Partitioning
First, basic partitioning divides the disk space into two parts: / (root) and a partition for swap. The partition for swap must be prepared.
1.Using gdisk commands
When gdisk is invoked, the following is displayed.
gdisk always requires a device file name as an argument
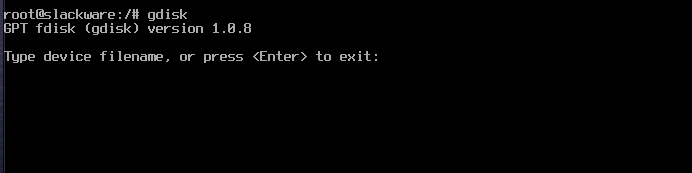
The device name is /dev/nvme0n1 if you are using an M.2 SSD, or /dev/sda if you are using an old device SSD.
In this case, enter the following for SSD use

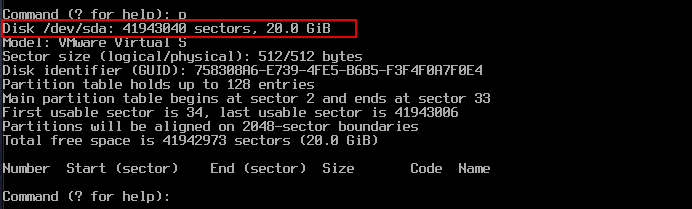
To confirm that you have specified the correct device file, enter p. If it is an SSD, you will see the following output
2.Create partition table
Create a partition table for the GUID.
This area will store the partition information you are about to create.
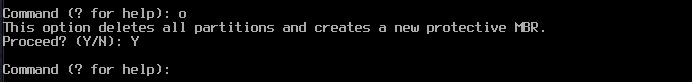
Type o, then Enter
Type Y to delete all partitions and create a new protective MBR
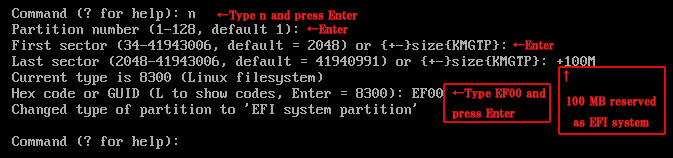
3.EFI System Partition Creation
Create EFI system partition with 100MB
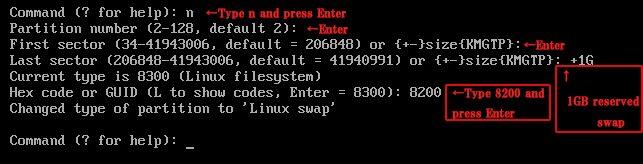
4.Create partition for swap
Create 1GB as swap space
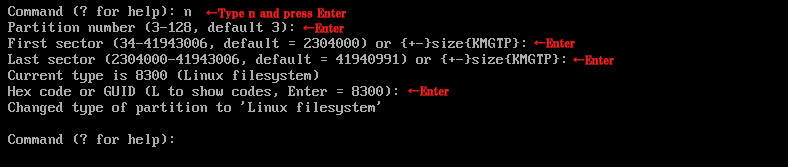
5.Create partition for /(root)
This time, create all remaining space as a partition for the root
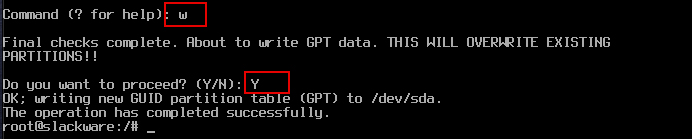
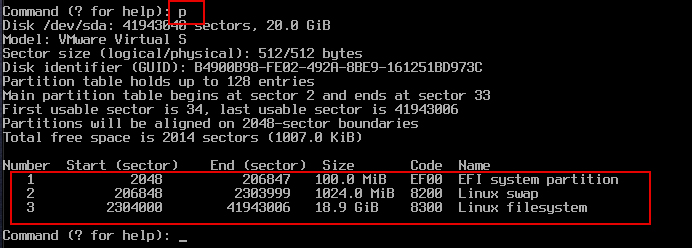
6.Checking and writing the created partitions
Confirm the partition you created by entering p
Enter "w" to write the partition table to disk and exit gdisk