Contents
1. Apache2 Install
1.1 httpd Install
|
1 |
# dnf -y install httpd |
Version Check
|
1 2 3 |
# httpd -v Server version: Apache/2.4.57 (MIRACLE LINUX) Server built: Aug 5 2024 00:00:00 |
1.2 Apache Configuration
①Edit httpd.conf file
|
1 |
# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf_bak |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf Line 91 : Administrator address specification ServerAdmin <mail address> Line 101 : add 「#ServerName www.example.com:80」 ServerName <domain> Line 149 : Change (Delete Indexes) Options FollowSymLinks Line 156 : Change AllowOverride All Line 169 : File names accessible by directory name only Add "index.php index.cgi index.htm" Add to the last line ServerTokens Prod |
②Firewalld is enabled, HTTP service permission is required; HTTP uses [80/TCP]
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
➂Apache Auto-Start Configuration
|
1 2 3 |
# systemctl start httpd # systemctl enable httpd Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service. |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# systemctl status httpd ● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-09-09 19:21:12 JST; 23s ago Docs: man:httpd.service(8) Main PID: 4387 (httpd) Status: "Total requests: 0; Idle/Busy workers 100/0;Requests/sec: 0; Bytes served/sec: 0 B/sec" Tasks: 177 (limit: 10886) Memory: 26.4M CPU: 58ms CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service tq4387 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND tq4388 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND tq4389 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND tq4390 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND mq4391 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND Sep 09 19:21:12 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server... Sep 09 19:21:12 Lepard systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server. Sep 09 19:21:12 Lepard httpd[4387]: Server configured, listening on: port 80 |
④operation check
If you access http://[server IP address] and see the MIRACLE LINUX Test Page as shown below, it is OK.
⑤Hide the Welcome page, create a new index.html file as a Test Page, and check apache operation
Rename the welcome page
|
1 |
# mv /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf.org |
Create HTML test page
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# vi /var/www/html/index.html <html> <body> <div style="width: 100%; font-size: 40px; font-weight: bold; text-align: center;"> Apache Test Page </div> </body> </html> |
If you access http://[server IP] and the Test Page is displayed as shown below, it is OK.

1.3 Virtual Host Settings
Assign and configure the domain name [FQDN] to the document root [/var/www/html/FQDN] directory for virtual host operation
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/vhost.conf Virtual Host Domain Settings <VirtualHost *:80> DocumentRoot /var/www/html/[FQDN] ServerName [FQDN] ServerAdmin <Email Address> ErrorLog logs/[FQDN].error_log CustomLog logs/[FQDN].access_log combined </VirtualHost> <Directory "/var/www/html/[FQDN]"> Options FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All </Directory> |
Creating a Document Directory
|
1 |
# mkdir /var/www/html/[FQDN] |
Restart Apache
|
1 |
# systemctl restart httpd |
2. Use of CGI Scripts
①CGI availability check
The following is displayed and available under “/var/www/cgi-bin/”.
|
1 2 |
# grep -n "^ *ScriptAlias" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 253: ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/var/www/cgi-bin/" |
②Create test scripts and check operation
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# vi /var/www/cgi-bin/index.cgi Describe the following contents #!/usr/bin/python3 print("Content-type: text/html\n") print("CGI Script Test Page") |
|
1 2 3 |
# chmod 755 /var/www/cgi-bin/index.cgi # curl localhost/cgi-bin/index.cgi CGI Script Test Page |
3. PHP installation and configuration
①Install
|
1 |
# dnf -y install php php-mbstring php-pear |
②Version Check
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# php -v PHP 8.0.30 (cli) (built: Aug 3 2023 17:13:08) ( NTS gcc x86_64 ) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.0.30, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.0.30, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies |
If you are installing Php8.3, you will need the Remi repository, so install it if you have not already done so.
|
1 2 |
# dnf -y install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm # dnf -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-9.rpm |
Stop PHP once
|
1 |
# dnf module disable php |
PHP 8.3 Install
|
1 |
# dnf module install php:remi-8.3 |
php-fpm configuration
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable php-fpm Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/php-fpm.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service. |
Apache Restart
After PHP installation, restarting Apache will invoke PHP-FPM (FPM : FastCGI Process Manager) by default, and php-fpm service will be started in conjunction with httpd startup.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# systemctl restart httpd # systemctl status php-fpm ● php-fpm.service - The PHP FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-09-09 19:34:09 JST; 6s ago Main PID: 7197 (php-fpm) Status: "Ready to handle connections" Tasks: 6 (limit: 10886) Memory: 14.6M CPU: 41ms CGroup: /system.slice/php-fpm.service tq7197 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php-fpm.conf)" tq7198 "php-fpm: pool www" tq7199 "php-fpm: pool www" tq7200 "php-fpm: pool www" tq7201 "php-fpm: pool www" mq7202 "php-fpm: pool www" Sep 09 19:34:09 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting The PHP FastCGI Process Manager... Sep 09 19:34:09 Lepard systemd[1]: Started The PHP FastCGI Process Manager. |
④Confirmation of PHP operation
Create the following files
|
1 2 3 4 |
# vi /var/www/html/[FQDN]/test.php <?php phpinfo(); ?> |
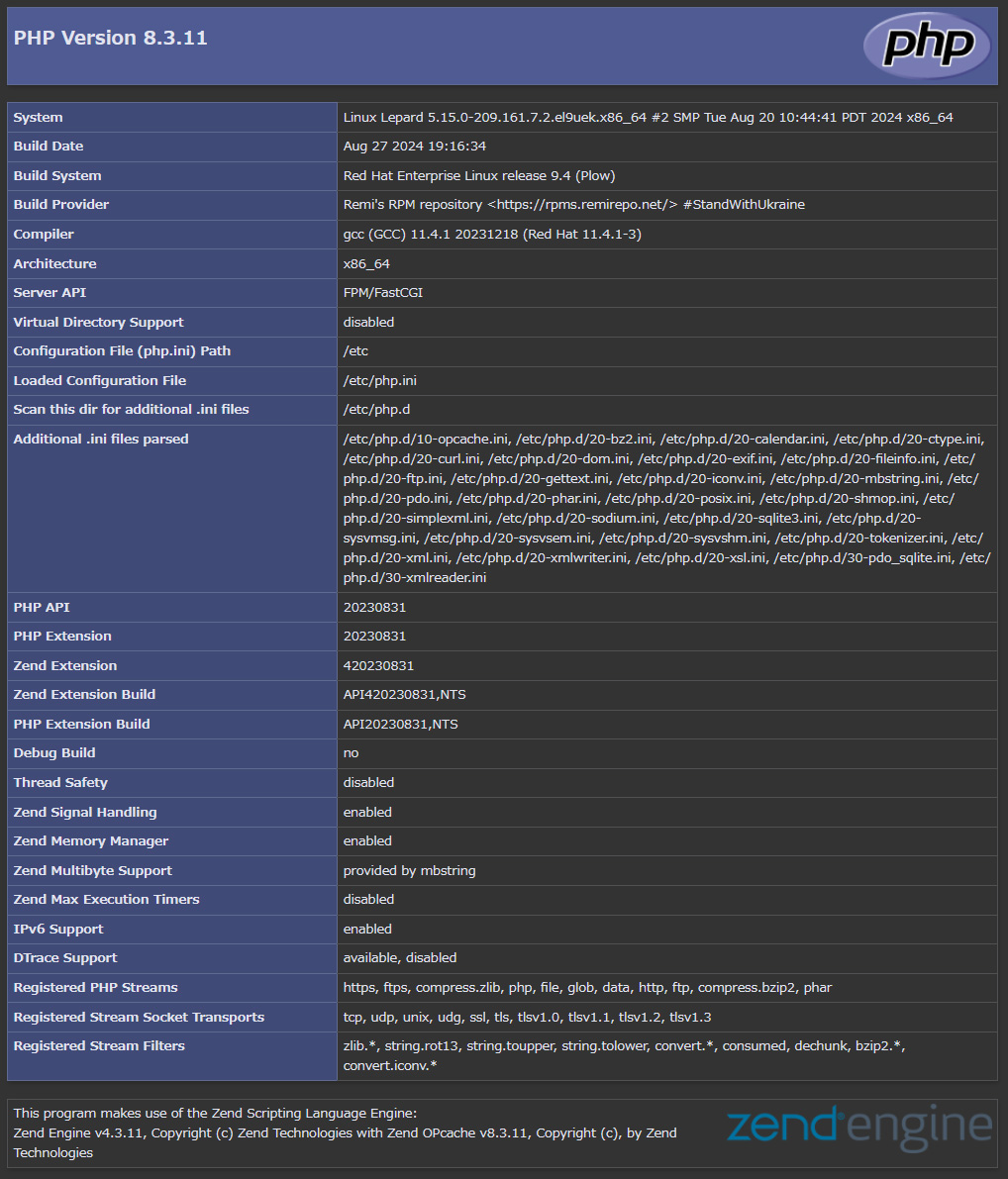
If you access http://[FQDN]/test.php in your browser and see the following screen, it is OK
4. Digest authentication with Apache2
Since Basic Authentication, a well-known authentication authorization method for http, sends authentication information in plain text, there is a risk of ID and password leakage if the packet is intercepted.
On the other hand, Digest Authentication encrypts and transmits authentication information, so there is almost no risk of information leakage.
4.1 Create password file for Digest authentication
Specify an authenticated area called realm. This realm allows the same directory to be accessed as authenticated.
For this example, the realm is "DigestAuth" and a user and password file named "secretuser" ".digestauth" is created.
|
1 |
# /usr/bin/htdigest -c /etc/httpd/.digestauth "DigestAuth" secretuser |
Confirmation
|
1 2 |
# cat /etc/httpd/.digestauth secretuser:DigestAuth:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
As above, secretuser and encrypted password are created
4.2 Edit Apache configuration file
Specify the directory to which Digest authentication will be applied. (In this case, specify the "secret" directory.)
|
1 |
# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf |
Add the following at the end
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<Directory "/var/www/html/[FQDN]/secret"> AuthType Digest AuthName "DigestAuth" AuthDigestDomain /[FQDN]/secret/ AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/.digestauth" Require valid-user </Directory> |
Create a directory for Digest authentication
|
1 |
# mkdir /var/www/html/[FQDN]/secret |
Enable Digest authentication and reboot
|
1 |
# systemctl restart httpd.service |
When accessing http://[FQDN]/secret with a browser, a screen appears asking for "user name" and "password".