Contents
1.Remote connection by SSH
SSH is a service for connecting remotely to a server, basically running immediately after OS installation, but the default settings are somewhat insecure.
Configure the default settings to increase the security of ssh connections.
1.1 SSH service configuration file changes
The SSH service configuration file is "/etc/ssh/sshd_config".
Open the configuration file in a vi editor.
|
1 |
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 |
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.104 2021/07/02 05:11:21 dtucker Exp $ # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See # sshd_config(5) for more information. # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/ usr/sbin # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the # default value. # To modify the system-wide sshd configuration, create a *.conf file under # /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/ which will be automatically included below Include /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/*.conf # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell # SELinux about this change. # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER # #Port 22 Port 2244 #AddressFamily any ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key # Ciphers and keying #RekeyLimit default none # Logging #SyslogFacility AUTH #LogLevel INFO # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin prohibit-password #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 #PubkeyAuthentication yes |
This time, we will change to "Port 2244" and proceed(Simply changing this port number can reduce unauthorized access)
②Find "#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0" and delete the preceding "#".
③Find "#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password" and delete the "#" at the beginning of the line
Since the root user already knows the user name and can log in to the server with administrator privileges once the password is known, the setting is set to deny this.
SSH restart
|
1 |
# systemctl restart sshd.service |
2.How to set up a firewall (firewalld)
In Fedora, firewalld is set as the default and is enabled during OS installation.
2.1 How to use the "firewall-cmd" command to control "firewalld
1)Command to check the status and settings of "firewalld
①Check firewalld operation status
|
1 |
# firewall-cmd --state |
If "firewalld" is running, the message "running" will be displayed; if it is not running, the message "not running" will be displayed.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# systemctl status firewalld ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor> Active: active (running) since Sun 2022-10-16 21:37:27 JST; 14min ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 845 (firewalld) Tasks: 2 (limit: 2274) Memory: 37.8M CPU: 550ms CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service mq 845 /usr/bin/python3 -s /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid Oct 16 21:37:25 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting firewalld.service - firewalld - dyn> Oct 16 21:37:27 Lepard systemd[1]: Started firewalld.service - firewalld - dyna> |
※If stopped
Active: inactive (dead) is displayed, indicating that the firewall is stopped
➁View default zone settings
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# firewall-cmd --list-all FedoraServer (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: ens160 sources: services: cockpit dhcpv6-client ntp ssh ports: protocols: forward: no masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: |
In the above example, we can see that the services "cockpit", "dhcpv6-client", "ntp", "ssh" are allowed, etc.
③About the "--permanent" option
To prevent the settings from disappearing when the server is restarted or the "firewalld" service is restarted, the
The "--permanent" option must be used to configure the settings.
If the "--permanent" option is specified, it is necessary to use "fiewall-cmd --reload" to reflect the settings, as they are not reflected in "firewalld" as they are.
Permanent use of HTTP service without initialization after system reboot
|
1 2 |
# firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload |
④How to start/stop
Since "firewalld" is controlled by "systemd", use the "systemctl" command to start and stop it.
|
1 2 3 4 |
Start firewalld # systemctl start firewalld Stop firewalld # systemctl stop firewalld |
2.2 Release modified SSH port 2244
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
# firewall-cmd --add-port=2244/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd --reload Confirmation # firewall-cmd --list-all FedoraServer (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: ens160 sources: services: cockpit dhcpv6-client http ntp ssh ports: 2244/tcp protocols: forward: no masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: |
2244 ports have been added
3.Remote connection from Windows
Configuration in Windows
The terminal emulator is "Tera Term".
Start Tera Term, cancel the startup screen, and then select "New Connection" from "File" in the Tera Term menu.
Enter your own settings in the "Server IP address" and "TCP port number" fields.
Finally, click "OK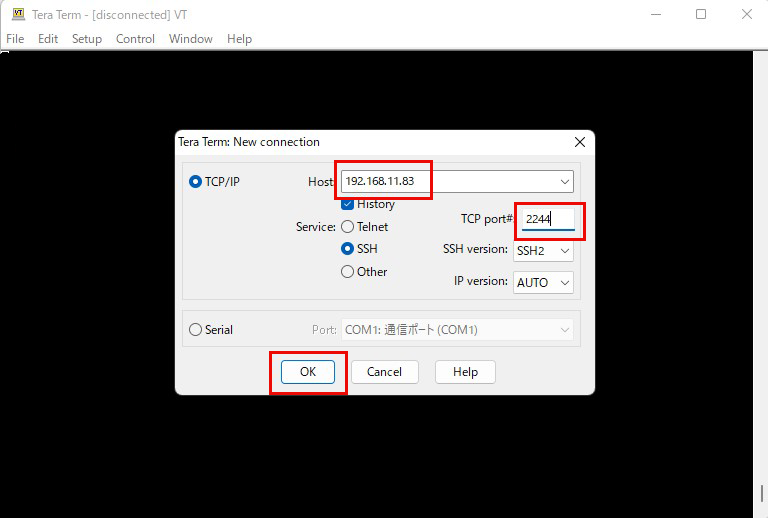
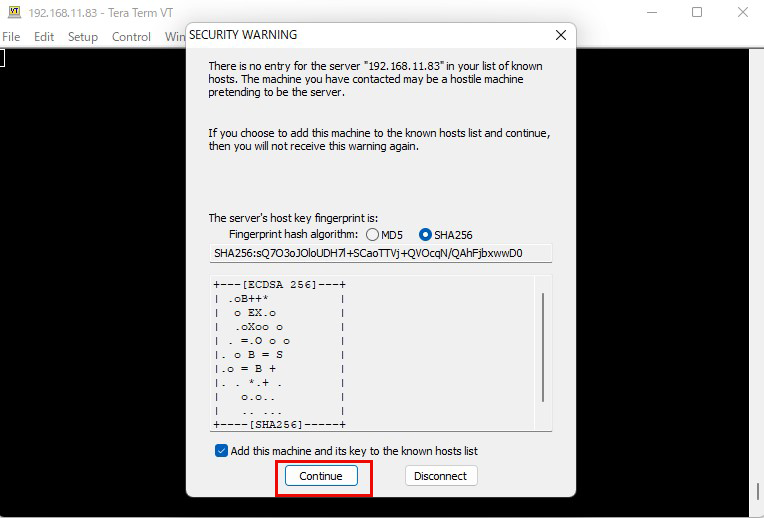
After clicking "OK," click "Continue" on the security confirmation screen.
Enter "User name" "Passphrasee" and click "OK".
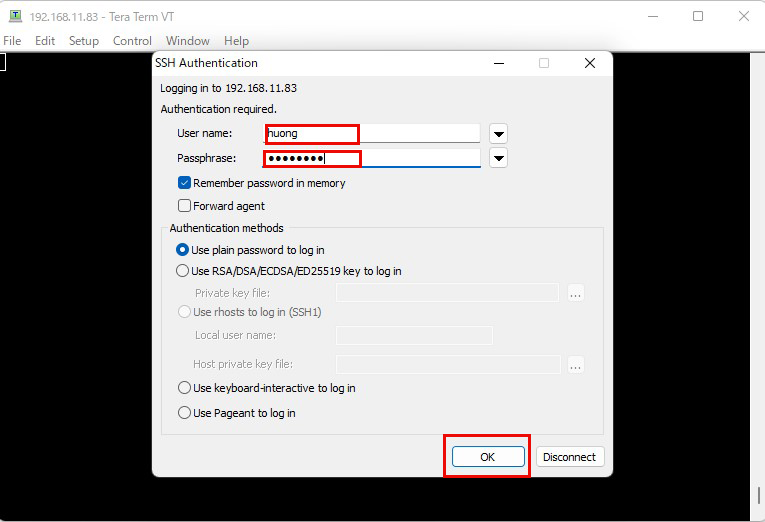
If the information is correct, you should be able to log in normally as shown below.