Contents
MySQL8 Install
|
1 |
# dnf -y install mysql-server |
charset.cnf Create a new one with the following contents
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
#vi /etc/my.cnf.d/charset.cnf # Set default character encoding utf8mb4 for 4-byte characters such as pictographs [mysqld] character-set-server = utf8mb4 [client] default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
|
1 2 |
#systemctl enable --now mysqld Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mysqld.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service. |
Use the "mysql_secure_installation" command to set the root user password and set some basic policies
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 |
# mysql_secure_installation Securing the MySQL server deployment. Connecting to MySQL using a blank password. VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords and improve security. It checks the strength of password and allows the users to set only those passwords which are secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component? # Enable/disable password quality check Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8 MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file # Select strength if password quality check is enabled Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 0 ←May be optional for each Please set the password for root here. # MySQL root password New password: ← Any password Re-enter new password: ← Same password again # Confirmation that the password you entered is correct Estimated strength of the password: 100 Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. # Whether to remove anonymous users or not Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. # Disable remote login for root user Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. # Whether to delete the test database or not Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y - Dropping test database... Success. - Removing privileges on test database... Success. Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. # Whether to reload privilege information or not Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. All done! |
WordPress Install
1. Create database for Word Press
As an example, assume database [wp_db] database user [wp_user] password [?Ww123456]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
# mysql -u root -p Enter password: ←Enter root password for MySQL Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 12 Server version: 8.0.30 Source distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. #Create a dedicated database controlled by WordPress mysql> CREATE DATABASE wp_db DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) #Check database mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | | sys | wp_db | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec) #Create an account, set a password, and grant access to the database you have created mysql>CREATE USER 'wp_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '?Ww123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) Informs the database that the user must have full access to the setup database mysql> GRANT ALL ON wp_db.* TO 'wp_user'@'localhost'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) #Reload Authority mysql> flush privileges; #Exit mysql mysql> exit; Bye |
2.Wordpress Install
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # wget http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz # tar xvf latest.tar.gz |
3.Edit WordPress configuration file
|
1 2 |
# cd wordpress/ # cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 |
# vi wp-config.php <?php /** * The base configuration for WordPress * * The wp-config.php creation script uses this file during the installation. * You don't have to use the web site, you can copy this file to "wp-config.php" * and fill in the values. * * This file contains the following configurations: * * * Database settings * * Secret keys * * Database table prefix * * ABSPATH * * @link https://wordpress.org/support/article/editing-wp-config-php/ * * @package WordPress */ // ** Database settings - You can get this info from your web host ** // /** The name of the database for WordPress */ define( 'DB_NAME', 'wp_db' ); /** Database username */ define( 'DB_USER', 'wp_user' ); /** Database password */ define( 'DB_PASSWORD', '?Ww123456' ); /** Database hostname */ define( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' ); /** Database charset to use in creating database tables. */ define( 'DB_CHARSET', 'utf8' ); /** The database collate type. Don't change this if in doubt. */ define( 'DB_COLLATE', '' ); /**#@+ * Authentication unique keys and salts. * * Change these to different unique phrases! You can generate these using * the {@link https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/ WordPress.org secret-key service}. * * You can change these at any point in time to invalidate all existing cookies. * This will force all users to have to log in again. * * @since 2.6.0 */ define( 'AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'NONCE_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' ); define( 'NONCE_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' ); /**#@-*/ /** * WordPress database table prefix. * * You can have multiple installations in one database if you give each * a unique prefix. Only numbers, letters, and underscores please! */ $table_prefix = 'wp_'; /** * For developers: WordPress debugging mode. * * Change this to true to enable the display of notices during development. * It is strongly recommended that plugin and theme developers use WP_DEBUG * in their development environments. * * For information on other constants that can be used for debugging, * visit the documentation. * * @link https://wordpress.org/support/article/debugging-in-wordpress/ */ define( 'WP_DEBUG', false ); /* Add any custom values between this line and the "stop editing" line. */ /* That's all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */ /** Absolute path to the WordPress directory. */ if ( ! defined( 'ABSPATH' ) ) { define( 'ABSPATH', __DIR__ . '/' ); } /** Sets up WordPress vars and included files. */ require_once ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php'; define('FS_METHOD', 'direct'); |
Add the following to the last line
If you do not do this, you will be asked for FTP connection information when you add the plugin.
define('FS_METHOD', 'direct');
4.Moving Files
①Move the expanded contents under /var/www/html/[domain name for wordpress]
|
1 2 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # mv wordpress/* . |
After confirming that the files have been moved, delete the wordpress directory and downloaded latest.tar.gz
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # rm -R -f wordpress # rm latest.tar.gz |
Make apache the owner of the wordpress directory.
|
1 |
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/[FQDN] |
5.Starting wordpress installation
You can use your browser to go to http://[FQDN]/wp-admin/install.php
If successful, the following WordPress installation information input screen will be output.
「Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress.」When displayed
Install php library-related software if not already installed.
|
1 2 3 |
# dnf install php-mysqlnd # systemctl restart mysqld # systemctl restart httpd |
again
Access http://[FQDN]/wp-admin/install.php
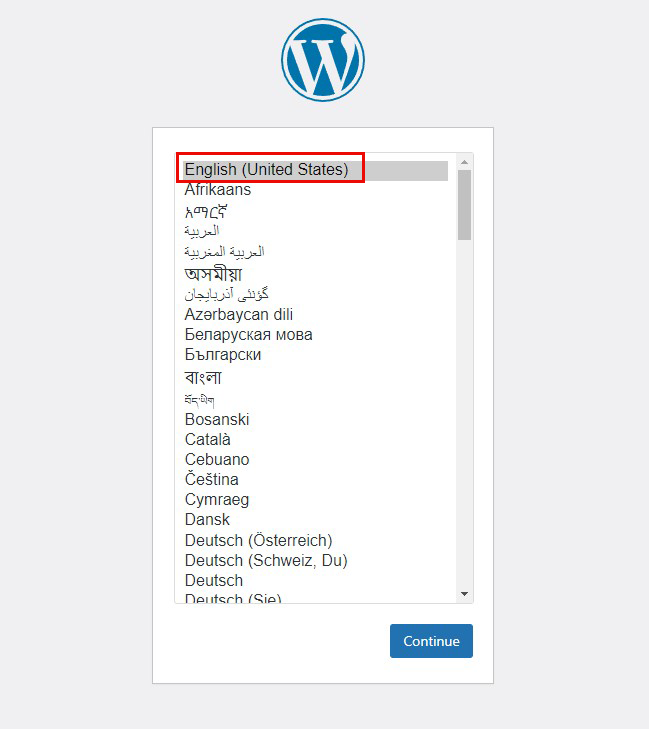
On the following input screen
Site Title Any name
Username Any name
Password Any password
Your Email Administrator's email address
Enter the information and click "Install WordPress". Remember to enter your "username" and "password" as they are required to access the WordPress administration screen.
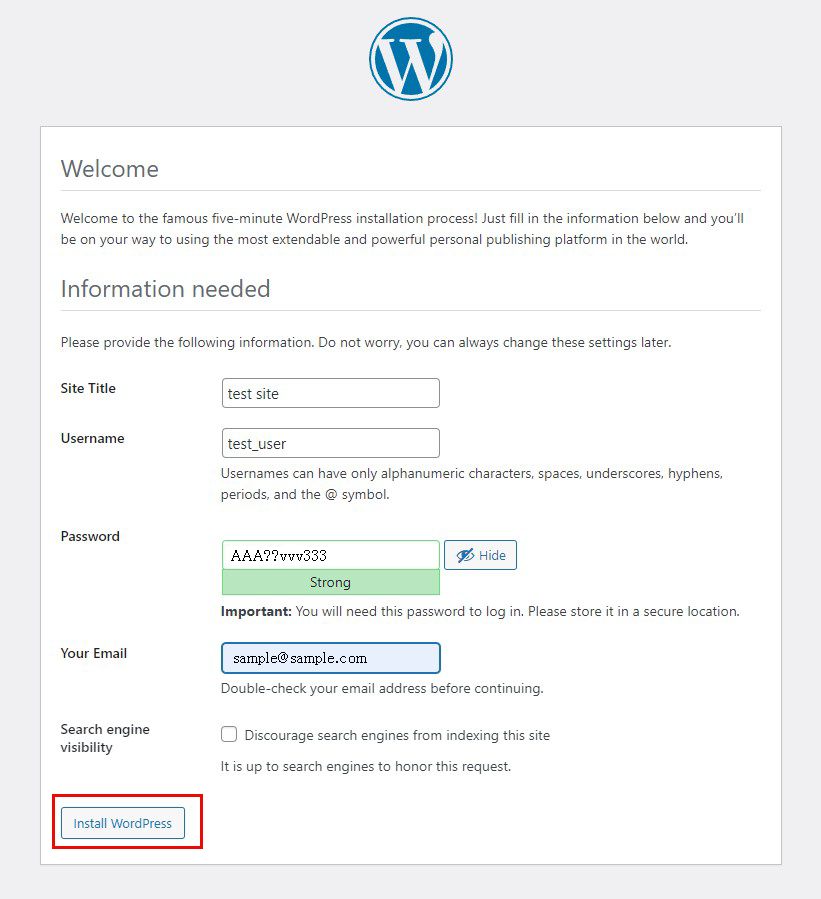
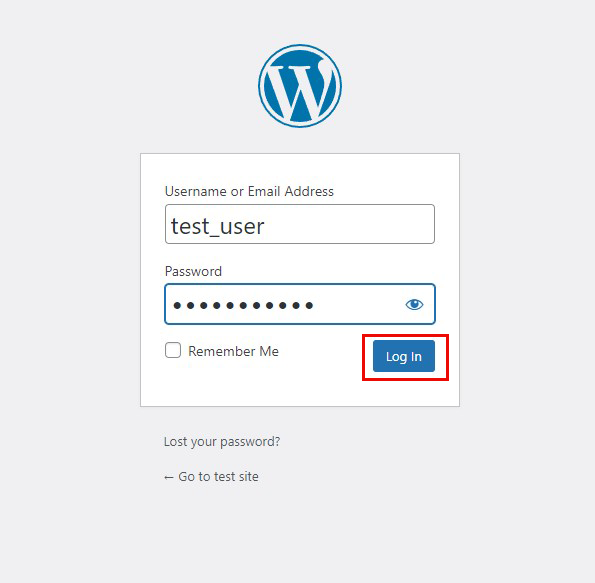
Click on "Login"
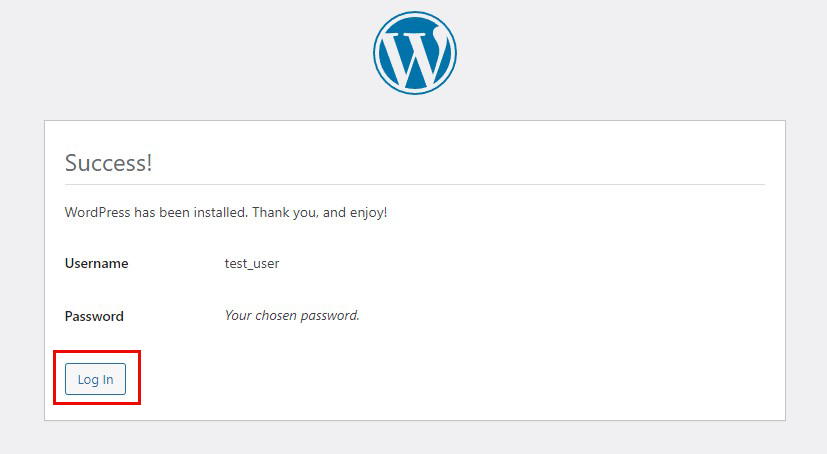
User Name : The user name you have just set
Password : User's password you have just set
and click "Login".
After successfully logging in, you will be able to access the following WordPress admin page