Contents
1. MySQL8
1. 1 Install
|
1 |
# apt -y install mysql-server |
|
1 2 3 4 |
# systemctl start mysql # systemctl enable mysql # systemctl is-enabled mysql enabled |
Version Check
|
1 2 |
# mysql --version mysql Ver 8.4.7-0ubuntu0.25.10.3 for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu)) |
1.2. Setting the root password for MySQL8
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
# mysql Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 8 Server version: 8.4.7-0ubuntu0.25.10.3 (Ubuntu) Copyright (c) 2000, 2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> ALTER USER root@localhost IDENTIFIED WITH caching_sha2_password BY 'Password'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> |
1.3. MySQL Server Security Settings
Run the tool mysql_secure_installation to configure security-related settings for the MySQL server.
|
1 |
# mysql_secure_installation |
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Enter password for user root:
VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component?
Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y
There are three levels of password validation policy:
LOW Length >= 8
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 0
Using existing password for root.
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
New password:[Password]
Re-enter new password:[Password]
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
- Dropping test database…
Success.
- Removing privileges on test database…
Success.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
Success.
All done!
From then on, when accessing MySQL, you must use the
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# mysql -u root -p Enter password: (Enter the password you set above) Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 11 Server version: 8.4.7-0ubuntu0.25.10.3 (Ubuntu) Copyright (c) 2000, 2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> |
2.WordPress Install
2.1 Create database
Create a database for Word Press (for example, in this case, the database name is "wp_db", the user name is "wp_user", and the password is "?Y123456y")
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
# mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 11 Server version: 8.4.7-0ubuntu0.25.10.3 (Ubuntu) Copyright (c) 2000, 2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> CREATE DATABASE wp_db; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> create user 'wp_user'@'localhost' identified by '?Y123456y'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> grant all on wp_db.* to 'wp_user'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> exit Bye |
2.2 WordPress Download and Install
①Download and Deployment
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/<FQDN> # wget http://ja.wordpress.org/latest-ja.tar.gz # tar xvf latest-ja.tar.gz |
②Edit WordPress configuration file
|
1 2 3 |
# cd wordpress/ # cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php # vi wp-config.php |
Edit contents of wp-config.php
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
// ** Database settings - You can get this info from your web host ** // /** The name of the database for WordPress */ define('DB_NAME', 'wp_db'); ←Database name created in "2.1 Database Creation" /** Database username */ define('DB_USER', 'wp_user'); ←User name created in "2.1 Database Creation" /** Database hostname */ define('DB_PASSWORD', '?Y123456y'); ←Password for the user created in "2.1 Database Creation" Also, add the following to the last line. If you do not do this, you will be asked for what amounts to FTP connection information when you add the plugin. define('FS_METHOD', 'direct'); |
③Moving Files
|
1 2 |
# cd /var/www/html/<FQDN> # mv wordpress/* . |
After confirming that the files have been moved, delete the wordpress directory and the downloaded latest.tar.gz
|
1 2 |
# rm -R -f wordpress # rm latest.tar.gz |
④Make apache the owner of the wordpress directory
|
1 |
# chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/<FQDN> |
⑤Access from a browser
Access http://FQDN/wp-admin.
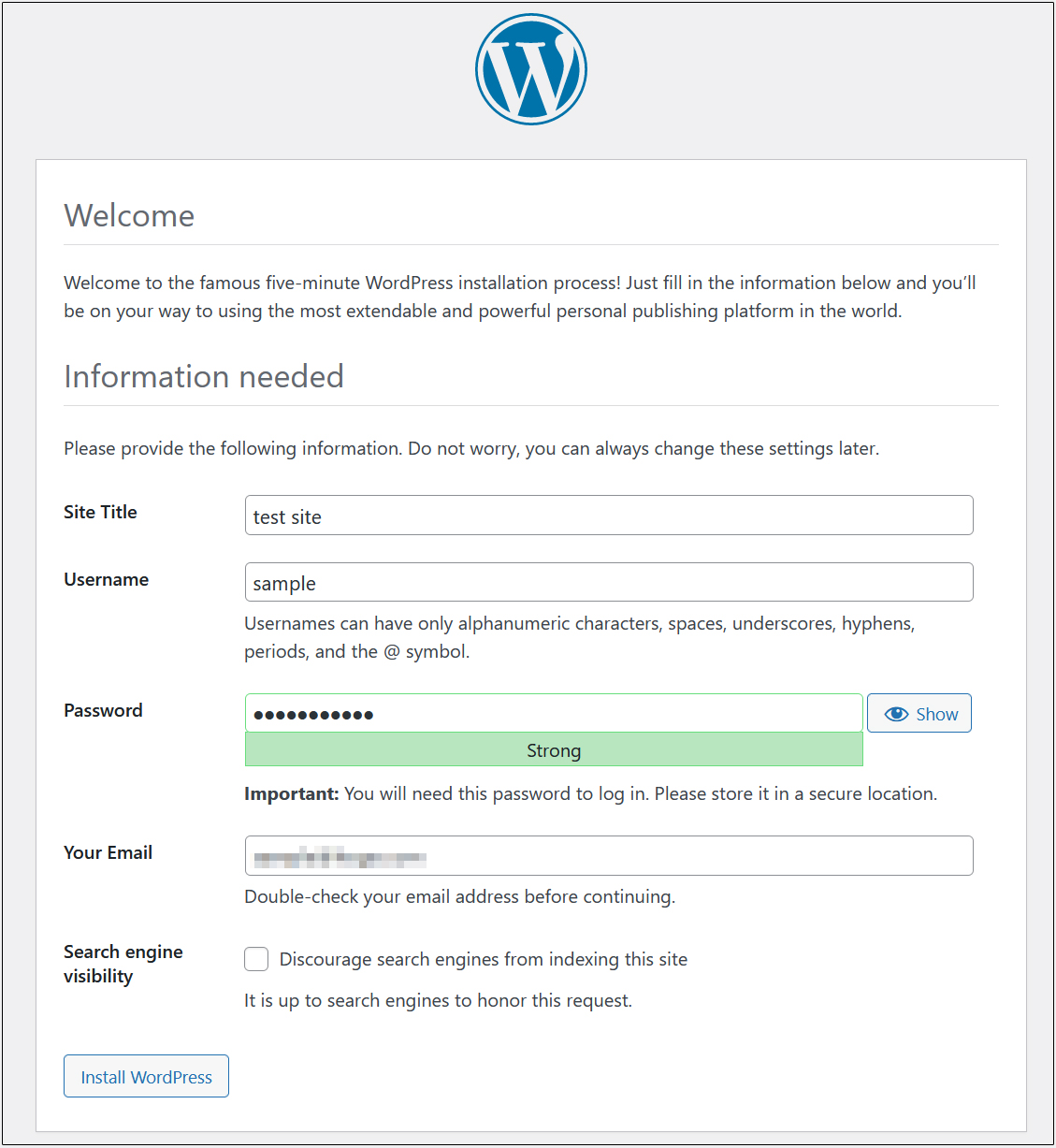
If successful, the following WordPress installation information input screen will be output.
「Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress.」When displayed
Installing the MySQL Module
|
1 |
# apt -y install php-mysqli |
Restart Apache after installation is complete.
|
1 |
# systemctl restart apache2 |
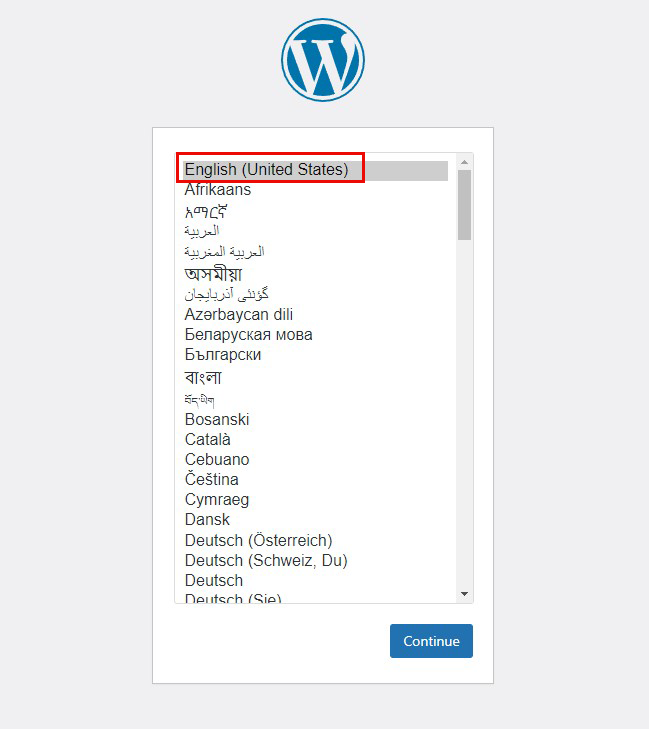
On the following input screen
Site Title Any name
Username Any name
Password Any password
Your Email Administrator's email address
Enter the information and click "Install WordPress". Remember to enter your "username" and "password" as they are required to access the WordPress administration screen.