Contents
Prerequisite.
We will install Suricata IDS and ElasticStack on the following servers
・1st server Suricata IDS & Filebeat : Debian13.0 IP address (192.168.11.83)
・2nd server ElasticStack & kibana : Ubunru24.04 IP address(192.168.11.85)
Run as a sudo user other than root
1st server Suricata Install
SURICATA IDS/IPS is an open source IDS that monitors communications on the network and detects suspicious traffic. Its basic mechanism is signature-based, so it can detect predefined unauthorized communications. Suricata is also characterized by its ability to provide protection as well as detection.
1.Suricata
①Install required packages
|
1 |
# apt -y install wget curl dirmngr apt-transport-https gnupg2 ca-certificates lsb-release debian-archive-keyring unzip |
➁Suricata install
|
1 2 |
# apt update # apt -y install suricata |
Check Version
|
1 2 |
# suricata -V This is Suricata version 7.0.10 RELEASE |
Enable suricata.service to run on system reboot
|
1 2 3 4 |
# systemctl enable suricata.service Synchronizing state of suricata.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable suricata |
Stop the Suricata service as it needs to be configured first.
|
1 |
# systemctl stop suricata.service |
2.Configure Suricata
①Determine interface and IP address where Suricata will inspect network packets
|
1 2 3 |
# ip --brief add lo UNKNOWN 127.0.0.1/8 ::1/128 ens33 UP 192.168.11.83/24 fe80::20c:29ff:febf:c38f/64 |
Edit /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml # Line 18 : Change (own network) HOME_NET: "[192.168.11.0/24]" # Line 135 : change community-id: false → community-id: true # Line 621 : change af-packet: - interface: eth0 ↓ af-packet: - interface: ens33 ←Change to your own interface name |
SURICATA supports live reloading of rules, allowing you to add, delete, or edit rules without restarting the running SURICATA process. To enable the live reload option, scroll to the bottom of the configuration file and add the following line
detect-engine:
- rule-reload: true
This setting allows the SIGUSR2 system signal to be sent to a running process, and SURICATA will reload the modified rules into memory. A command such as the following will signal the SURICATA process to reload the rule set without restarting the process:
|
1 |
# kill -usr2 $(pidof suricata) |
➁Add rule set
Suricata has a tool called suricata-update that allows you to retrieve rulesets from external providers. You can download the latest rulesets for your suricata server by running
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
# suricata-update -o /etc/suricata/rules 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Using data-directory /var/lib/suricata. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Using Suricata configuration /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Using /etc/suricata/rules for Suricata provided rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Found Suricata version 7.0.10 at /usr/bin/suricata. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Loading /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Disabling rules for protocol pgsql 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Disabling rules for protocol modbus 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Disabling rules for protocol dnp3 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Disabling rules for protocol enip 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- No sources configured, will use Emerging Threats Open 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:06 - <Info> -- Fetching https://rules.emergingthreats.net/open/suricata-7.0.10/emerging.rules.tar.gz. 100% - 5023988/5023988 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:08 - <Info> -- Done. -----Abbreviation--------- 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:08 - <Info> -- Ignoring file f625293e2432dbf07497d06349de6f0b/rules/emerging-deleted.rules 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Loaded 60469 rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Disabled 13 rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Enabled 0 rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Modified 0 rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Dropped 0 rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Enabled 136 rules for flowbit dependencies. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Backing up current rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:11 - <Info> -- Writing rules to /etc/suricata/rules/suricata.rules: total: 60469; enabled: 44686; added: 60469; removed 0; modified: 0 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:12 - <Info> -- Writing /etc/suricata/rules/classification.config 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:12 - <Info> -- Testing with suricata -T. 20/8/2025 -- 10:24:39 - <Info> -- Done. |
It shows that suricata-update has retrieved the free Emerging Threats ET Open Rules and saved them in Suricata's /etc/suricata/rules/suricata.rules file. It also shows the number of rules processed, in this example 60469 were added, of which 44686 were activated.
➂Adding Rule Set Providers
List Default Providers
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 |
# suricata-update list-sources Name: abuse.ch/feodotracker Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Feodo Tracker Botnet C2 IP ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-blacklist Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch SSL Blacklist License: CC0-1.0 Replaces: sslbl/ssl-fp-blacklist Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-c2 Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Suricata Botnet C2 IP Ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Name: abuse.ch/sslbl-ja3 Vendor: Abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch Suricata JA3 Fingerprint Ruleset License: CC0-1.0 Replaces: sslbl/ja3-fingerprints Name: abuse.ch/urlhaus Vendor: abuse.ch Summary: Abuse.ch URLhaus Suricata Rules License: CC0-1.0 Name: aleksibovellan/nmap Vendor: aleksibovellan Summary: Suricata IDS/IPS Detection Rules Against NMAP Scans License: MIT Name: et/open Vendor: Proofpoint Summary: Emerging Threats Open Ruleset License: MIT Name: et/pro Vendor: Proofpoint Summary: Emerging Threats Pro Ruleset License: Commercial Replaces: et/open Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.proofpoint.com/us/threat-insight/et-pro-ruleset Name: etnetera/aggressive Vendor: Etnetera a.s. Summary: Etnetera aggressive IP blacklist License: MIT Name: oisf/trafficid Vendor: OISF Summary: Suricata Traffic ID ruleset License: MIT Name: pawpatrules Vendor: pawpatrules Summary: PAW Patrules is a collection of rules for IDPS / NSM Suricata engine License: CC-BY-SA-4.0 Name: ptrules/open Vendor: Positive Technologies Summary: Positive Technologies Open Ruleset License: Custom Name: scwx/enhanced Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-enhanced ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: scwx/malware Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-malware ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: scwx/security Vendor: Secureworks Summary: Secureworks suricata-security ruleset License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.secureworks.com/contact/ (Please reference CTU Countermeasures) Name: stamus/lateral Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Lateral movement rules License: GPL-3.0-only Name: stamus/nrd-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, complete License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, complete License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-entropy-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, high entropy License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-entropy-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, high entropy License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-phishing-14-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 14 day list, phishing License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: stamus/nrd-phishing-30-open Vendor: Stamus Networks Summary: Newly Registered Domains Open only - 30 day list, phishing License: Commercial Parameters: secret-code Subscription: https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-labs/subscribe-to-threat-intel-feed Name: tgreen/hunting Vendor: tgreen Summary: Threat hunting rules License: GPLv3 |
If you include the tgreen/hunting ruleset as an example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# suricata-update enable-source tgreen/hunting -D /etc/suricata/rules 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Using Suricata configuration /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Using /etc/suricata/rules for Suricata provided rules. 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Found Suricata version 7.0.10 at /usr/bin/suricata. 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Warning> -- Source index does not exist, will use bundled one. 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Warning> -- Please run suricata-update update-sources. 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Creating directory /etc/suricata/rules/update/sources 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Enabling default source et/open 20/8/2025 -- 10:32:45 - <Info> -- Source tgreen/hunting enabled |
Perform update
|
1 |
# suricata-update -o /etc/suricata/rules |
3.Suricata Configuration Testing
①Run Verification Tool
Change the path of suricata.rules in the suricata configuration file before executing
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml Line 2187 : Comment and add the following below it #default-rule-path: /var/lib/suricata/rules default-rule-path: /etc/suricata/rules |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# suricata -T -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -v Notice: suricata: This is Suricata version 7.0.10 RELEASE running in SYSTEM mode Info: cpu: CPUs/cores online: 2 Info: suricata: Running suricata under test mode Info: suricata: Setting engine mode to IDS mode by default Info: exception-policy: master exception-policy set to: auto Info: logopenfile: fast output device (regular) initialized: fast.log Info: logopenfile: eve-log output device (regular) initialized: eve.json Info: logopenfile: stats output device (regular) initialized: stats.log Info: detect: 1 rule files processed. 44686 rules successfully loaded, 0 rules failed, 0 Info: threshold-config: Threshold config parsed: 0 rule(s) found Info: detect: 44689 signatures processed. 964 are IP-only rules, 4384 are inspecting packet payload, 39119 inspect application layer, 109 are decoder event only Notice: suricata: Configuration provided was successfully loaded. Exiting. |
Suricata service restart
|
1 |
# systemctl start suricata |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# systemctl status suricata ● suricata.service - Suricata IDS/IDP daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-08-20 10:49:39 JST; 40s ago Invocation: 0574b8b9b965426a8b68ceb4d6a4bbfa Docs: man:suricata(8) man:suricatasc(8) https://suricata.io/documentation/ Process: 3737 ExecStart=/usr/bin/suricata -D --af-packet -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 3738 (Suricata-Main) Tasks: 8 (limit: 4595) Memory: 467.7M (peak: 468.2M) CPU: 25.822s CGroup: /system.slice/suricata.service mq3738 /usr/bin/suricata -D --af-packet -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid Aug 20 10:49:39 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting suricata.service - Suricata IDS/IDP daemon... Aug 20 10:49:39 Lepard suricata[3737]: i: suricata: This is Suricata version 7.0.10 RELEASE running in SYSTEM mode Aug 20 10:49:39 Lepard systemd[1]: Started suricata.service - Suricata IDS/IDP daemon. |
Check log files
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# tail -f /var/log/suricata/suricata.log [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:39 Info: logopenfile: fast output device (regular) initialized: fast.log [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:39 Info: logopenfile: eve-log output device (regular) initialized: eve.json [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:39 Info: logopenfile: stats output device (regular) initialized: stats.log [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:53 Info: detect: 1 rule files processed. 44686 rules successfully loaded, 0 rules failed, 0 [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:53 Info: threshold-config: Threshold config parsed: 0 rule(s) found [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:49:53 Info: detect: 44689 signatures processed. 964 are IP-only rules, 4384 are inspecting packet payload, 39119 inspect application layer, 109 are decoder event only [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:50:04 Warning: af-packet: ens33: AF_PACKET tpacket-v3 is recommended for non-inline operation [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:50:04 Info: runmodes: ens33: creating 2 threads [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:50:05 Info: unix-manager: unix socket '/var/run/suricata-command.socket' [3738 - Suricata-Main] 2025-08-20 10:50:05 Notice: threads: Threads created -> W: 2 FM: 1 FR: 1 Engine started. |
4.Testing the Suricata Rule
①Test ET Open rule number 2100498 using the following command
|
1 2 |
# curl http://testmynids.org/uid/index.html uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root) |
②Check the log file using the specified rule number
|
1 2 3 |
# grep 2100498 /var/log/suricata/fast.log 08/20/2025-10:51:30.373730 [**] [1:2100498:7] GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root [**] [Classification: Potentially Bad Traffic] [Priority: 2] {TCP} 143.204.80.119:80 -> 192.168.11.83:41568 |
③Check events in /var/log/suricata/eve.log
Install jq
|
1 |
# apt -y install jq |
Filter EVE Log events by searching for 2100498 signatures
Display alert objects with signature_id keys that match the values in 2100498
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
# jq 'select(.alert .signature_id==2100498)' /var/log/suricata/eve.json { "timestamp": "2025-08-20T10:51:30.373730+0900", "flow_id": 646171449384620, "in_iface": "ens33", "event_type": "alert", "src_ip": "143.204.80.119", "src_port": 80, "dest_ip": "192.168.11.83", "dest_port": 41568, "proto": "TCP", "pkt_src": "wire/pcap", "community_id": "1:HIQMV6BNl507wC8/GcjRtQBp/8M=", "tx_id": 0, "tx_guessed": true, "alert": { "action": "allowed", "gid": 1, "signature_id": 2100498, "rev": 7, "signature": "GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root", "category": "Potentially Bad Traffic", "severity": 2, "metadata": { "confidence": [ "Medium" ], "created_at": [ "2010_09_23" ], "signature_severity": [ "Informational" ], "updated_at": [ "2019_07_26" ] } }, -------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------- |
④Creating and Applying Custom Rules
Create the following custom signature to scan SSH traffic to non-SSH ports and include it in the file /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules (IPv4 only this time)
|
1 2 |
# vi /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules alert ssh any any -> 192.168.11.83 !2244 (msg:"SSH TRAFFIC on non-SSH port"; flow:to_client, not_established; classtype: misc-attack; target: dest_ip; sid:1000000;) |
Editing suricata.yaml
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml Add local.rules around line 2191 rule-files: - suricata.rules - local.rules |
Verify SURICATA settings
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# suricata -T -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -v Notice: suricata: This is Suricata version 7.0.10 RELEASE running in SYSTEM mode Info: cpu: CPUs/cores online: 2 Info: suricata: Running suricata under test mode Info: suricata: Setting engine mode to IDS mode by default Info: exception-policy: master exception-policy set to: auto Info: logopenfile: fast output device (regular) initialized: fast.log Info: logopenfile: eve-log output device (regular) initialized: eve.json Info: logopenfile: stats output device (regular) initialized: stats.log Info: detect: 2 rule files processed. 44687 rules successfully loaded, 0 rules failed, 0 Info: threshold-config: Threshold config parsed: 0 rule(s) found Info: detect: 44690 signatures processed. 964 are IP-only rules, 4384 are inspecting packet payload, 39120 inspect application layer, 109 are decoder event only Notice: suricata: Configuration provided was successfully loaded. Exiting. |
Edit the custom signature you just created and convert it to use the drop action.
|
1 2 3 |
# vi /etc/suricata/rules/local.rules drop ssh any any -> 192.168.11.83 !2244 (msg:"SSH TRAFFIC on non-SSH port"; flow:to_client, not_established; classtype: misc-attack; target: dest_ip; sid:1000000;) |
⑤Reconfigure SURICATA and reboot in IPS mode
SURICATA operates in IDS mode by default and does not actively block network traffic; to switch to IPS mode, SURICATA's default settings must be changed.
Create a new systemd override file using the systemctl edit command:
|
1 |
# systemctl edit suricata.service |
Add the following section in red at the beginning
###Editing /etc/systemd/system/suricata.service.d/override.conf
###Anything between here and the comment below will become the new contents of the file
[Service]
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/bin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid -q 0 -vvv
Type=simple
###Edits below this comment will be discarded
Reload systemd to detect new Suricata settings
|
1 2 |
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl restart suricata.service |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
# systemctl status suricata.service ● suricata.service - Suricata IDS/IDP daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/suricata.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/suricata.service.d mqoverride.conf Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-08-20 11:02:11 JST; 16s ago Invocation: c0e0f6216d8c412bb56e4e9a986f60d4 Docs: man:suricata(8) man:suricatasc(8) https://suricata.io/documentation/ Main PID: 4046 (Suricata-Main) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4595) Memory: 443.5M (peak: 443.6M) CPU: 16.819s CGroup: /system.slice/suricata.service mq4046 /usr/bin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml --pidfile /run/suricata.pid -q 0 -vvv Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (http)": 17 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (http)": 2 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toclient file_data (http2)": 17 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toclient file_data (http2)": 2 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (http2)": 17 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (http2)": 2 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (smtp)": 17 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: AppLayer MPM "toserver file_data (smtp)": 2 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: Pkt MPM "icmpv6.hdr": 1 Aug 20 11:02:26 Lepard suricata[4046]: [4046] Perf: detect: Pkt MPM "ipv6.hdr": 1 |
With this change, we are ready to send traffic to Suricata through the UFW firewall.
⑥Configure UFW to send traffic to Suricata
To add the rules needed for Suricata to UFW, you must directly edit the firewall files in /etc/ufw/before.rules and /etc/ufw/before6.rules.
|
1 |
# vi /etc/ufw/before.rules |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
# # rules.before # # Rules that should be run before the ufw command line added rules. Custom # rules should be added to one of these chains: # ufw-before-input # ufw-before-output # ufw-before-forward # # Don't delete these required lines, otherwise there will be errors *filter :ufw-before-input - [0:0] :ufw-before-output - [0:0] :ufw-before-forward - [0:0] :ufw-not-local - [0:0] # End required lines #Add 7 lines to the bottom of the page. ## Start Suricata NFQUEUE rules -I INPUT 1 -p tcp --dport 2244 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypass -I OUTPUT 1 -p tcp --sport 2244 -j NFQUEUE --queue-bypass -I FORWARD -j NFQUEUE -I INPUT 2 -j NFQUEUE -I OUTPUT 2 -j NFQUEUE ## End Suricata NFQUEUE rules # allow all on loopback |
Similarly, change /etc/ufw/before6.rules
Restart UFW
|
1 |
# systemctl restart ufw.service |
Ensure that packets matching the aforementioned signature sid:2100498 are dropped
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi /etc/suricata/rules/suricata.rules Find line matching sid:2100498 and change alert to drop drop ip any any -> any any (msg:"GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root"; content:"uid=0|28|root|29|"; classtype:bad-unknown; sid:2100498; rev:7; metadata:created_at 2010_09_23, updated_at 2019_07_26;) |
Reload signatures
|
1 |
# kill -usr2 $(pidof suricata) |
Test this rule using curl
|
1 2 |
# curl --max-time 5 http://testmynids.org/uid/index.html curl: (28) Operation timed out after 5002 milliseconds with 0 bytes received |
Checking eve.log using jq, "action" is set to "blocked
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
# jq 'select(.alert .signature_id==2100498)' /var/log/suricata/eve.json { "timestamp": "2025-08-20T11:16:47.370226+0900", "flow_id": 2061264724130643, "event_type": "alert", "src_ip": "143.204.80.46", "src_port": 80, "dest_ip": "192.168.11.83", "dest_port": 48730, "proto": "TCP", "pkt_src": "wire/pcap", "community_id": "1:3/y3oPBRWY4A6yp2K7OUTLkakjo=", "tx_id": 0, "tx_guessed": true, "alert": { "action": "blocked", "gid": 1, "signature_id": 2100498, "rev": 7, "signature": "GPL ATTACK_RESPONSE id check returned root", "category": "Potentially Bad Traffic", "severity": 2, "metadata": { "confidence": [ "Medium" ], "created_at": [ "2010_09_23" ], "signature_severity": [ "Informational" ], "updated_at": [ "2019_07_26" ] } }, ---------------------------------------- ---------------------------------------- |
Elastic stack 9.x installation
Install & configure Elastic Stack to visualize & search SURICATA logs
This section is basically done on a second Ubuntu24.04 server
①Install Elastic stack 9.x repository signing key
|
1 |
# apt update |
|
1 |
# apt install gnupg2 -y |
|
1 2 |
# wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | \ gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/elastic.gpg |
➁Install Elastic Stack 9.x repository
|
1 |
# echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/apt stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-9.x.list |
update
|
1 |
# apt update |
➂Installing Elasticsearch 9.x on Ubuntu 24.04
|
1 |
# apt install elasticsearch -y |
During installation, security features are enabled by default;
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
The following NEW packages will be installed: elasticsearch 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 665 MB of archives. After this operation, 1,261 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/apt stable/main amd64 elasticsearch amd64 9.1.2 [665 MB] Fetched 665 MB in 34s (19.5 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package elasticsearch. (Reading database ... 129938 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../elasticsearch_9.1.2_amd64.deb ... Creating elasticsearch group... OK Creating elasticsearch user... OK Unpacking elasticsearch (9.1.2) ... Setting up elasticsearch (9.1.2) ... --------------------------- Security autoconfiguration information ------------------------------ Authentication and authorization are enabled. TLS for the transport and HTTP layers is enabled and configured. The generated password for the elastic built-in superuser is : qPb8Zf1kVka5x+E53V0i If this node should join an existing cluster, you can reconfigure this with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reconfigure-node --enrollment-token <token-here>' after creating an enrollment token on your existing cluster. You can complete the following actions at any time: Reset the password of the elastic built-in superuser with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic'. Generate an enrollment token for Kibana instances with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana'. Generate an enrollment token for Elasticsearch nodes with '/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s node'. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ### NOT starting on installation, please execute the following statements to configure elasticsearch service to start automatically using systemd sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service ### You can start elasticsearch service by executing sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.service Scanning processes... Scanning processor microcode... Scanning linux images... Pending kernel upgrade! Running kernel version: 6.8.0-71-generic Diagnostics: The currently running kernel version is not the expected kernel version 6.8.0-78-generic. Restarting the system to load the new kernel will not be handled automatically, so you should consider rebooting. |
Certifications and authorizations are in effect.
TLS at the transport and HTTP layers is enabled and configured.
An Elastic super user account (elastic) and its password will be created.
④Configuring Elasticsearch 9.x on Ubuntu
Since this is a basic single-node cluster, we will use the default settings.
Check the Elasticsearch configuration file /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml and you will see that the security settings are enabled
|
1 |
# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
#----------------------- BEGIN SECURITY AUTO CONFIGURATION ----------------------- # # The following settings, TLS certificates, and keys have been automatically # generated to configure Elasticsearch security features on 20-08-2025 03:55:02 # # -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Enable security features xpack.security.enabled: true xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true # Enable encryption for HTTP API client connections, such as Kibana, Logstash, and Agents xpack.security.http.ssl: enabled: true keystore.path: certs/http.p12 # Enable encryption and mutual authentication between cluster nodes xpack.security.transport.ssl: enabled: true verification_mode: certificate keystore.path: certs/transport.p12 truststore.path: certs/transport.p12 # Create a new cluster with the current node only # Additional nodes can still join the cluster later cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["Lion"] # Allow HTTP API connections from anywhere # Connections are encrypted and require user authentication http.host: 0.0.0.0 # Allow other nodes to join the cluster from anywhere # Connections are encrypted and mutually authenticated #transport.host: 0.0.0.0 #----------------------- END SECURITY AUTO CONFIGURATION ------------------------- |
⑤Start Elasticsearch
Start Elasticsearch and allow it to run at system startup
|
1 |
# systemctl daemon-reload |
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable --now elasticsearch # systemctl start elasticsearch |
Check Status
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
# systemctl status elasticsearch ● elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-08-20 13:01:49 JST; 21s ago Docs: https://www.elastic.co Main PID: 8969 (java) Tasks: 106 (limit: 9364) Memory: 4.3G (peak: 4.3G) CPU: 44.207s CGroup: /system.slice/elasticsearch.service tq8969 /usr/share/elasticsearch/jdk/bin/java -Xms4m -Xmx64m -XX:+UseSerialGC -Dcli.name=server -Dcli.script=/usr/share/elasticsearch/b> tq9035 /usr/share/elasticsearch/jdk/bin/java -Des.networkaddress.cache.ttl=60 -Des.networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10 -XX:+AlwaysPre> mq9057 /usr/share/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-ml/platform/linux-x86_64/bin/controller Aug 20 13:01:09 Lion systemd[1]: Starting elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch... Aug 20 13:01:49 Lion systemd[1]: Started elasticsearch.service - Elasticsearch. |
You can also check the status of the ES using the curl command; replace IP as appropriate
|
1 |
# curl https://192.168.11.85:9200 --cacert /etc/elasticsearch/certs/http_ca.crt -u elastic |
When prompted, enter the Elasticsearch password generated during the Elasticsearch installation
The output will look like this
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
Enter host password for user 'elastic': { "name" : "Lion", "cluster_name" : "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid" : "WSBFzJjKTkaNIcnBcug1-Q", "version" : { "number" : "9.1.2", "build_flavor" : "default", "build_type" : "deb", "build_hash" : "ca1a70216fbdefbef3c65b1dff04903ea5964ef5", "build_date" : "2025-08-11T15:04:41.449624592Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "10.2.2", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "8.19.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "8.0.0" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" } |
Also, make sure that both the HTTP and transport ports are open;
|
1 2 3 4 |
# ss -altnp | grep -E "9200|9300" LISTEN 0 4096 [::1]:9300 [::]:* users:(("java",pid=9035,fd=582)) LISTEN 0 4096 *:9200 *:* users:(("java",pid=9035,fd=585)) LISTEN 0 4096 [::ffff:127.0.0.1]:9300 *:* users:(("java",pid=9035,fd=583)) |
⑥Reset Elasticsearch Password
The auto-generated Elastic user password is too complex, reset it using the command /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password
To reset the password, run the command
|
1 |
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic -i |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
This tool will reset the password of the [elastic] user. You will be prompted to enter the password. Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y Enter password for [elastic]: Re-enter password for [elastic]: Password for the [elastic] user successfully reset. |
⑦Elasticsearch Logs
Elasticsearch writes logs to the /var/log/elasticsearch path; the log you need to check if there is a problem with your Elasticsearch instance is /var/log/elasticsearch/CLUSTER_NAME.log The logs you need to check if there is a problem with your Elasticsearch instance are
CLUSTER_NAME is the value of the cluster.name option in the elasticsearch.yaml file. If this value is not changed, the default is elasticsearch and the log file is /var/log/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.log.
|
1 |
# tail -f /var/log/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.log |
logs
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
[2025-08-20T04:03:23,949][INFO ][o.e.c.m.MetadataCreateIndexService] [Lion] creating index [.ds-ilm-history-7-2025.08.20-000001] in project [default], cause [initialize_data_stream], templates [provided in request], shards [1]/[1] [2025-08-20T04:03:23,949][INFO ][o.e.c.m.MetadataCreateDataStreamService] [Lion] adding data stream [ilm-history-7] with write index [.ds-ilm-history-7-2025.08.20-000001], backing indices [], and aliases [] [2025-08-20T04:03:23,950][INFO ][o.e.c.r.a.AllocationService] [Lion] in project [default] updating number_of_replicas to [0] for indices [.ds-ilm-history-7-2025.08.20-000001] [2025-08-20T04:03:40,408][INFO ][o.e.x.s.s.QueryableBuiltInRolesSynchronizer] [Lion] Successfully synced [29] built-in roles to .security index [2025-08-20T04:03:44,830][INFO ][o.e.x.s.s.SecurityMigrationExecutor] [Lion] Security migration not needed. Setting current version to: [2] [2025-08-20T04:03:44,832][INFO ][o.e.c.r.a.AllocationService] [Lion] current.health="GREEN" message="Cluster health status changed from [YELLOW] to [GREEN] (reason: [shards started [[.ds-ilm-history-7-2025.08.20-000001][0]]])." previous.health="YELLOW" reason="shards started [[.ds-ilm-history-7-2025.08.20-000001][0]]" [2025-08-20T04:07:09,352][INFO ][o.e.x.s.a.f.FileUserPasswdStore] [Lion] users file [/etc/elasticsearch/users] changed. updating users... [2025-08-20T04:07:09,354][INFO ][o.e.x.s.a.f.FileUserRolesStore] [Lion] users roles file [/etc/elasticsearch/users_roles] changed. updating users roles... [2025-08-20T04:07:34,364][INFO ][o.e.x.s.a.f.FileUserPasswdStore] [Lion] users file [/etc/elasticsearch/users] changed. updating users... [2025-08-20T04:07:34,366][INFO ][o.e.x.s.a.f.FileUserRolesStore] [Lion] users roles file [/etc/elasticsearch/users_roles] changed. updating users roles... |
Kibana 9.x installation
This section is basically done on a second Ubuntu 24.04 server
①Install
|
1 |
# apt install kibana |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: kibana 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 362 MB of archives. After this operation, 1,122 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/apt stable/main amd64 kibana amd64 9.1.2 [362 MB] Fetched 362 MB in 1min 20s (4,506 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package kibana. (Reading database ... 131496 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../kibana_9.1.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking kibana (9.1.2) ... Setting up kibana (9.1.2) ... Creating kibana group... OK Creating kibana user... OK Created Kibana keystore in /etc/kibana/kibana.keystore |
➁Configure Kibana 9
Kibana is configured by default to run on localhost:5601. To allow external access, edit the configuration file and replace the server.host value with the interface IP.
|
1 |
# vi /etc/kibana/kibana.yml |
Rewrite as follows
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. server.port: 5601 ... # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. #server.host: "localhost" server.host: "192.168.11.85" |
➂Generate Kibana-Elasticsearch Enrollment Token
To configure your Kibana instance to communicate with an existing Elasticsearch cluster with security features enabled, you need an Enrollment Token.
|
1 |
# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana |
eyJ2ZXIiOiI4LjE0LjAiLCJhZHIiOlsiMTkyLjE2OC4xMS44NTo5MjAwIl0sImZnciI6IjMwYzRiYWNjMjgxZDkzMGY5NzMyMzM5N2Q1ZjUxNTYzYzQyZDk1NTdmNDNlNDIwZjkxMWFjMTgzMjFmMzUwMjciLCJrZXkiOiI1ejVPWDVnQi1hWGhacW92LTR4MDp6VzJrMGNTVW03NEpBQkxSYVduTG13In0=④Generate Kibana encryption keys
Kibana uses encryption keys in several areas, from encrypting data for Kibana-related indexes to storing session information. The required keys are as follows
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey:Used to encrypt stored objects such as dashboards and visualizationsxpack.reporting.encryptionKey: Used to encrypt saved reportsxpack.security.encryptionKey: Used to encrypt session information
These can be generated using the command below
|
1 |
# /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-encryption-keys generate |
The command will give such an output
|
1 2 3 4 |
Settings: xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: 789e09eede8e552d877251f45e74b277 xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: c8a1d297e4bf0dbbdbb68fbee7d45b88 xpack.security.encryptionKey: 26433f15715a29f207b4cb7dd3597341 |
Insert these lines into Kibana config file, kibana.yml
|
1 2 3 |
# echo -e "xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: 789e09eede8e552d877251f45e74b277 xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: c8a1d297e4bf0dbbdbb68fbee7d45b88 xpack.security.encryptionKey: 26433f15715a29f207b4cb7dd3597341" >> /etc/kibana/kibana.yml |
⑤Running Kibana
Start Kibana 9 and allow it to run at system startup.
|
1 2 |
# systemctl enable --now kibana # systemctl start kibana |
status
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
# systemctl status kibana ● kibana.service - Kibana Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/kibana.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-08-20 13:32:01 JST; 24s ago Docs: https://www.elastic.co Main PID: 10203 (node) Tasks: 11 (limit: 9364) Memory: 268.5M (peak: 446.0M) CPU: 13.508s CGroup: /system.slice/kibana.service mq10203 /usr/share/kibana/bin/../node/glibc-217/bin/node /usr/share/kibana/bin/../src/cli/dist Aug 20 13:32:02 Lion kibana[10203]: Native global console methods have been overridden in production environment. Aug 20 13:32:05 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:05.878+09:00][INFO ][root] Kibana is starting Aug 20 13:32:05 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:05.913+09:00][INFO ][node] Kibana process configured with roles: [background_tasks, ui] Aug 20 13:32:11 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:11.870+09:00][INFO ][plugins-service] The following plugins are disabled: "cloudChat,cloudExperiments,cloudFullStory,dataUsage,profilingDataAccess,prof> Aug 20 13:32:11 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:11.958+09:00][INFO ][http.server.Preboot] http server running at http://192.168.11.85:5601 Aug 20 13:32:12 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:12.113+09:00][INFO ][plugins-system.preboot] Setting up [1] plugins: [interactiveSetup] Aug 20 13:32:12 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:12.135+09:00][INFO ][preboot] "interactiveSetup" plugin is holding setup: Validating Elasticsearch connection configuration… Aug 20 13:32:12 Lion kibana[10203]: [2025-08-20T13:32:12.166+09:00][INFO ][root] Holding setup until preboot stage is completed. Aug 20 13:32:19 Lion kibana[10203]: i Kibana has not been configured. Aug 20 13:32:19 Lion kibana[10203]: Go to http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=642051 to get started. |
The following appears at the end of the output
|
1 2 |
i Kibana has not been configured. Go to http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=642051 to get started. |
Copy the provided Kibana URL (including code) and use it in your browser to access Kibana and complete the setup.
Similarly, Kibana logs are available in /var/log/kibana/kibana.log and /var/log/syslog.
⑥Accessing the Kibana9 Dashboard
You can now access http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=642051
(copy the appropriate address for each person)
If UFW is running, open Kibana port
|
1 2 3 4 |
# ufw allow 5601/tcp Rule added # ufw reload Firewall reloaded |
When you access Kibana 9, the welcome page asks you to configure Elastic.
First, enter the generated registration token.
Copy the Kibana token generated using the command /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana, and paste it into the box
You can now access http://192.168.11.85:5601/?code=642051
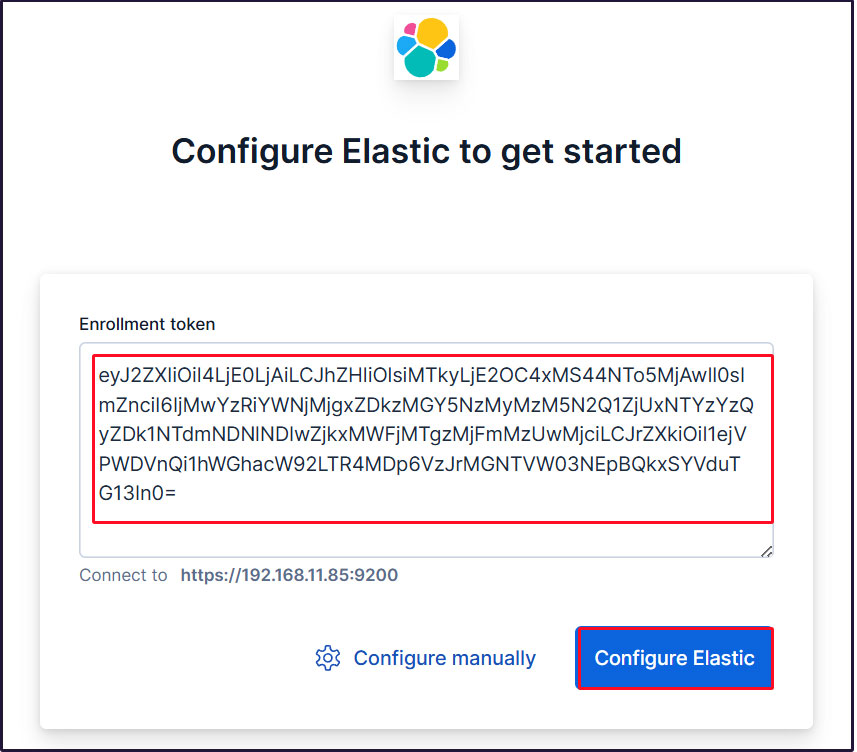
Paste the token and Kibana will automatically connect to Elasticsearch.
Click Configure Elastic. Your settings will be saved and Elasticsearch will be configured and restarted.
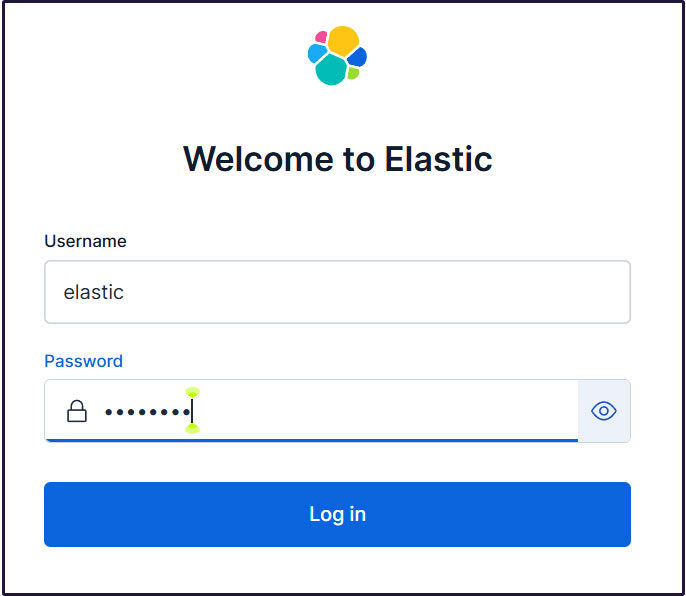
Go to the login page. Log in using the generated Elastic user credentials.
Username : elastic
Password : Easy-to-understand regenerated passwords
On the welcome page, click "Explore on my own" to proceed to the Kibana 9.x dashboard.
Installing Filebeat 9
To collect and monitor logs from Debian 13.0 using the ELK stack, Filebeat must be installed.
This work will be performed on the first server Debian13.0 IP address (192.168.11.83).
①Install Elastic Repos
To install Filebeat 9, you must install the Elastic 9.x repository.
|
1 2 |
# wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | \ gpg --dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/elk.gpg |
|
1 2 |
# echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/apt stable main" \ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-9.list |
update
|
1 |
# apt update |
Install Filebeat 9
|
1 |
# apt install filebeat |
➁Configuring Filebeat Logging
The default filebeat configuration file is /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
To make Filebeat write logs to its own log file, enter the following settings in the configuration file
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
# cat >> /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml << 'EOL' logging.level: info logging.to_files: true logging.files: path: /var/log/filebeat name: filebeat keepfiles: 7 permissions: 0640 EOL |
➂Connecting Filebeat to the data processing system
Configure Filebeat to connect to a data processing system. In this case, it is Elasticsearch.
To send logs directly to Elasticsearch, edit the Filebeat configuration file and update the Output Settings section.
Connecting to Elasticsearch 9 requires SSL and authentication.
Make sure you can connect to Elasticsearch port 9200/tcp
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# telnet 192.168.11.85 9200 Trying 192.168.11.85... Connected to 192.168.11.85. Escape character is '^]'. |
④Elasticsearch CA certificate creation
Download the Elasticsearch CA certificate and save it in a directory of your choice (this time as /etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt)
|
1 2 3 |
# openssl s_client -connect 192.168.11.85:9200 \ -showcerts </dev/null 2>/dev/null | \ openssl x509 -outform PEM > /etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt |
Get the credentials that Filebeat uses to authenticate to Elasticsearch. In this case, we will use the default superadmin and Elastic user credentials.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
# vi /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml Per line 127 Change Kibana section as follows #host: "localhost:5601" host: "192.168.11.85:5601" Change the Elasticsearch Output section per line 161 as follows output.elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. #hosts: ["localhost:9200"] hosts: ["192.168.11.85:9200"] # Performance preset - one of "balanced", "throughput", "scale", # "latency", or "custom". preset: balanced # Protocol - either `http` (default) or `https`. protocol: "https" ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/filebeat/elastic-ca.crt"] # Authentication credentials - either API key or username/password. #api_key: "id:api_key" username: "elastic" password: "Password" ←Password for elastic created on the second server |
⑤Configuration File Test
|
1 2 |
# filebeat test config Config OK |
⑥Test Filebeat output connections
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
# filebeat test output elasticsearch: https://192.168.11.85:9200... parse url... OK connection... parse host... OK dns lookup... OK addresses: 192.168.11.85 dial up... OK TLS... security: server's certificate chain verification is enabled handshake... OK TLS version: TLSv1.3 dial up... OK talk to server... OK version: 9.1.2 |
⑦Enable Filebeat's Suricata module
Change modules.d/suricata.yml as follows
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# cp /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml.disabled /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml # vi /etc/filebeat/modules.d/suricata.yml # Module: suricata # Docs: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/beats/filebeat/main/filebeat-module-suricata.html - module: suricata # All logs eve: enabled: true var.paths: ["/var/log/suricata/eve.json"] # Set custom paths for the log files. If left empty, # Filebeat will choose the paths depending on your OS. #var.paths: |
Enable Filebeat's Suricata module
|
1 |
# filebeat modules enable suricata |
⑧Set up initial environment
Load the SIEM dashboard and pipeline into Elasticsearch
filebeat setup command
|
1 |
# filebeat setup -e |
⑨Filebeat service launched
|
1 |
# systemctl start filebeat.service |
⑩Check with Kibana
Log back into Kibana at accsess http://192.168.11.85:5601
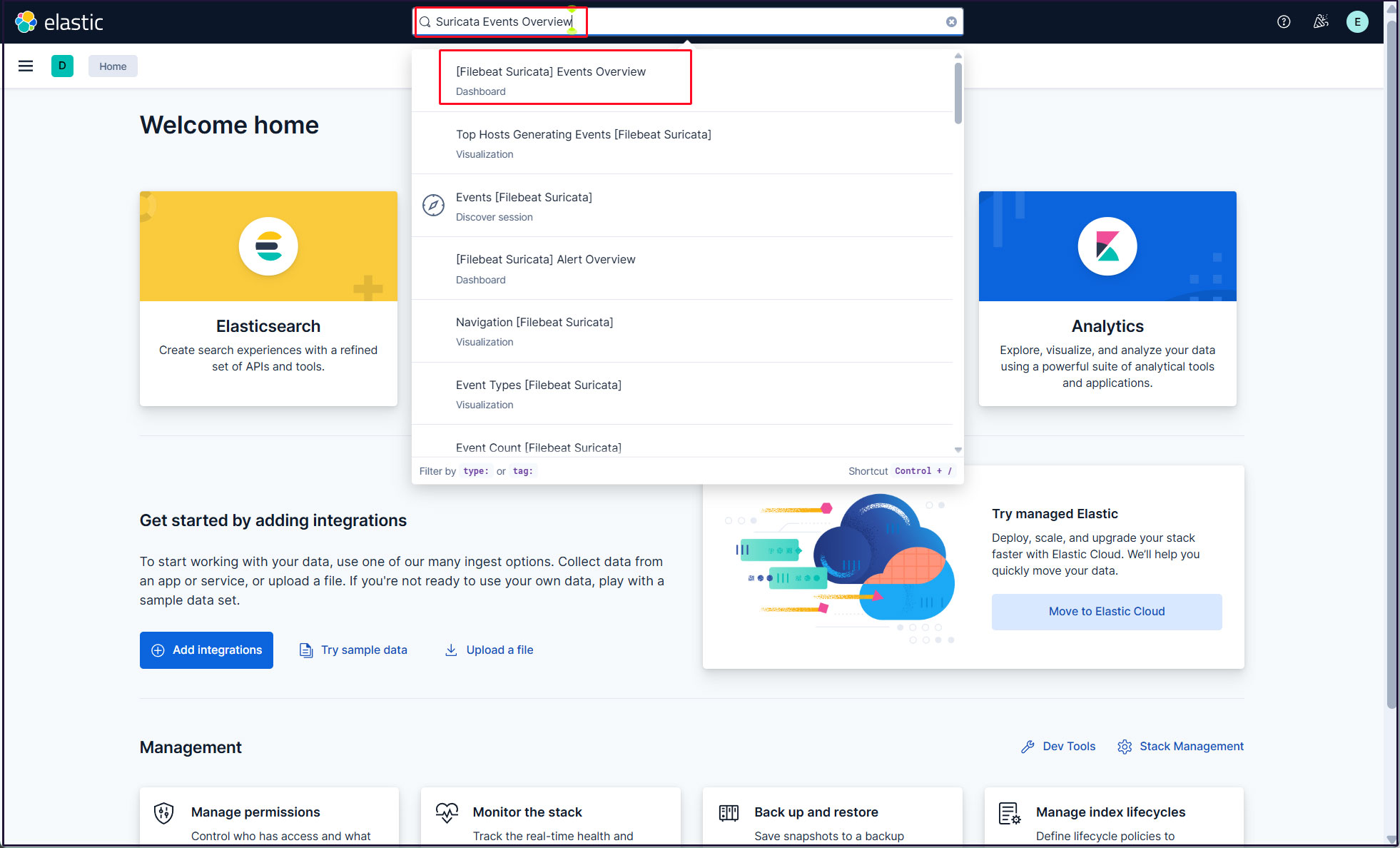
Type "Suricata Events Overview" in the top search field and click [Filebeat Suricata]Events Overview
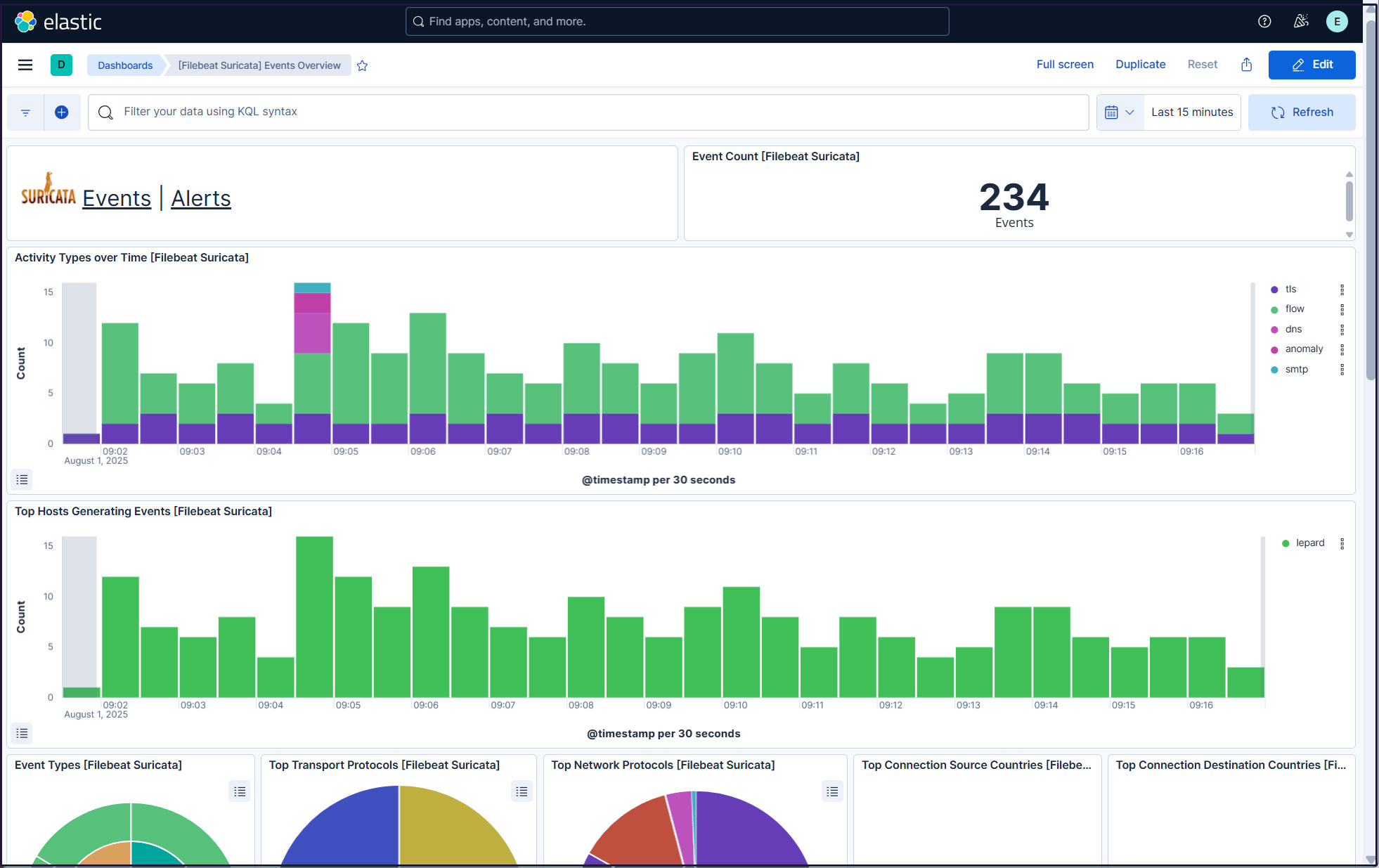
All Suricata events in the last 15 minutes are displayed
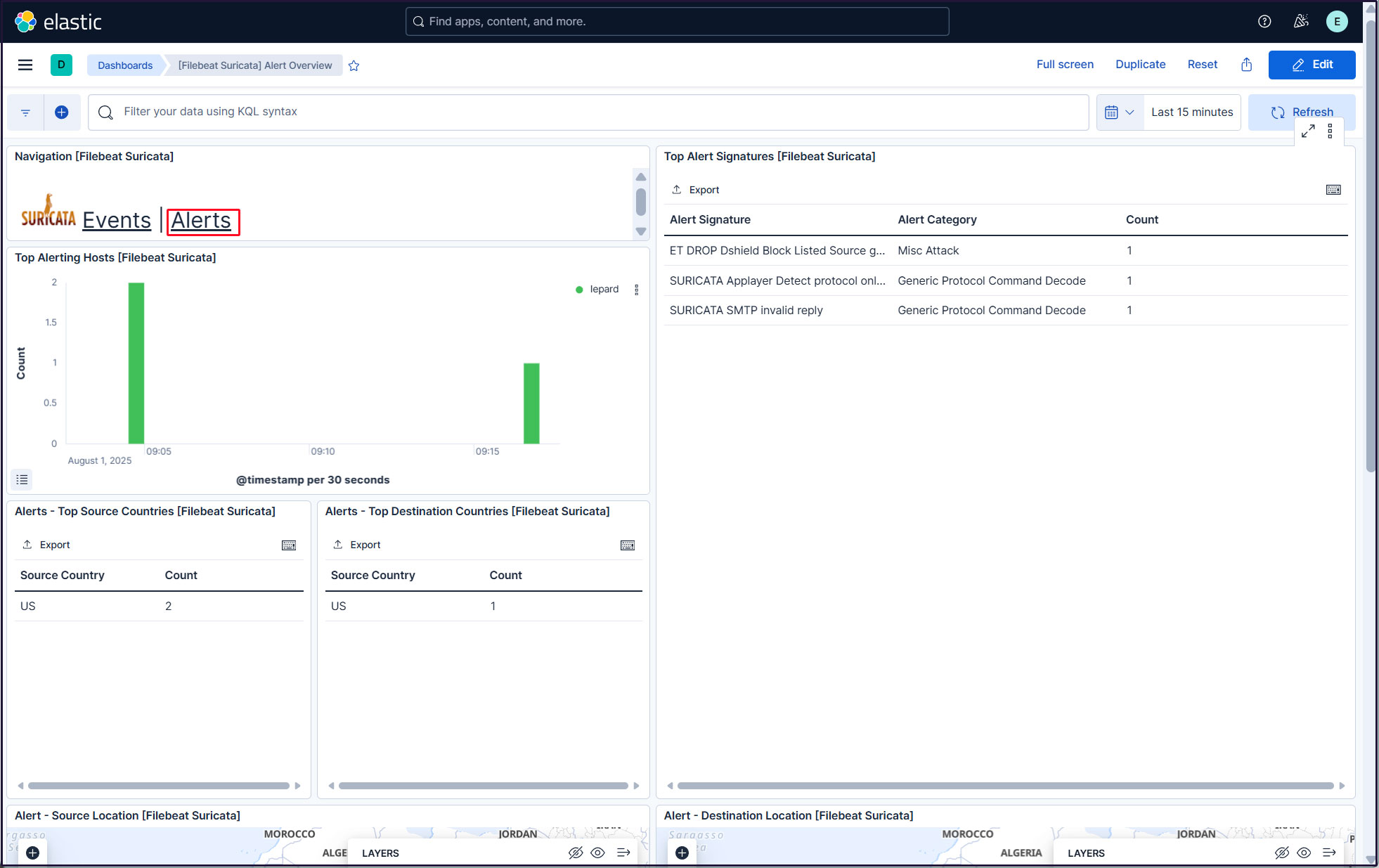
Click on the Alerts text next to the Suricata logo for malicious traffic alerts
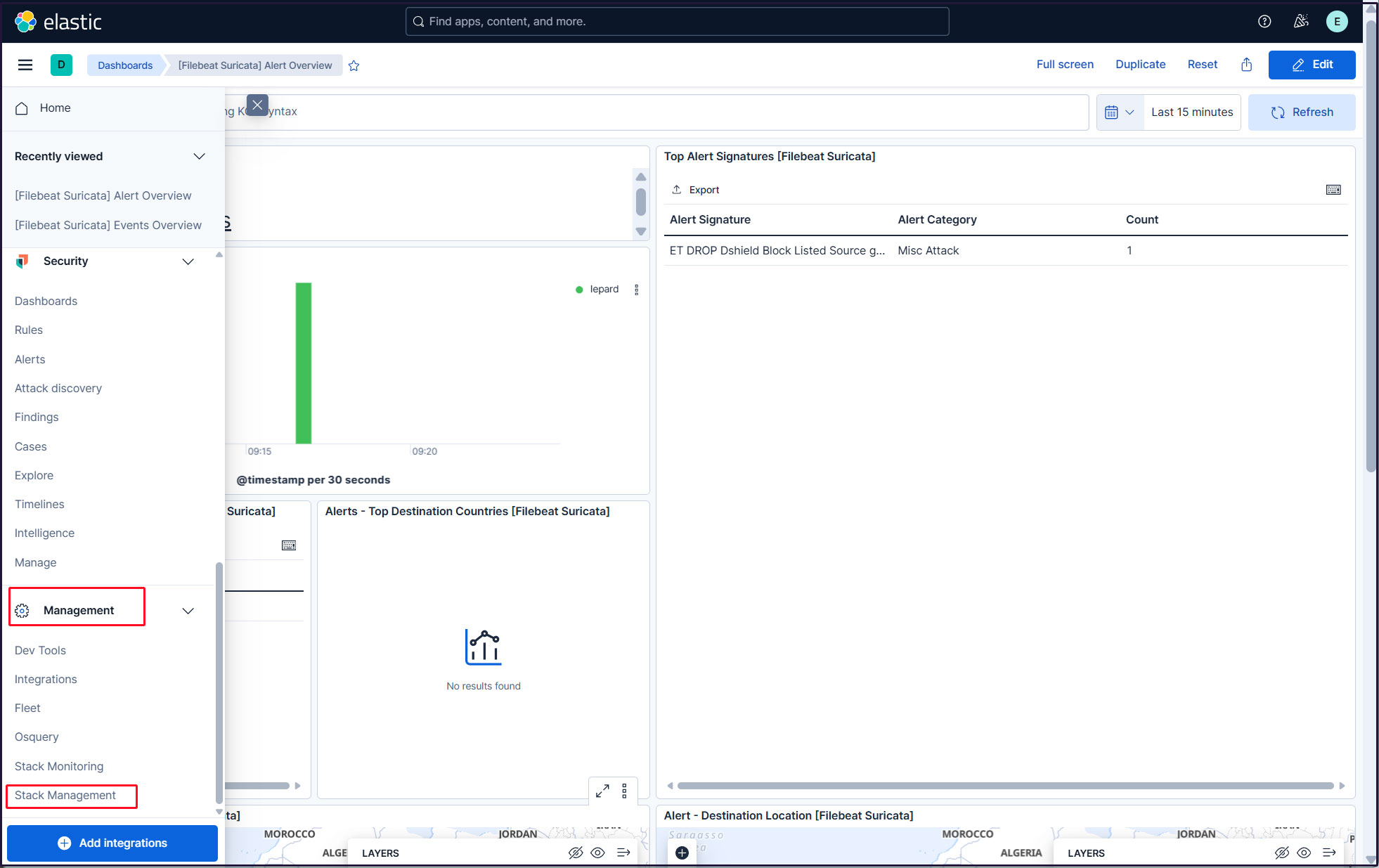
Create a new user account so that you do not have to use the elastic superuser account.
Click on the three-line mark in the upper left corner and select "Stack Management" under "Management"
Select "security" and "Users"
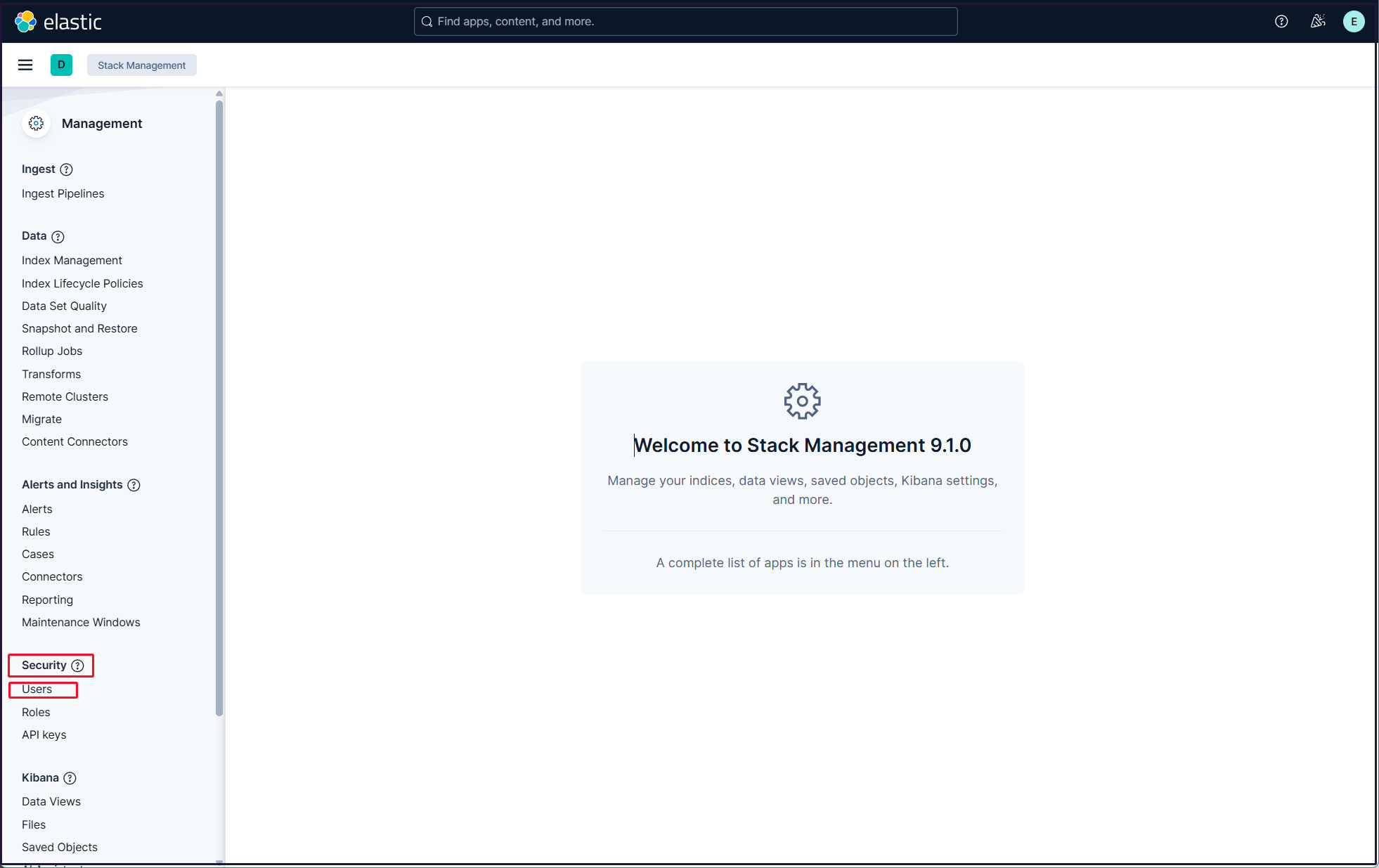
Click on the "Create user" button in the upper right corner
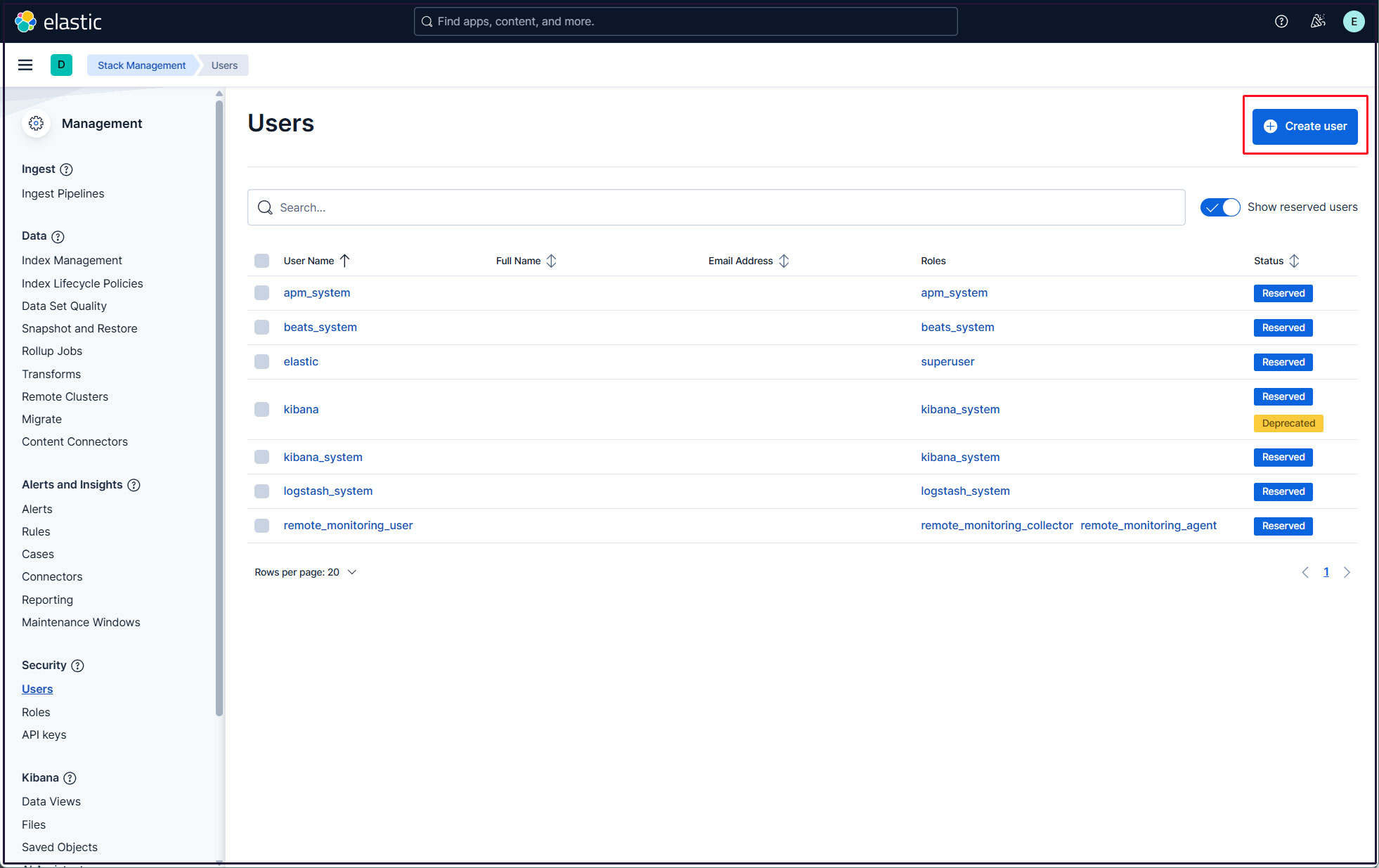
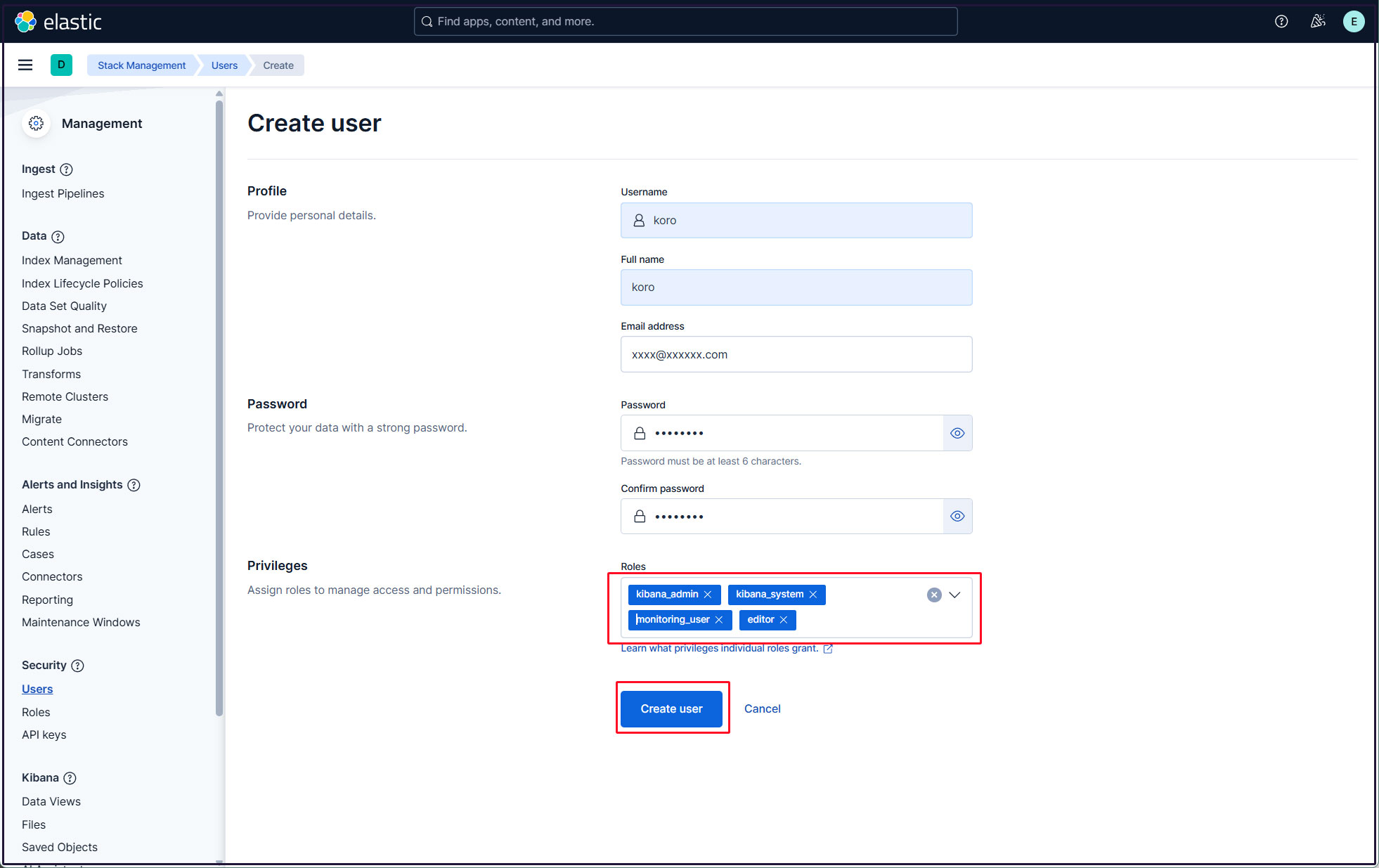
Enter new user information, assign the roles kibana_admin, kibana_system, monitoring_user, and editor in Privileges, and finally click Create user
Log out of the current profile and confirm that you can log in with the newly created user account.

