Contents
1. Install bash completion extension package
|
1 2 |
# dnf -y install bash-completion # reboot |
2. Disabling SELinux
First, disable selinux. selinux is a feature that improves auditing and security in Linux, but when enabled, it can limit the behavior of services and the contents of the configuration considerably.
Therefore, it is basically a case of invalidation in many cases.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# getenforce ← Check SELinux functionality Enforcing ← SELinux enabled # setenforce 0 ← Disable SELinux functionality # getenforce ← Reconfirmation of SELinux functionality Permissive ← SELinux is disabled |
If this is not done, seinux will be enabled again when the server is restarted, so to permanently disable selinux, modify the /etc/sysconfig/selinux file.
|
1 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux |
Change "SELINUX=enforcing" to "SELINUX=disabled"
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. #SELINUX=enforcing SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected. # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted |
3. System Modernization
Update packages as soon as possible after OS installation.
However, when a dnf update is performed, a kernel update is also performed at the same time.
A kernel update may require rebooting the system or stopping services, or worse, a kernel panic may occur and the system may not boot. It is wiser to exclude the kernel from the update.
Run dnf -y update with "--exclude=kernel*" after it.
Kernel can be excluded from updates
|
1 |
# dnf -y update --exclude=kernel* |
4. Services to be stopped due to security measures
Stop the following services that you deem unnecessary.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# systemctl stop atd.service # systemctl disable atd.service # systemctl stop kdump.service # systemctl disable kdump.service # systemctl stop lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl disable lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl stop mdmonitor.service # systemctl disable mdmonitor.service # systemctl stop smartd.service # systemctl disable smartd.service # systemctl stop tuned.service # systemctl disable tuned.service # systemctl stop dm-event.socket # systemctl disable dm-event.socket |
5. Adding Repositories
5.1 Add EPEL repository
|
1 |
# dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm -y |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo [epel] name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch # It is much more secure to use the metalink, but if you wish to use a local mirror # place its address here. #baseurl=https://download.example/pub/epel/$releasever/Everything/$basearch metalink=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-$releasever&arch=$basearch&infra=$infra&content=$contentdir enabled=1 ← Repository enabled (0 : Repository disabled) priority=10 ← Specify priority in the range of 1~99 gpgcheck=1 countme=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-8 [epel-debuginfo] name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux $releas |
5.2 Add Remi's RPM repository
|
1 |
# dnf -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/remi-safe.repo # This repository is safe to use with RHEL/CentOS base repository # it only provides additional packages for the PHP stack # all dependencies are in base repository or in EPEL[remi-safe] name=Safe Remi's RPM repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - $basearch #baseurl=http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/httpsmirror mirrorlist=http://cdn.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/mirror enabled=1 ← Repository enabled (0 : Repository disabled) priority=10 ← Specify priority in the range of 1~99 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi.el8[remi-safe-debuginfo] name=Remi's RPM repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - $basearch - debuginfo baseurl=http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/debug-remi/$basearch/ |
6. Network configuration (command line configuration method)
6.1 Host Name Change
Change the host name to Lepard
|
1 2 3 |
# hostnamectl set-hostname Lepard # reboot [huong@Lepard:~]$ |
6.2 Static IP address settingStatic IP address setting
If the default setting is to obtain an IP address via DHCP during OS installation, change the network settings to a fixed IP address if necessary.
First, find out the name of your network interface with the following command
This time it is "ens160"
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: ens160: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:3f:48:ad brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.11.83/24 brd 192.168.11.255 scope global noprefixroute ens160 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever |
Edit the network configuration file and change the static IP address to "192.168.11.11
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens160 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=no IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no NAME=ens160 UUID=dccaab30-4028-439e-a0ec-b385375811d1 DEVICE=ens160 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.11.11 ← Change PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.11.1 DNS1=192.168.11.1 IPV6_DISABLED=yes |
Reflect settings
|
1 |
# systemctl restart network |
7. Network configuration (how to configure via GUI)
|
1 |
# nmtui |
7.1 Static IP address setting
If the default setting is to obtain an IP address via DHCP during OS installation, change the network settings to a fixed IP address if necessary. In this case, the network interface is named "ens160"
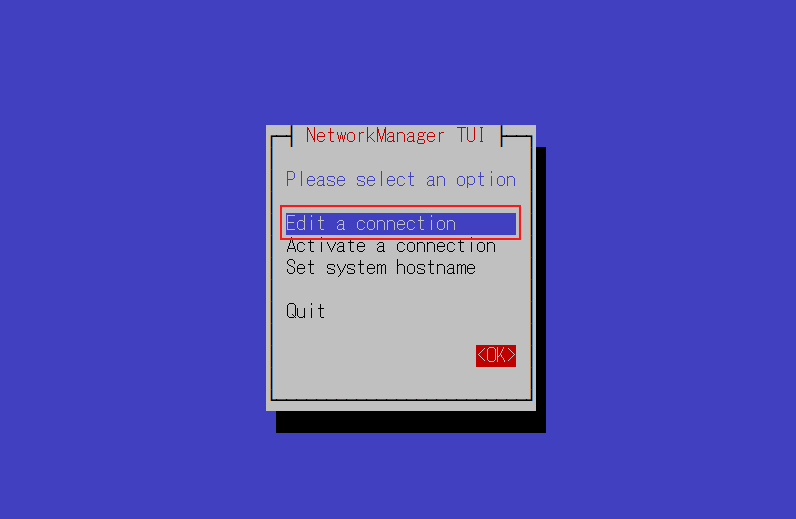
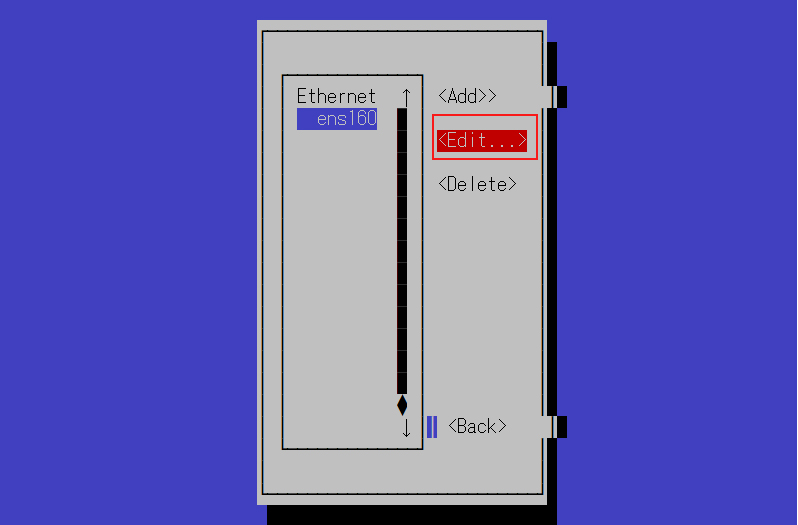
Change the address of the IPv4 configuration
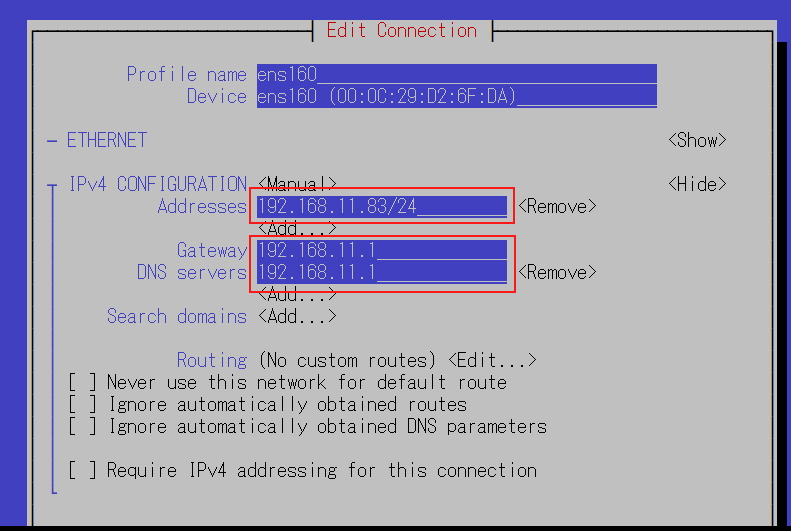
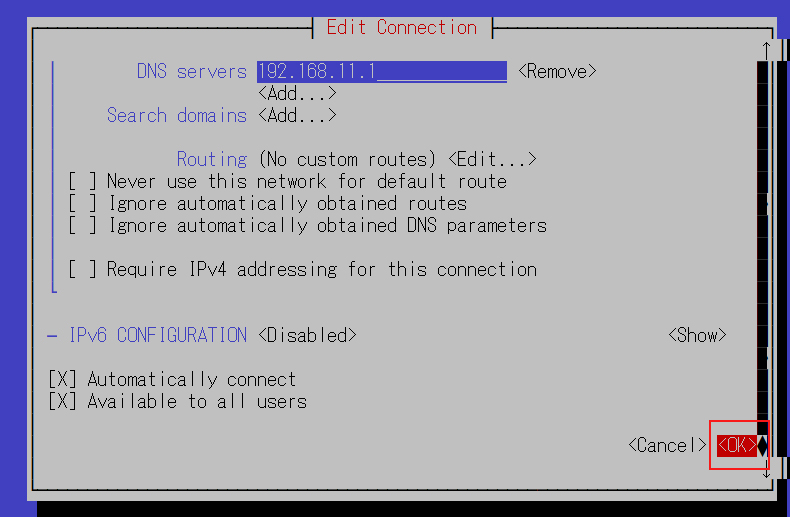
Scroll down and click OK
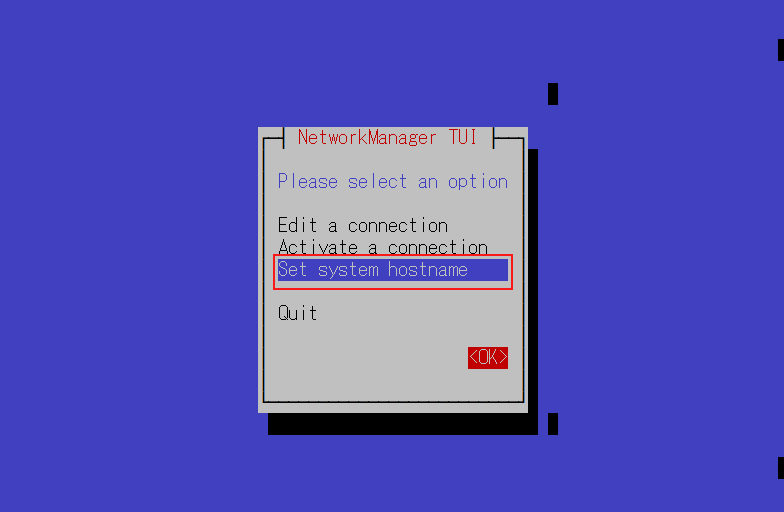
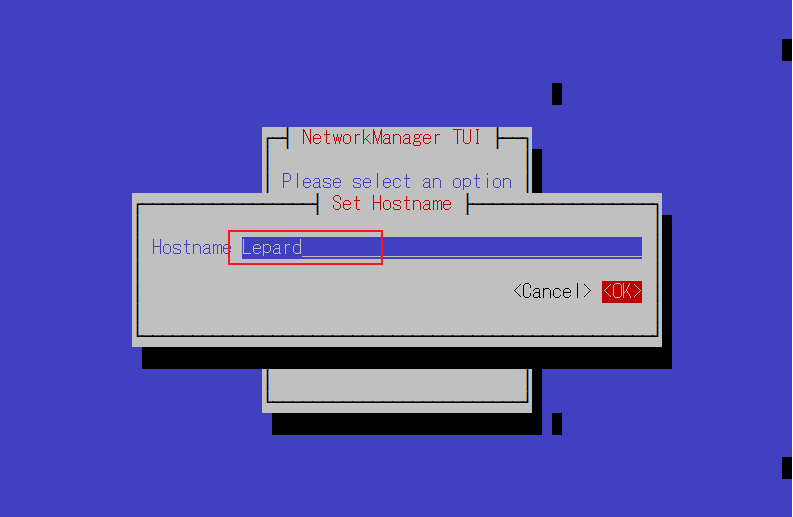
7.2 Host Name Change
change the host name to Lepard

8. Vim Settings
①Installing Vim Extensions
|
1 |
# dnf -y install vim-enhanced |
②Apply and reflect Vim
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi ~/.bashrc #Alias appended to the last line alias vi='vim' # source ~/.bashrc |
③Configure Vim as a user-specific environment
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
# vi ~/.vimrc " Use vim's own extensions (not compatible with vi) set nocompatible " Specify character code set encoding=utf-8 " Specify file encoding (read from the beginning until success) set fileencodings=utf-8,iso-2022-jp,sjis,euc-jp " Specify the line feed code to be recognized automatically set fileformats=unix,dos " Get Backup set backup " Specify the directory from which to obtain backups set backupdir=~/backup " Number of generations to keep search history set history=50 " Do not distinguish between upper and lower case letters when searching set ignorecase " Mixing capital letters in search terms makes the search case sensitive set smartcase " Highlight words matching your search term set hlsearch " Use incremental search set incsearch " Display line numbers set number " Visualize line breaks ( $ ) and tabs ( ^I ) set list " Highlight corresponding parentheses when entering parentheses set showmatch " No newlines at the end of files set binary noeol " Enable automatic indentation set autoindent " Color-coded display by syntax syntax on " Change color of comment text in case of syntax on highlight Comment ctermfg=LightCyan " Wrap lines by window width set wrap |

