe-server.service mq11474 /usr/sbin/nrpe -n -c /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg -f Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan systemd[1]: Started nagios-nrpe-server.service - Nagios Remote Plugin Executor. Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan (nrpe)[11474]: nagios-nrpe-server.service: Referenced but unset environment variable evaluates to an empty string: NRPE_OPTS Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Starting up daemon Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Server listening on 0.0.0.0 port 5666. Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Server listening on :: port 5666. Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Warning: Daemon is configured to accept command arguments from clients! Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Listening for connections on port 5666 Oct 10 13:34:03 Lan nrpe[11474]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,::1,192.168.11.83 |
6.1.4 Open NRPE ports 5666/tcp and 5666/udp on the firewall.
|
1 2 3 |
# ufw allow 5666/tcp # ufw allow 5666/udp # ufw reload |
6.2 Nagios Server-Side Configuration
6.2.1 Installing the NRPE Plugin
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
# wget https://github.com/NagiosEnterprises/nrpe/releases/download/nrpe-4.1.3/nrpe-4.1.3.tar.gz # tar xzf nrpe-4.1.3.tar.gz # cd nrpe-4.1.3 # zypper install gcc make # ./configure # make all # make install-plugin |
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 -d /usr/local/nagios/bin
/usr/bin/install -c -m 755 ../uninstall /usr/local/nagios/bin/nrpe-uninstall
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/libexec
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/libexec
/usr/bin/install -c -m 775 -o nagios -g nagios check_nrpe /usr/local/nagios/libexec
6.2.2 Copy to the Nagios plugin directory
|
1 |
# cp /usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe /usr/lib/nagios/plugins |
6.2.3 Editing commands.cfg
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# vi /etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg # Add to the last line define command { command_name check_nrpe command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$ } |
6.2.4 Edit and add to the korodes.cfg file created when adding the host earlier.
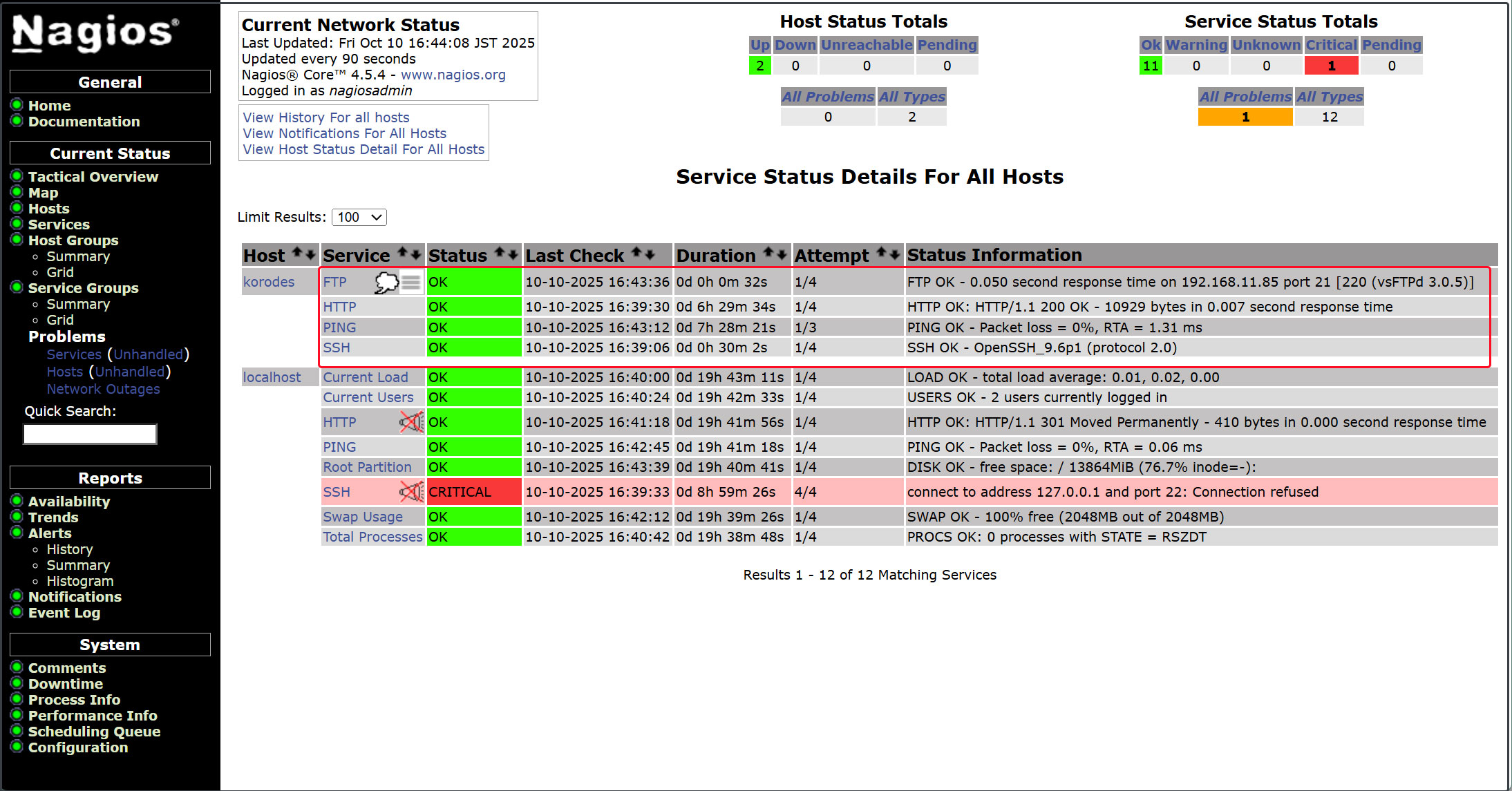
This time, let's add HTTP, SSH, and FTP.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
# vi /etc/nagios/servers/korodes.cfg # Add the following: # 'HTTP' command definition define service{ use local-service host_name korodes service_description HTTP check_command check_http } # 'SSH' command definition define service{ use local-service host_name korodes service_description SSH check_command check_ssh } # 'FTP' command definition define service{ use local-service host_name korodes service_description FTP check_command check_ftp } |
6.2.5 Nagios Restart
|
1 |
# systemctl restart nagios.service |
6.2.6 Access http://[Nagios Server IP Address]/nagios
The newly added monitoring service appears as shown in the figure below.