Contents
1.Configuring Remote Connections via SSH
SSH is a service for remotely connecting to servers, and it typically runs immediately after OS installation. However, the default configuration has some security vulnerabilities.
Here, we will modify the default settings to enhance the security of SSH connections.
1.1 Modifying the SSH Service Configuration File
Modify the configuration file to change the SSH service settings.
The path for the SSH service configuration file has been changed from the previous "/etc/ssh/sshd_config" to "/usr/etc/ssh/sshd_config".
|
1 |
# vi /usr/etc/ssh/sshd_config |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
Line 20: Uncomment and change to any port number other than the default port. Port 2244 Line 22: Uncomment ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 Line 39: Uncomment PermitRootLogin prohibit-password |
Restarting SSH
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable sshd.service # systemctl restart sshd.service |
If you leave it as is, you won't be able to connect remotely via SSH after the next reboot. Please open SSH port 2244 in the following firewall settings.
2.How to configure the firewall (firewalld)
On openSUSE, firewalld is set as the default firewall and is enabled during OS installation.
To briefly explain "firewalld," when configuring communication control policies, it applies rules to allow or block traffic for predefined zones, then assigns those zones to each NIC (network interface card).
2.1 How to Use the "firewall-cmd" Command to Control "firewalld"
①firewalld operational status check
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd --state |
If "firewalld" is running, it will display "running"; if it is stopped, it will display "not running".
OR
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-10-05 07:22:58 JST; 8min ago Invocation: fcd96fa04a9d449f852fa930fc0f1729 Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 881 (firewalld) Tasks: 2 (limit: 2228) CPU: 520ms CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service mq881 /usr/bin/python3.13 /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid Oct 05 07:22:57 lepard systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon... Oct 05 07:22:58 lepard systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon. |
※When stopped
Active: inactive (dead) is displayed, indicating that firewalld is stopped.
➁About the "--permanent" Option
To prevent settings from being lost when restarting the server or the "firewalld" service,
you must configure settings using the "--permanent" option. When configuring with the "--permanent" option, the settings will not be reflected in "firewalld" immediately; you must use "firewall-cmd --reload" to apply the changes.
For example, to ensure an HTTP service remains available permanently without being reset upon system restart,
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
➂Startup and Shutdown Procedures
firewalld is controlled by systemd, so use the systemctl command to start and stop it.
|
1 2 3 4 |
Starting firewalld # systemctl start firewalld Stopping firewalld # systemctl stop firewalld |
2.2 Release the modified SSH port 2244
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-port=2244/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
3.Remote connection from Windows
Windows Settings
Begin configuring remote connections from Windows. Use the terminal emulator "Tera Term".
Launch Tera Term, cancel the startup screen, then select "New Connection" from the "File" menu in Tera Term.
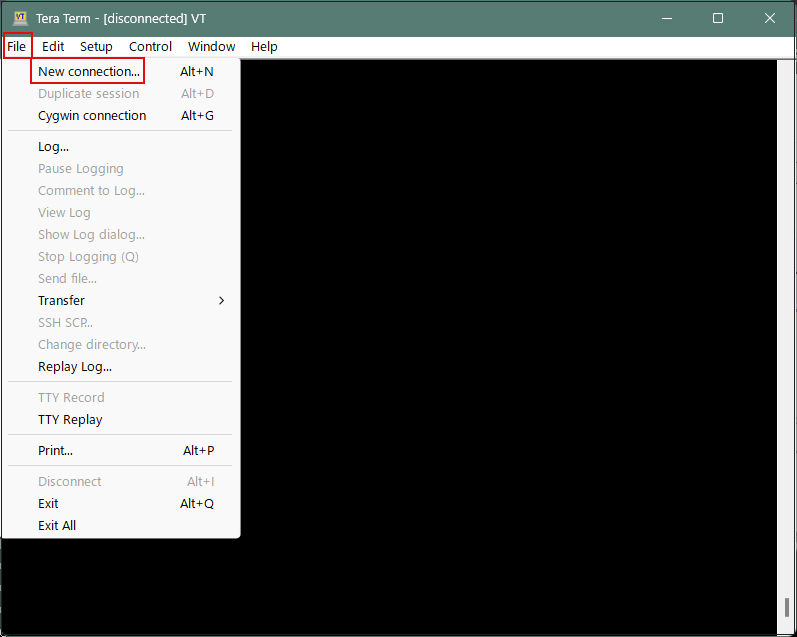
The next screen will appear, so enter the following:
Host: The server's IP address
TCP port: The SSH port number you changed above
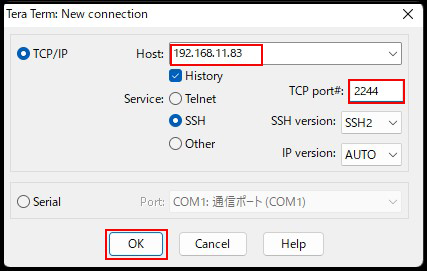
Click "OK" to proceed to the security confirmation screen. Check the box next to "Replace the exit key with this new key" and click "Continue".
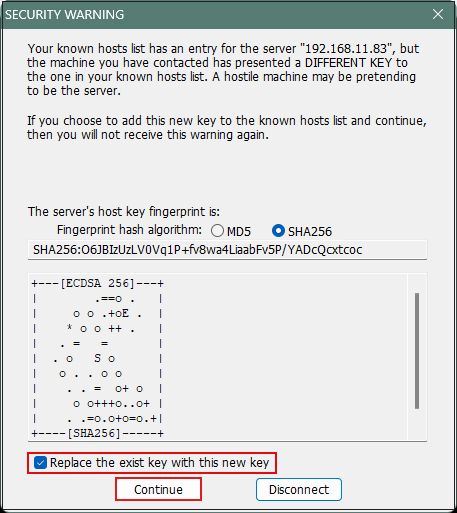
The next screen will appear
User name: General login username
Passphrase: Password for the above user
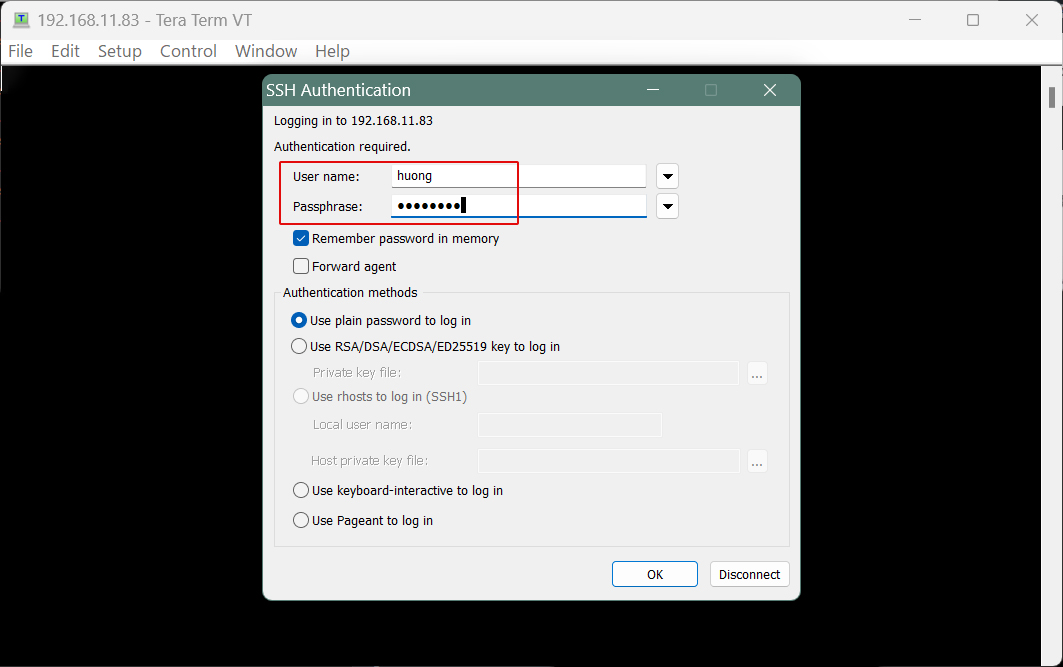
If the information is correct, you should be able to log in normally.
4. NTP Server Configuration
Install Chrony to set up an NTP server for time synchronization. Note that NTP uses port 123/UDP.
① Chrony Installation
|
1 |
# zypper -n install chrony |
➁ Chrony Configuration
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# vi /etc/chrony.conf # Line 3: Comment it out and add the following below it. #! pool pool.ntp.org iburst pool ntp.nict.jp iburst # Around line 25: Added the permitted range for time synchronization. allow 192.168.11.0/24 |
|
1 2 |
# systemctl start chronyd # systemctl enable chronyd |
➂ Opening the NTP port
If Firewalld is enabled, you must allow the NTP service. Note that NTP uses port 123/UDP.
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp --permanent success # firewall-cmd --reload success |
④ Functionality Verification
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# chronyc sources MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== ^* ntp-b2.nict.go.jp 1 6 77 23 +389us[ +725us] +/- 5339us ^+ ntp-a2.nict.go.jp 1 6 77 21 -1649us[-1649us] +/- 7218us ^- ntp-a3.nict.go.jp 1 6 77 22 -518us[ -518us] +/- 6755us ^+ ntp-k1.nict.jp 1 6 77 22 -240us[ -240us] +/- 4109us |

