Contents
1. SSH remote connection
SSH is a service for connecting remotely to a server and is basically running immediately after the OS is installed, but the default settings are somewhat insecure.
Here we will configure the default settings to increase the security of ssh connections.
1.1 SSH service configuration file changes
|
1 |
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
1 # $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.104 2021/07/02 05:11:21 dtucker Exp $ 2 3 # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See 4 # sshd_config(5) for more information. 5 6 # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/ usr/sbin 7 8 # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with 9 # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where 10 # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the 11 # default value. 12 13 # To modify the system-wide sshd configuration, create a *.conf file under 14 # /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/ which will be automatically included below 15 Include /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/*.conf 16 17 # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell 18 # SELinux about this change. 19 # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER 20 # 21 #Port 22 22 Port 2244 23 #AddressFamily any 24 ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 25 #ListenAddress :: 26 27 #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key 28 #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key 29 #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key 30 31 # Ciphers and keying 32 #RekeyLimit default none 33 34 # Logging 35 #SyslogFacility AUTH 36 #LogLevel INFO 37 38 # Authentication: 39 40 #LoginGraceTime 2m 41 PermitRootLogin prohibit-password 42 #StrictModes yes |
Line 21 "Port 22" This time change to "Port 2244" and proceed
Delete "#" from line 23 "#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0".
Line 40, "#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password", delete "#".
The root user can log in to the server with administrator privileges if the user name is already known and the password is known, so the settings are set to deny this.
Restart SSH
|
1 |
# systemctl restart sshd.service |
If this is not done, the next time you reboot, you will not be able to connect remotely via SSH. Please free SSH port 2244 in the following firewall settings.
2.How to set up a firewall (firewalld)
In AlmaLinux, the firewall is set to firewalld by default and is enabled during OS installation.
2.1 How to use the "firewall-cmd" command to control "firewalld"
1)How to use the "firewall-cmd" command to control "firewalld"
①Check firewalld operation status
|
1 2 3 4 |
# firewall-cmd --state running If "firewalld" is running, the message "running" will be displayed; if it is not running, the message "not running" will be displayed |
or
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; preset> Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-04-15 15:23:59 JST; 1h 8min ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 750 (firewalld) Tasks: 2 (limit: 10892) Memory: 41.4M CPU: 510ms CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service mq750 /usr/bin/python3 -s /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid Apr 15 15:23:57 localhost systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall dae> Apr 15 15:23:59 localhost systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daem> |
➁View default zone settings
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# firewall-cmd --list-all public (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: ens160 sources: services: cockpit dhcpv6-client ssh ports: protocols: forward: no masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: |
In the above example, the services "cockpit", "dhcpv6-client" and "ssh" are allowed.
③About the "--permanent" option
To prevent the settings from disappearing when the server is restarted or the "firewalld" service is restarted, the
The "--permanent" option must be used to configure the settings.
If the "--permanent" option is specified, the setting is not reflected in "firewalld" as it is, so it is necessary to use "fiewall-cmd --reload" to reflect the setting.
To use the HTTP service permanently without initialization even if the system is rebooted
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
④How to start/stop
Since "firewalld" is controlled by "systemd", use the "systemctl" command to start and stop it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Start firewalld # systemctl start firewalld Stop firewalld # systemctl stop firewalld |
2.2 Allow modified SSH port 2244
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
# firewall-cmd --add-port=2244/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload # firewall-cmd --list-all public (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: ens160 sources: services: cockpit dhcpv6-client ssh ports: 2244/tcp protocols: forward: no masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: |
2244 ports have been added
3.Remote connection from Windows
Setup in Windows
Start setting up a remote connection from Windows, using "Tera Term" as the terminal emulator.
Start Tera Term, cancel the startup screen, and then select "New Connection" from "File" in the Tera Term menu.
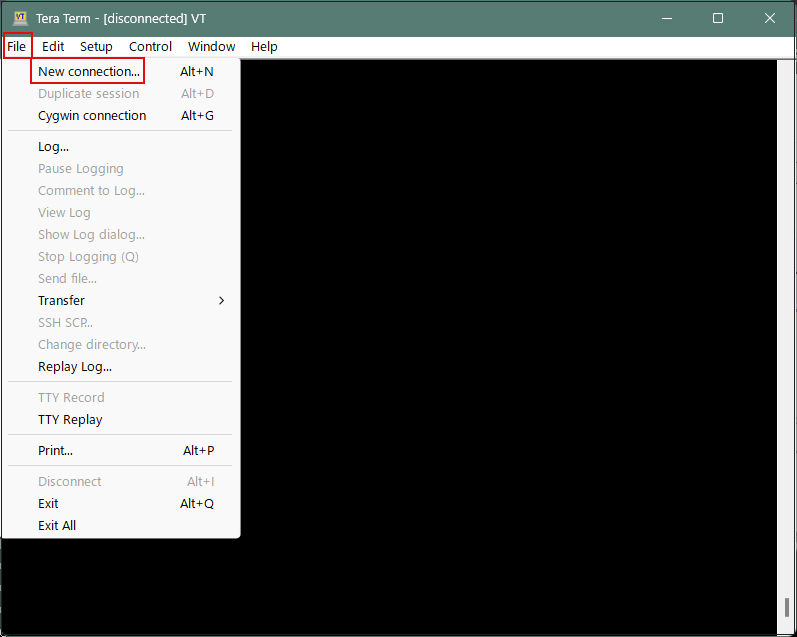
Enter your own settings in the "Server IP address" and "TCP port number" fields. Finally, click "OK.
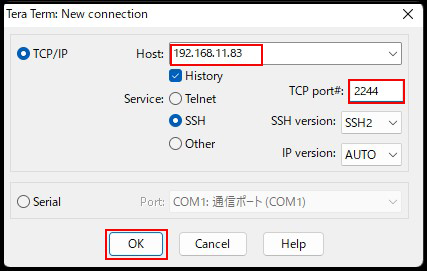
After clicking "OK," click "Continue" on the security confirmation screen.
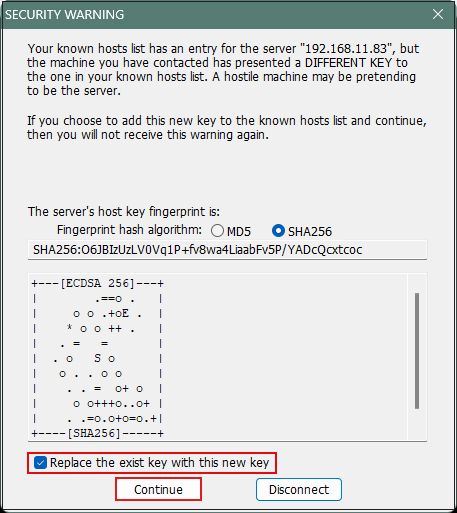
Enter "User name" Passphrase" and click "OK".
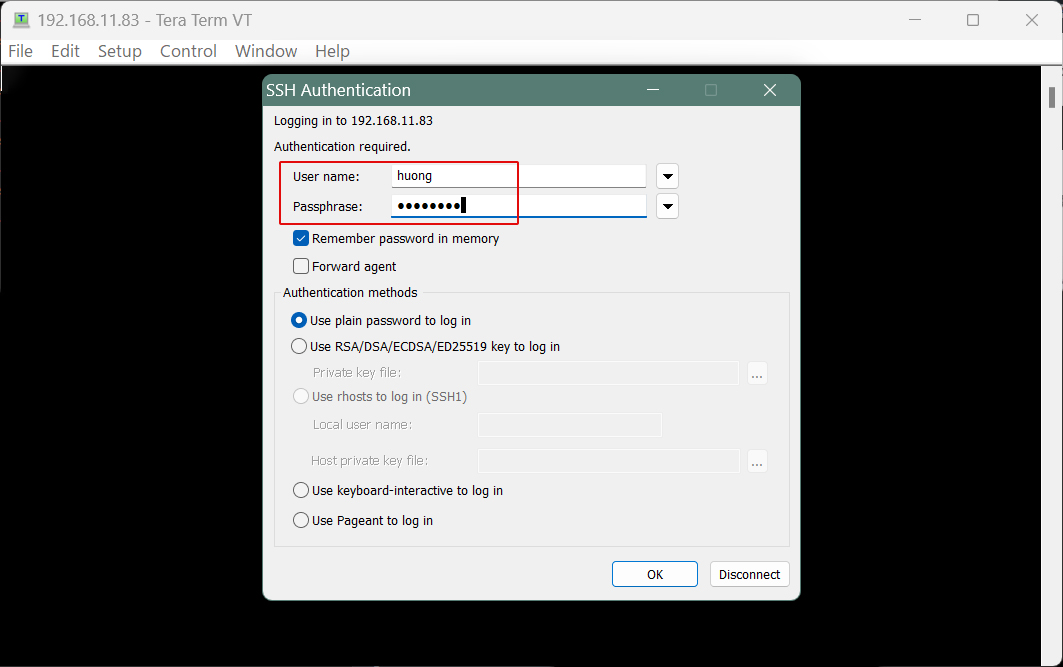
If the information is correct, you should be able to log in normally as shown below.
4.NTP Server
Build an NTP server to synchronize the server time with Japan Standard Time
①Chrony Installation and Configuration
|
1 |
# dnf -y install chrony |
|
1 2 3 4 |
# vi /etc/chrony.conf Line 3 : Comment out and add under it #pool 2.almalinux.pool.ntp.org iburst pool ntp.nict.jp iburst |
➁Restart chrony and enable chrony after system reboot
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable chronyd.service # systemctl restart chronyd.service |
③NTP port allowed in firewall
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
④Check chronyd status (behavior)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# chronyc sources MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== ^+ ntp-b3.nict.go.jp 1 6 177 24 +838us[ +838us] +/- 5486us ^+ ntp-a2.nict.go.jp 1 6 177 22 -86us[ -86us] +/- 6281us ^+ ntp-b2.nict.go.jp 1 6 177 22 +1075us[+1075us] +/- 5403us ^* ntp-a3.nict.go.jp 1 6 177 24 +462us[ +941us] +/- 5944us |
If it is marked with *, it has been synchronized.

