Contents
Prerequisites
1.Suricata
SURICATA IDS/IPS is an open source IDS that monitors communications on the network and detects suspicious traffic.
The basic mechanism is signature-based, so it can detect predefined unauthorized communications. Suricata is also characterized by its ability to provide protection as well as detection.
2.Elastic Stack,Kibana,Filebeat
Install and configure the Elastic Stack to enable visualization and search of SURICATA logs using Kibana and Filebeat.
This time, we will install Suricata IDS and ElasticStack on the following server.
・First Server Suricata IDS & Filebeat : AlmaLinux10.1 IP address(192.168.11.83)
・Second server ElasticStack & kibana : AlmaLinux10.0 IP address(192.168.11.85)
Run as a sudo user other than root
First Server: Suricata Installation
1.Installing and Configuring Suricata
①Suricata Install
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
# dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-10.noarch.rpm # dnf install yum-plugin-copr # dnf copr enable @oisf/suricata-8.0 # dnf install suricata -y Version Check # suricata -V This is Suricata version 8.0.2 RELEASE |
②Determine interface and IP address where Suricata will inspect network packets
|
1 2 3 |
# ip --brief add lo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128 ens160 UP 192.168.11.83/24 fe80::20c:29ff:fec4:c9d1/64 |
③Edit configuration file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
# vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml # Line 18: Comment it out and add below (in the vars section, define the network) #HOME_NET: "[192.168.0.0/16,10.0.0.0/8,172.16.0.0/12]" HOME_NET: "[192.168.11.0/24]" EXTRNAL_NET: "!$HOME_NET" # Around line 158: Change community-id: false → community-id: true # Around line 661: Set the interface name in the af-packet section af-packet: - interface: ens160 |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/suricata # Line 8 :Specify interface # Add options to be passed to the daemon OPTIONS="-i ens160 --user suricata " |
④Suricata rules update
|
1 |
# suricata-update |
⑤Activate Suricata
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable --now suricata Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multiuser.target.wants/suricata.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service. |
⑥Confirm Suricata startup
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
# systemctl status suricata ● suricata.service - Suricata Intrusion Detection Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-11-26 14:43:55 JST; 1min 5s ago Invocation: 65e8ed1c88de49d3a6dc1e79ada0b488 Docs: man:suricata(1) Process: 30824 ExecStartPre=/bin/rm -f /var/run/suricata.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 30825 (Suricata-Main) Tasks: 8 (limit: 16792) Memory: 1G (peak: 1.1G) CPU: 5.152s CGroup: /system.slice/suricata.service └─30825 /sbin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /var/run/suricata.pid -i ens160 --user suricata Nov 26 14:43:55 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting suricata.service - Suricata Intrusion Detection Service... Nov 26 14:43:55 Lepard systemd[1]: Started suricata.service - Suricata Intrusion Detection Service. Nov 26 14:43:55 Lepard suricata[30825]: i: suricata: This is Suricata version 8.0.2 RELEASE running in SYSTEM mode Nov 26 14:44:00 Lepard suricata[30825]: i: threads: Threads created -> W: 2 FM: 1 FR: 1 Engine started. |
Check Log
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# tail /var/log/suricata/suricata.log [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:55 Info: logopenfile: fast output device (regular) initialized: fast.log [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:55 Info: logopenfile: eve-log output device (regular) initialized: eve.json [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:55 Info: logopenfile: stats output device (regular) initialized: stats.log [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:56 Info: detect: 1 rule files processed. 46530 rules successfully loaded, 0 rules failed, 0 rules skipped [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:56 Info: threshold-config: Threshold config parsed: 0 rule(s) found [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:43:56 Info: detect: 46533 signatures processed. 974 are IP-only rules, 4423 are inspecting packet payload, 40903 inspect application layer, 110 are decoder event only [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:44:00 Info: unix-manager: unix socket '/var/run/suricata/suricata-command.socket' [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:44:00 Info: runmodes: ens160: creating 2 threads [30829 - W#01-ens160] 2025-11-26 14:44:00 Info: ioctl: ens160: MTU 1500 [30825 - Suricata-Main] 2025-11-26 14:44:00 Notice: threads: Threads created -> W: 2 FM: 1 FR: 1 Engine started. |
Check the stats.log file for statistics (updated every 8 seconds by default)
|
1 |
# tail -f /var/log/suricata/stats.log |
A more advanced output, EVE JSON, can be generated with the following command
|
1 |
# tail -f /var/log/suricata/eve.json |
2.Suricata Testing
①Run ping test with curl utility
|
1 2 |
# curl http://testmynids.org/uid/index.html uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root) |
②Check the log file using the specified rule number.
Suricata comes with the following two log files enabled by default:
/var/log/suricata/fast.log
/var/log/suricata/eve.log
To check the log entries corresponding to the curl request, use the grep command to examine the /var/log/suricata/fast.log log file.
2100498 Searches for log entries using the rule identifier. (For IPv4)
|
1 2 3 |
# grep 2100498 /var/log/suricata/fast.log 11/26/2025-14:56:33.030657 [**] [1:2100498:7] GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root [**] [Classification: Potentially Bad Traffic] [Priority: 2] {TCP} 143.204.80.116:80 -> 192.168.11.83:45006 |
③Checking events in /var/log/suricata/eve.log
Install jq
|
1 |
# dnf -y install jq |
Search for signature 2100498 to filter EVE log events
Display the alert object with the signature_id key matching the value 2100498
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
# jq 'select(.alert .signature_id==2100498)' /var/log/suricata/eve.json { "timestamp": "2025-11-26T14:56:33.030657+0900", "flow_id": 318839977757728, "in_iface": "ens160", "event_type": "alert", "src_ip": "143.204.80.116", "src_port": 80, "dest_ip": "192.168.11.83", "dest_port": 45006, "proto": "TCP", "ip_v": 4, "pkt_src": "wire/pcap", "alert": { "action": "allowed", "gid": 1, "signature_id": 2100498, "rev": 7, "signature": "GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root", "category": "Potentially Bad Traffic", "severity": 2, "metadata": { "confidence": [ "Medium" ], "created_at": [ "2010_09_23" ], "signature_severity": [ "Informational" ], "updated_at": [ "2019_07_26" ] } }, -------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------- |
3.Setting Suricata Rules
①Display of rule sets packaged in Suricata
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# ls -al /var/lib/suricata/rules/ total 39900 drwxr-s--- 2 root suricata 57 Nov 26 14:42 . drwxrws--- 4 suricata suricata 33 Nov 26 14:41 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 root suricata 3228 Nov 26 14:42 classification.config -rw-r--r-- 1 root suricata 40853329 Nov 26 14:42 suricata.rules |
②Index list of sources providing rule sets
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 |
# suricata-update list-sources Name: abuse.ch/feodotracker Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Feodo Tracker Botnet C2 IP ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-blacklist Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch SSL Blacklist License: CC0-1.0 Replaces: sslbl/ssl-fp-blacklist Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-c2 Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Suricata Botnet C2 IP Ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-ja3 Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Suricata JA3 Fingerprint Ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Replaces: sslbl/ja3-fingerprints Name: abuse.ch/urlhaus Vendor: abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch URLhaus Suricata Rules License: CC0-1.0 Name: aleksibovellan/nmap Vendor: aleksibovellan Summary: Suricata IDS/IPS Detection Rules Against NMAP Scans License: MIT Name: et/open Vendor: Proofpoint Summary: Emerging Threats Open Ruleset License: MIT Name: et/pro Vendor: Proofpoint Summary: Emerging Threats Pro Ruleset License: Commercial Replaces: et/open Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.proofpoint.com/us/threat-insight/et-pro-ruleset Name: etnetera/aggressive Vendor: Etnetera a.s. Summary: Etnetera aggressive IP blacklist License: MIT Name: oisf/trafficid Vendor: OISF Summary: Suricata Traffic ID ruleset License: MIT Name: pawpatrules Vendor: pawpatrules Summary: PAW Patrules is a collection of rules for IDPS / NSM Suricata engine License: CC-BY-SA-4.0 Name: ptrules/open Vendor: Positive Technologies Summary: Positive Technologies Open Ruleset License: Custom Name: scwx/enhanced Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-enhanced ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: scwx/malware Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-malware ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: scwx/security Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-security ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: stamus/lateral Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Lateral movement rules License: GPL-3.0-only Name: stamus/nrd-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, complete License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, complete License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-entropy-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, high entropy License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-entropy-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, high entropy License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-phishing-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, phishing License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-phishing-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, phishing License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: tgreen/hunting Vendor: tgreen Summary: Threat hunting rules License: GPLv3 |
③Enable source (if tgreen/hunting is enabled)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# suricata-update enable-source tgreen/hunting 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Loaded 62630 rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Disabled 13 rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Enabled 0 rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Modified 0 rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Dropped 0 rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Enabled 136 rules for flowbit dependencies. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:08 - <Info> -- Backing up current rules. 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:11 - <Info> -- Writing rules to /var/lib/suricata/rules/suricata.rules: total: 62630; enabled: 46785; added: 0; removed 0; modified: 0 26/11/2025 -- 15:14:11 - <Info> -- Writing /var/lib/suricata/rules/classification.config 26/11/2025 -- 14:06:26 - <Info> -- Source tgreen/hunting enabled |
Perform update
|
1 |
# suricata-update update-sources |
Restart Suricata service
|
1 |
# systemctl restart suricata |
4. Configuring Suricata as an IPS
Configure Suricata to run in IPS mode to drop malicious network traffic.
Create the following custom signature to scan SSH traffic to non-SSH ports, and include it in the file /var/lib/suricata/rules/local.rules.
(Assuming the SSH port is 22)
|
1 2 |
# vi /var/lib/suricata/rules/local.rules alert ssh any any -> 192.168.11.100 !22 (msg:"SSH TRAFFIC on non-SSH port"; flow:to_client, not_established; classtype: misc-attack; target: dest_ip; sid:1000000;) |
Edit the /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml configuration file and include local.rules.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml Added on line 2303 rule-files: - suricata.rules - local.rules |
Verify SURICATA Configuration
|
1 2 3 4 |
# suricata -T -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -v Info: detect: 46789 signatures processed. 974 are IP-only rules, 4541 are inspecting packet payload, 41041 inspect application layer, 110 are decoder event only Notice: suricata: Configuration provided was successfully loaded. Exiting. |
Edit the SURICATA configuration file located at /etc/sysconfig/suricata
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/suricata Find the line OPTIONS="-i ens160 --user suricata " and add a # at the beginning of the line to comment it out. Next, add the line OPTIONS="-q 0 -vvv --user suricata" to instruct SURICATA to run in IPS mode. . . . # OPTIONS="-i ens160 --user suricata" OPTIONS="-q 0 -vvv --user suricata" . . . |
Restart Suricata
|
1 |
# systemctl restart suricata.service |
Status Check
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
# systemctl status suricata.service ● suricata.service - Suricata Intrusion Detection Service Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-11-26 15:29:50 JST; 12s ago Invocation: ad1b7464bd0e447fa3ed0679abea5f48 Docs: man:suricata(1) Process: 5533 ExecStartPre=/bin/rm -f /var/run/suricata.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 5535 (Suricata-Main) Tasks: 10 (limit: 16792) Memory: 1G (peak: 1.1G, swap: 4K, swap peak: 4K) CPU: 4.246s CGroup: /system.slice/suricata.service └─5535 /sbin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /var/run/suricata.pid -q 0 -vvv --user suricata Nov 26 15:29:52 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Perf: detect: Pkt MPM "ipv6.hdr": 1 Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Info: unix-manager: unix socket '/var/run/suricata/suricata-command.socket' Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Config: tmqh-flow: AutoFP mode using "Hash" flow load balancer Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5541] Info: nfq: binding this thread 0 to queue '0' Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5541] Info: nfq: setting queue length to 4096 Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5541] Info: nfq: setting nfnl bufsize to 6144000 Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Config: flow-manager: using 1 flow manager threads Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Config: flow-manager: using 1 flow recycler threads Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Config: log-flush: log flusher thread not used with heartbeat.output-flush-interval of 0 Nov 26 15:30:01 Lepard suricata[5535]: [5535] Notice: threads: Threads created -> RX: 1 W: 2 TX: 1 FM: 1 FR: 1 Engine started. |
Direct incoming network traffic to Suricata's NFQUEUE
Firewalld is installed and enabled, so add the necessary rules for Suricata to Firewalld.(Assuming the SSH port is 22)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
# firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 0 -p tcp --dport 22 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypass # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter OUTPUT 0 -p tcp --sport 22 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypass Add the same rule for IPv6: # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 filter INPUT 0 -p tcp --dport 22 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypass # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 filter OUTPUT 0 -p tcp --sport 22 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypas # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter FORWARD 0 -j NFQUEUE # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 filter FORWARD 0 -j NFQUEUE # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 1 -j NFQUEUE # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter OUTPUT 1 -j NFQUEUE Add the same rule for IPv6: # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 filter INPUT 1 -j NFQUEUE # firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --add-rule ipv6 filter OUTPUT 1 -j NFQUEUE # firewall-cmd --reload |
Verify that SURICATA is correctly dropping traffic.
Switch the signature's default action from alert or log to active dropping traffic.
Open the /var/lib/suricata/rules/suricata.rules file and comment out any entries matching sid:2100498.
|
1 2 |
# vi /var/lib/suricata/rules/suricata.rules #alert ip any any -> any any (msg:"GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root"; content:"uid=0|28|root|29|"; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2100498; rev:7; metadata:created_at 2010_09_23, confidence Medium, signature_severity Informational, updated_at 2019_07_26;) |
Create a new rule named sid:2100498 in /var/lib/suricata/rules/local.rules.
|
1 2 3 |
# vi /var/lib/suricata/rules/local.rules drop ip any any -> any any (msg:"GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root"; content:"uid=0|28|root|29|"; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2100498; rev:7; metadata:created_at 2010_09_23, confidence Medium, signature_severity Informational, updated_at 2019_07_26;) |
Reload signatures
|
1 |
# kill -usr2 $(pidof suricata) |
Test this rule using curl
|
1 2 |
# curl --max-time 5 http://testmynids.org/uid/index.html curl: (28) Operation timed out after 5001 milliseconds with 0 out of 39 bytes received |
Use jq to examine the eve.log file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 |
# jq 'select(.alert .signature_id==2100498)' /var/log/suricata/eve.json { "timestamp": "2025-11-26T15:41:33.124342+0900", "flow_id": 1568738346888606, "event_type": "alert", "src_ip": "143.204.80.116", "src_port": 80, "dest_ip": "192.168.11.83", "dest_port": 48144, "proto": "TCP", "ip_v": 4, "pkt_src": "wire/pcap", "community_id": "1:Jil6tlIG4ACz4Efo4MNLNXCJVDk=", "alert": { "action": "blocked", "gid": 1, "signature_id": 2100498, "rev": 7, "signature": "GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root", "category": "Potentially Bad Traffic", "severity": 2, "metadata": { "confidence": [ "Medium" ], "created_at": [ "2010_09_23" ], "signature_severity": [ "Informational" ], "updated_at": [ "2019_07_26" ] } }, "app_proto": "http", "direction": "to_client", "flow": { "pkts_toserver": 3, "pkts_toclient": 4, "bytes_toserver": 256, "bytes_toclient": 754, "start": "2025-11-26T15:41:33.103106+0900", "src_ip": "192.168.11.83", "dest_ip": "143.204.80.116", "src_port": 48144, "dest_port": 80 } } |
"action": "blocked", is set
Integration of the ELK Stack and SURICATA
Install and configure the Elastic Stack to visualize and search SURICATA logs more efficiently.
This section is primarily performed on the second AlmaLinux 10.0 server.
1. Elasticsearch Install
1.1 Download and install the GPG key
|
1 |
# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch |
1.2 Create the repository definition in the /etc/yum/yum.repos.d directory.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo The following content description [elasticsearch] name=Elasticsearch repository for 9.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=0 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md |
1.3 Elasticsearch Install
|
1 |
# dnf -y install --enablerepo=elasticsearch elasticsearch |
2. Elasticsearch Settings
Elasticsearch is configured by default to accept only local connections.
Additionally, tools such as Filebeat cannot send logs because authentication is not enabled.
This time, we will configure Elasticsearch's network settings and enable the xpack security module built into Elasticsearch.
2.1 Elasticsearch Network Configuration
Since the Elasticsearch and SURICATA servers are separate, Elasticsearch must be configured to listen for connections on the private network interface.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# vi /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml Line 57 : Add the local address of the Elasticsearch server #network.host: 192.168.0.1 network.host: 192.168.11.85 Line 62 : Uncomments http.port: 9200 |
2.2 Start Elasticsearch
|
1 2 3 |
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl enable elasticsearch.service # systemctl start elasticsearch.service |
2.3 Create passwords for elastic and kibana_system
Be sure to copy the passwords for the elastic user and kibana_system user, as they will be needed later.
The kibana_system user is used for configuring Kibana.
The elastic user is used for configuring Filebeat and Auditbeat, and for logging into Kibana.
If you forget your password, you can use the command again to reset it.
[elastic] User password creation
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin # ./elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user to an autogenerated value. The password will be printed in the console. Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset. New value: e3ABOUZpDfRREpqyX-_s |
※Resetting Elasticsearch Passwords
The automatically generated Elastic user password is too complex, so you can reset it using the /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password command.
To reset your password, execute the command.
|
1 |
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user. You will be prompted to enter the password. Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y Enter password for [elastic]: Re-enter password for [elastic]: Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset. |
[kibana_system] User Password Creation
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin # ./elasticsearch-reset-password -u kibana_system This tool will reset the password of the [kibana_system] user to an autogenerated value. The password will be printed in the console. Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y Password for the [kibana_system] user successfully reset. New value: KQtW6F3vaM63MUQ2RSvc |
3. Installing and Configuring Kibana
This section is primarily performed on the second AlmaLinux 10.0 server.
3.1 Kibana Installation
|
1 |
# dnf -y install --enablerepo=elasticsearch kibana |
3.2 xpack Security Module Configuration
Enable Kibana's xpack security features to generate several encryption keys that Kibana uses to store data in Elasticsearch.
Encryption keys are created using the kibana-encryption-keys utility located in the /usr/share/kibana/bin directory.
Store the three keys you created in a secure location.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# cd /usr/share/kibana/bin/ # ./kibana-encryption-keys generate -q --force xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: 013d3f165f67c3057bc7127ad442beb5 xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: e0eb69e8fa00cf827557be116b7a5e1e xpack.security.encryptionKey: 66ebdeba5666d8aeca69d26f4e6ea371 |
Add these keys to Kibana's /etc/kibana/kibana.yml configuration file.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# vi /etc/kibana/kibana.yml Described in the last line xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: 013d3f165f67c3057bc7127ad442beb5 xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: e0eb69e8fa00cf827557be116b7a5e1e xpack.security.encryptionKey: 66ebdeba5666d8aeca69d26f4e6ea371 |
3.2 Kibana Network Configuration
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
# vi /etc/kibana/kibana.yml Line 6 : Uncomments server.port: 5601 Line 12 : Add the server's private IP address (192.168.11.85) #server.host: "localhost" server.host: "192.168.11.85" |
3.3 Generating a Kibana-Elasticsearch Enrollment Token
To configure a Kibana instance to communicate with an existing Elasticsearch cluster with security enabled, an enrollment token is required. An enrollment token for Kibana can be generated using the following command:
|
1 2 3 |
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana eyJ2ZXIiOiI4LjE0LjAiLCJhZHIiOlsiMTkyLjE2OC4xMS44NTo5MjAwIl0sImZnciI6IjI2NjRlYjIwMDQ4MTYyNDIyYWVlYjIyNTUxNGFiY2RjYTUwZDZkMTExNTg3N2NmMDcxZDlhOTg4MmNhMDBjMDAiLCJrZXkiOiJjQ3Vqd3BvQlRMRzFRSmVWVzZBNDpadDBTQ08zWmE2b3hYbHItR0NuLUlBIn0= |
3.4 Starting Kibana
Launch Kibana 9 and configure it to run at system startup.
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable --now kibana # systemctl start kibana |
Status Check
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
# systemctl status kibana ● kibana.service - Kibana Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kibana.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2025-11-27 09:08:54 JST; 1min 39s ago Invocation: 4081e2530c23441693b720ed9c2cb7c0 Docs: https://www.elastic.co Main PID: 118796 (node) Tasks: 11 (limit: 22946) Memory: 463M (peak: 463.5M) CPU: 17.766s CGroup: /system.slice/kibana.service └─118796 /usr/share/kibana/bin/../node/glibc-217/bin/node /usr/share/kibana/bin/../src/cli/dist Nov 27 09:08:59 Lion kibana[118796]: Native global console methods have been overridden in production environment. Nov 27 09:09:05 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:09:05.309+09:00][INFO ][root] Kibana is starting Nov 27 09:09:05 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:09:05.342+09:00][INFO ][node] Kibana process configured with roles: [background_tasks, ui] Nov 27 09:10:23 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:10:23.803+09:00][INFO ][plugins-service] The following plugins are disabled: "cloudChat,cloudExperiments,cloudFullStor> Nov 27 09:10:23 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:10:23.904+09:00][INFO ][http.server.Preboot] http server running at http://192.168.11.85:5601 Nov 27 09:10:24 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:10:24.140+09:00][INFO ][plugins-system.preboot] Setting up [1] plugins: [interactiveSetup] Nov 27 09:10:24 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:10:24.188+09:00][INFO ][preboot] "interactiveSetup" plugin is holding setup: Validating Elasticsearch connection confi> Nov 27 09:10:24 Lion kibana[118796]: [2025-11-27T09:10:24.225+09:00][INFO ][root] Holding setup until preboot stage is completed. Nov 27 09:10:30 Lion kibana[118796]: i Kibana has not been configured. Nov 27 09:10:30 Lion kibana[118796]: Go to http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=078825 to get started. |
The following appears toward the end of the output:
Go to http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=078825 to get started.
Copy the provided Kibana URL (including the code) and use it in your browser to access Kibana and complete the setup.
4. Accessing the Kibana 9 Dashboard
Accsess http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=078825
If the firewall is running, open the Kibana port.
|
1 2 3 |
# firewall-cmd --add-port=5601/tcp --permanent # firewall-cmd reload |
When you access Kibana 9, the welcome page prompts you to configure Elastic.
First, enter the generated registration token.
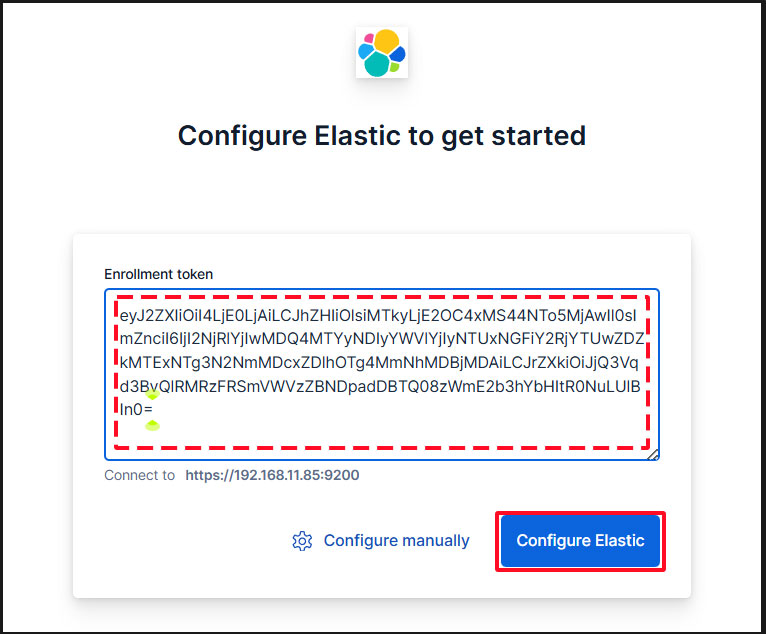
Paste the token, and Kibana will automatically connect to Elasticsearch.
Click Configure Elastic. The settings will be saved, and Elasticsearch will be configured and restarted.
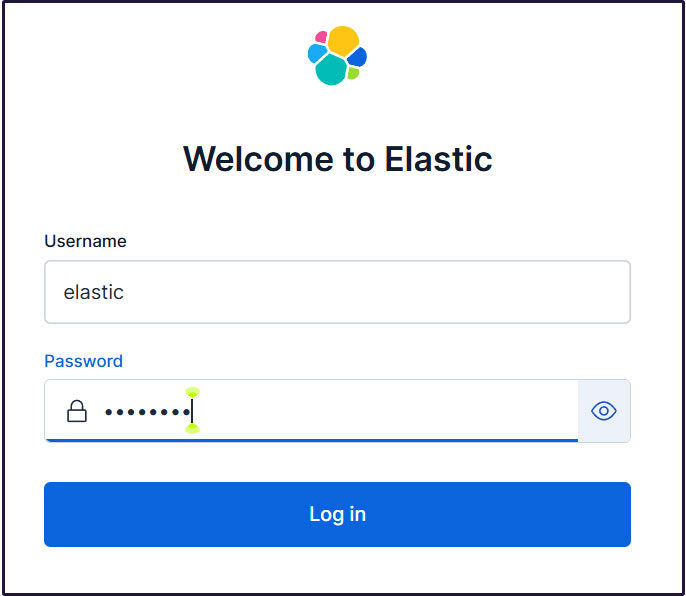
Proceed to the login page. Log in using the generated Elastic user credentials.
Username : elastic
Password : Password regenerated for clarity
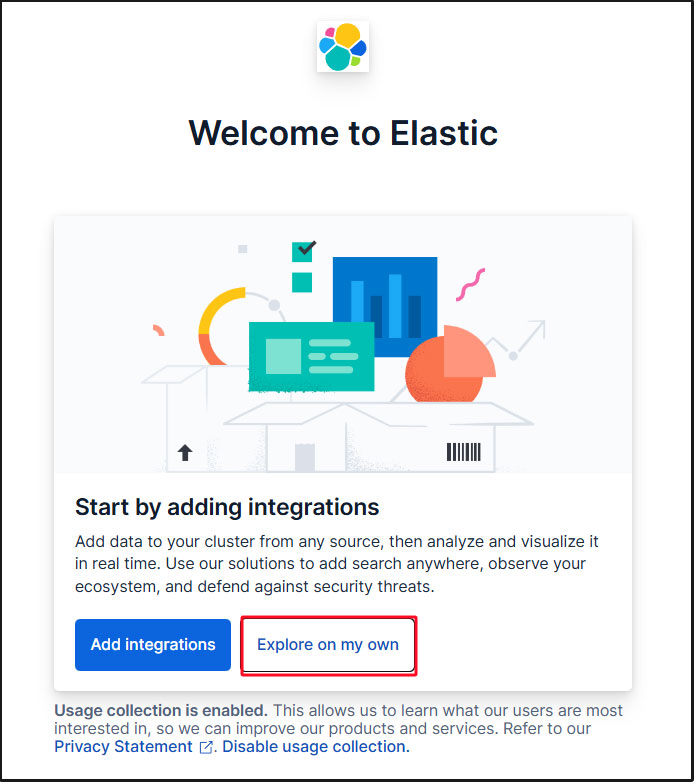
On the welcome page, click "Explore on my own" to proceed to the Kibana 9.x dashboard.
Create a new user account so that you do not need to use the elastic superuser account.
Open the main menu, then navigate to Stack Management > Security > Users
Click the "Create user" button in the upper right corner.
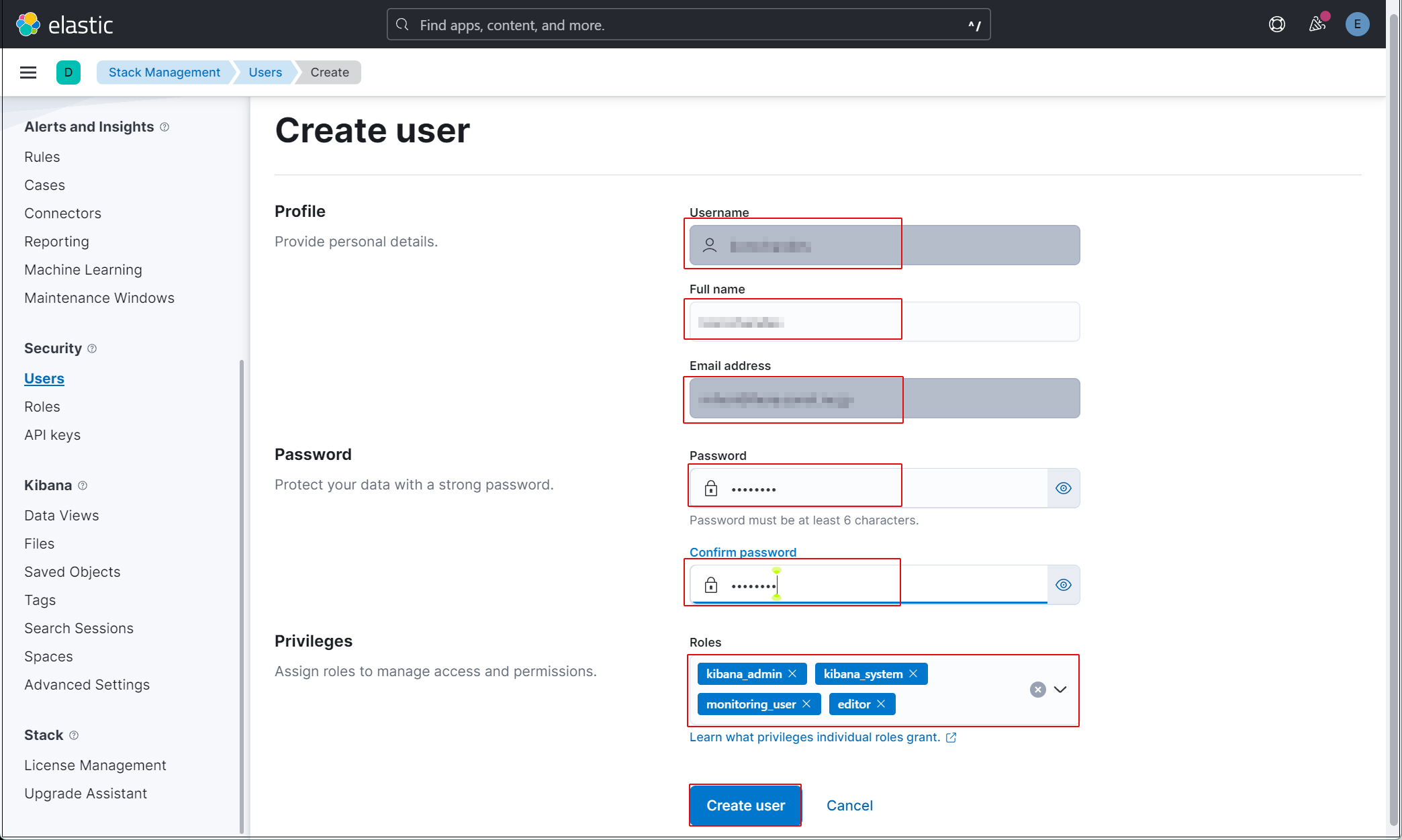
Enter new user information and assign the kibana_admin, kibana_system, monitoring_user, and editor roles under Privileges.
Finally, click [Create user].
Log out of the current profile and verify that you can log in with the newly created user account.
Currently, there is no data available to display in Kibana because Filebeat and Auditbeat are not configured on the SURICATA host.
Install Filebeat on the SURICATA server
This task will be performed on the first AlmaLinux 10.1 server where Suricata has been installed.
1. Filebeat Install
1.1 Download Elastic GPG Key
|
1 |
# rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch |
1.2 Create an elasticsearch.repo file in the /etc/yum/yum.repos.d directory with the following content:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo Please describe the following content. [elasticsearch] name=Elasticsearch repository for 9.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=0 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md |
1.3 Install Filebeat
|
1 2 3 |
# dnf -y install --enablerepo=elasticsearch filebeat Installed: filebeat-9.2.1-1.x86_64 |
1.4 Creating an Elasticsearch CA Certificate
Download the Elasticsearch CA certificate and save it to any directory (in this case, save it as /etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt).
※Keep port 9200 open on the second server (the server running AlmaLinux 10.0 with Elasticsearch installed).
|
1 2 3 |
# openssl s_client -connect 192.168.11.85:9200 \ -showcerts </dev/null 2>/dev/null | \ openssl x509 -outform PEM > /etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt |
1.4 Configure Filebeat to connect to Elasticsearch and Kibana
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# vi /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml Below the commented-out line `#host: "localhost:5601"` on line 137, add a line pointing to the private IP address and port of your Kibana instance. host: "192.168.11.85:5601" Line 164 : comment out #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] Line 165 : Enter the Elastic Stack IP address and Elasticsearch port number. hosts: ["https://192.168.11.85:9200"] Line 171 : Uncomments protocol: "https" Line 172 : Elasticsearch CA Certificate Specification ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt"] Line 175,176 : Uncomment the line, leave [username] as the default, and enter the password for the [elastic] user in [password]. username: "elastic" password: “xxxxxxxxx" |
1.5 Configuration File Test
|
1 2 |
# filebeat test config Config OK |
1.6 Enable the built-in Suricata module in Filebeats
|
1 |
# filebeat modules enable suricata |
The above command will change /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml.disabled to /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml, but the contents remain unchanged. Therefore, edit it as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# vi /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml # Module: suricata # Docs: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/main/filebeat-module-suricata.html - module: suricata # All logs eve: enabled: true var.paths: ["/var/log/suricata/eve.json"] # Set custom paths for the log files. If left empty, # Filebeat will choose the paths depending on your OS. #var.paths: |
1.7 Set up the initial environment
Load the pipeline into the Suricata service
Load the SIEM dashboard into Elasticsearch
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# filebeat setup -e -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.556+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-pipeline","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.608+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-dns","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.645+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-dns-answer-v1","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.697+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-dns-answer-v2","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.859+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-tls","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} {"log.level":"info","@timestamp":"2025-11-27T10:17:27.948+0900","log.logger":"modules","log.origin":{"function":"github.com/elastic/beats/v7/filebeat/fileset.LoadPipeline","file.name":"fileset/pipelines.go","file.line":134},"message":"Elasticsearch pipeline loaded.","service.name":"filebeat","pipeline":"filebeat-9.2.1-suricata-eve-http","ecs.version":"1.6.0"} ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
1.6 Start the Filebeat service
|
1 |
# systemctl start filebeat.service |
2. Check in Kibana
Log back into Kibana using the user you created. Accsses http://192.168.11.85:5601
Enter "Suricata Events Overview" in the top search field, then click Events Overview.
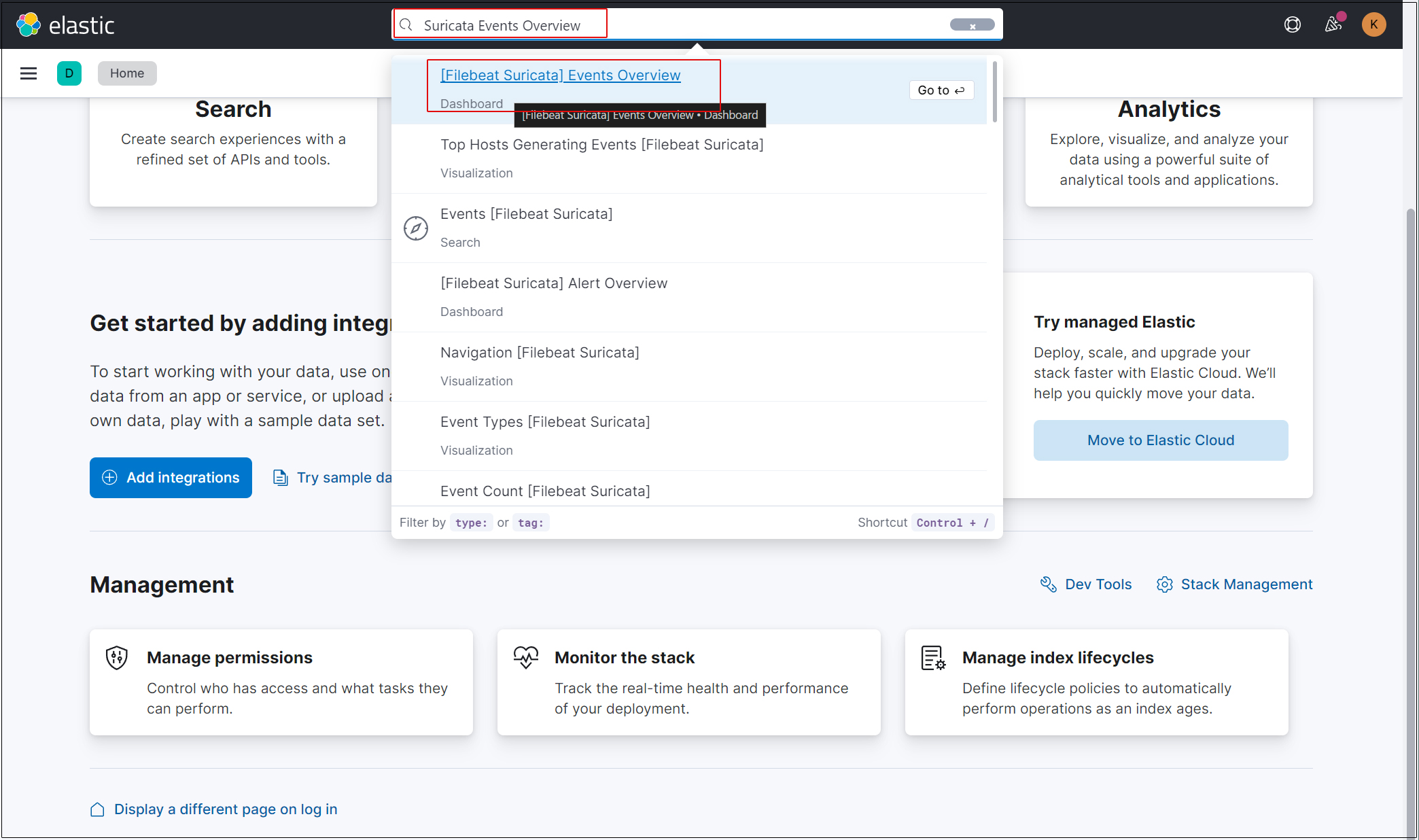
All Suricata events from the past 15 minutes are displayed.
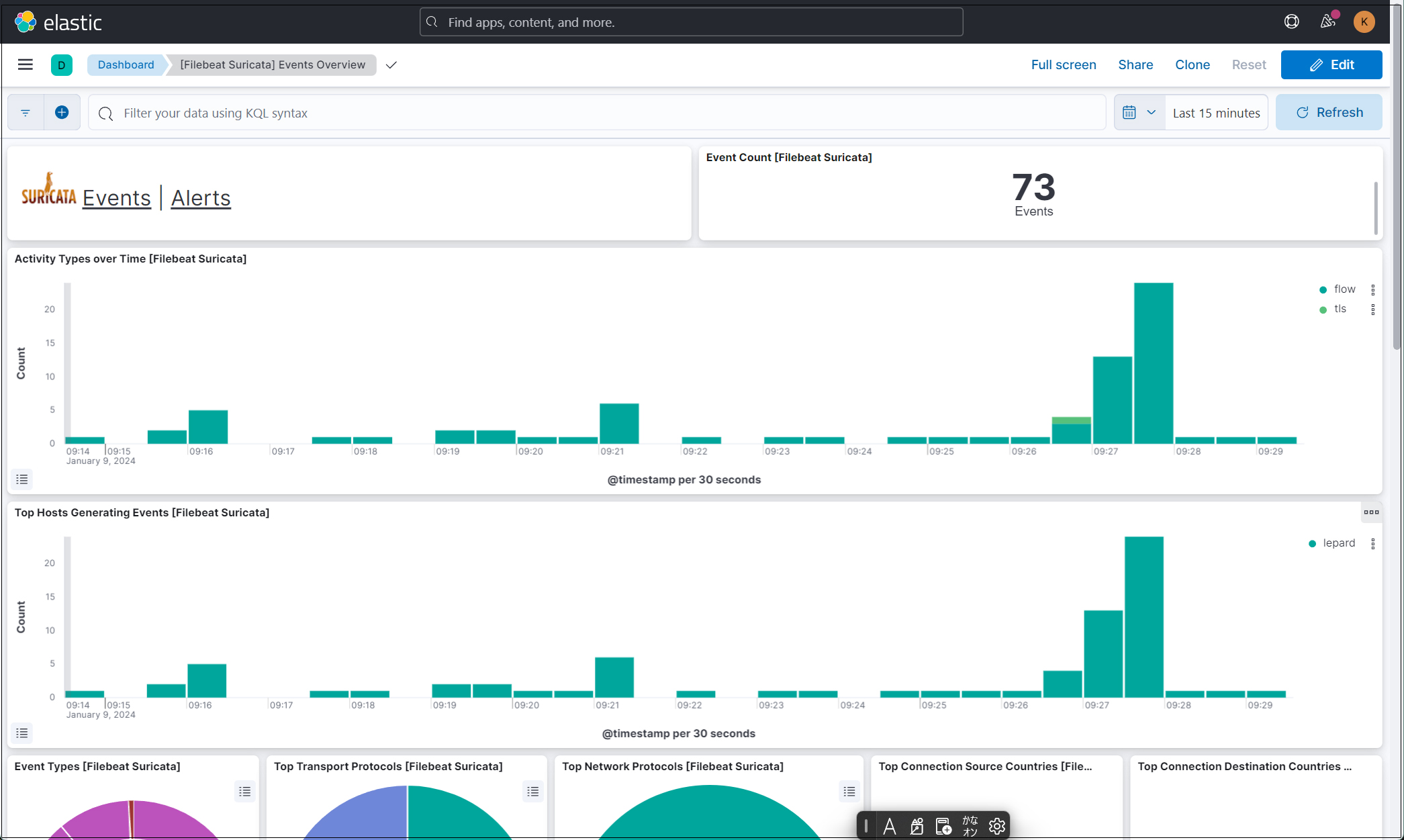
To display alerts for malicious traffic, click the "Alerts" text next to the Suricata logo.
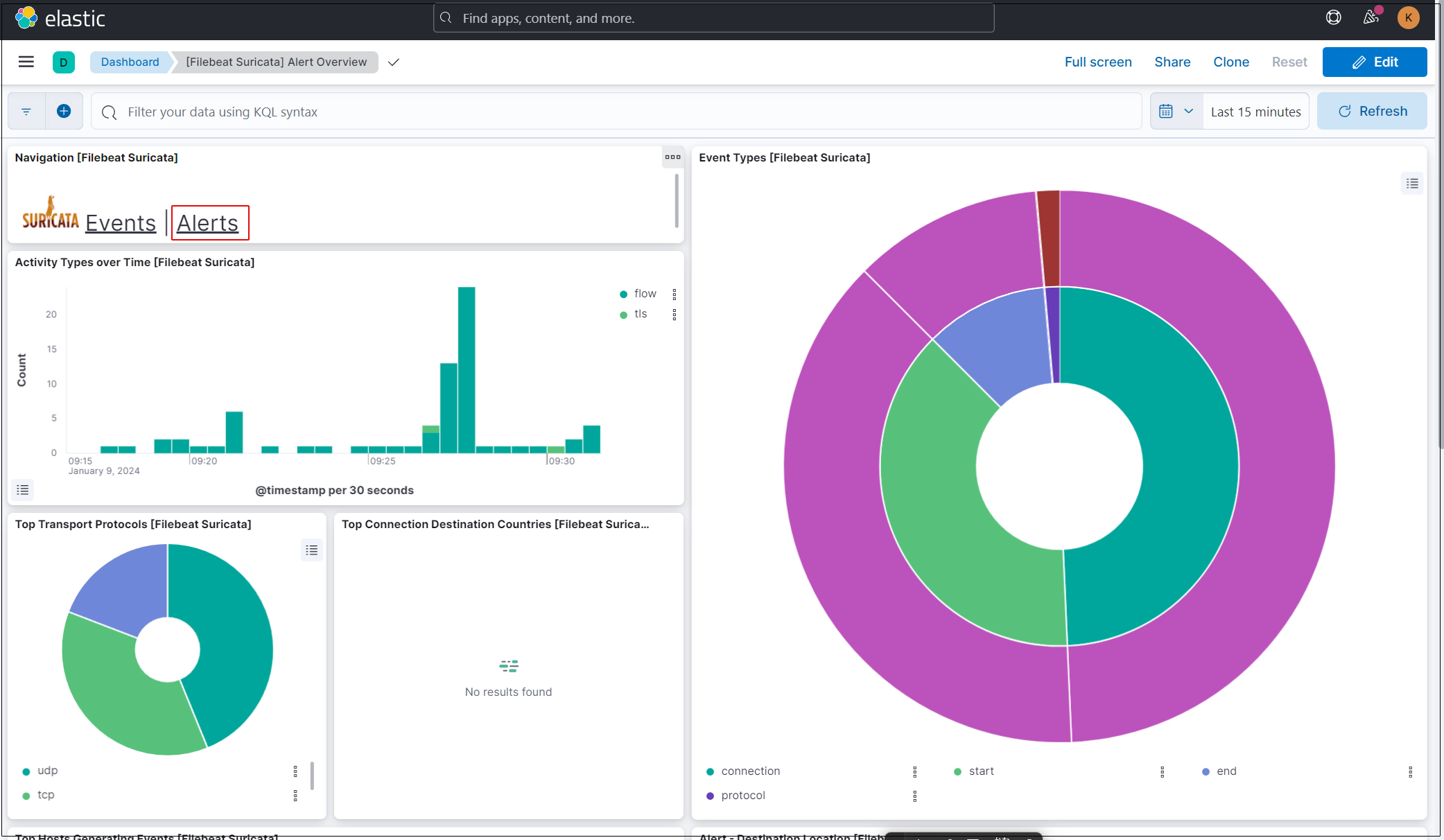
Kibana offers a variety of features and tools for visualizing logs, so feel free to experiment with them.

