Contents
OracleLinux8.10 インストール
Oracle Linuxは、Red Hat Enterprise LinuxやCentOS Linuxに代わる100%アプリケーション・バイナリ互換性のある選択肢を提供し、ハイブリッド環境とマルチクラウド環境の両方に対応しています。
2006年以降、Oracle Linuxは完全に無料でダウンロードして使用できます。ソースコード、バイナリ、アップデートは無料で提供されます。自由に再配布可能です。本番環境での使用は無料です。
今回は、Vo.8の最新アップデートされたOracle Linux8.10(2024年8月29日リリース)で進めていきます。
Oracle Linux8.10 のインストールイメージ(OracleLinux-R8-U10-x86_64-dvd.iso )は下記サイトからダウンロード可能
https://www.oracle.com/linux/
以降インストールについてはOracleLinux8.8と同様ですので下記ページを参照してください。
OracleLinux8.10 初期設定
1.bash補完機能拡張パッケージのインストール
|
1 2 |
# dnf -y install bash-completion # reboot |
2.SELinuxの無効化
まず、selinuxを無効化します。selinuxはLinuxの監査やセキュリティを向上させる機能ですが、有効になっているとサービスの動作や、設定内容にかなりの制限が出てきます。そのため、基本的には無効にする場合が多いのが実情です。
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# getenforce ← SELinux機能の確認 Enforcing ← SELinux有効 # setenforce 0 ← SELinux機能を無効にする # getenforce ← SELinux機能の再確認 Permissive ← SELinux機能が無効である |
このままでは、サーバーを再起動すればseinuxは有効に戻りますので、永久にselinuxを無効にするには/etc/sysconfig/selinuxファイルを修正します。
|
1 |
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux |
「SELINUX=enforcing」を「SELINUX=disabled」に変更する
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. #SELINUX=enforcing SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected. # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted |
3.システムの最新化
OSインストール直後にはできるだけ早期にパッケージのアップデートを行います。
しかし、dnf updateを行うと、カーネルアップデートも同時に行われます。
カーネルアップデートを行うと、システムの再起動やサービスの停止が必要だったり、最悪カーネルパニックが発生して、システムが起動しない場合があります。カーネルを除外してアップデートする方が賢明です。
dnf -y updateの後ろに「--exclude=kernel*」を指定して実行することで
カーネルをアップデート対象から除外することできます。
|
1 |
# dnf -y update --exclude=kernel* |
4.セキュリティ対策のため停止するサービス
次の不要と思われるサービスを停止します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
# systemctl stop atd.service # systemctl disable atd.service # systemctl stop kdump.service # systemctl disable kdump.service # systemctl stop lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl disable lvm2-monitor.service # systemctl stop mdmonitor.service # systemctl disable mdmonitor.service # systemctl stop smartd.service # systemctl disable smartd.service # systemctl stop tuned.service # systemctl disable tuned.service # systemctl stop dm-event.socket # systemctl disable dm-event.socket |
5.リポジトリーの追加
5.1 EPEL repository を追加
|
1 |
# dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm -y |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo [epel] name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux $releasever - $basearch # It is much more secure to use the metalink, but if you wish to use a local mirror # place its address here. #baseurl=https://download.example/pub/epel/$releasever/Everything/$basearch metalink=https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/metalink?repo=epel-$releasever&arch=$basearch&infra=$infra&content=$contentdir enabled=1 ← リポジトリー有効(0 : リポジトリー無効) priority=10 ← 優先度を1~99の範囲で指定 gpgcheck=1 countme=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-8 [epel-debuginfo] name=Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux $releas |
5.2 Remi's RPM repository を追加
|
1 |
# dnf -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/remi-safe.repo # This repository is safe to use with RHEL/CentOS base repository # it only provides additional packages for the PHP stack # all dependencies are in base repository or in EPEL[remi-safe] name=Safe Remi's RPM repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - $basearch #baseurl=http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/httpsmirror mirrorlist=http://cdn.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/safe/$basearch/mirror enabled=1 ← リポジトリー有効(0 : リポジトリー無効) priority=10 ← 優先度を1~99の範囲で指定 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi.el8[remi-safe-debuginfo] name=Remi's RPM repository for Enterprise Linux 8 - $basearch - debuginfo baseurl=http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/8/debug-remi/$basearch/ |
6.ネットワークの設定(コマンドラインで設定の方法)
6.1 ホスト名の変更
試しにホスト名をLepardに変更します
|
1 2 3 |
# hostnamectl set-hostname Lepard # reboot [huong@Lepard:~]$ |
6.2 固定IPアドレス設定
OSインストール時にデフォルトの DHCP による IP アドレス取得の設定になっている場合は、必要に応じてネットワークの設定を変更し固定IPアドレスにします。
先に自ネットワークインターフェースの名称を下記コマンドで調べる
今回は「ens160」である
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
# ip addr 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: ens160: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:6d:ac:73 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff altname enp3s0 inet 192.168.11.26/24 brd 192.168.11.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute ens160 valid_lft 172749sec preferred_lft 172749sec inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fe6d:ac73/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever |
固定IPアドレスを「192.168.11.83」に変更します
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
// 自動取得を手動設定に変更 # nmcli con mod ens160 ipv4.method manual // IPアドレス変更 # nmcli con mod ens160 ipv4.addresses "192.168.11.83/24" // ネットワーク再起動 # nmcli con down ens160 # nmcli con up ens160 |
設定内容の確認
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
# nmcli -f ipv4 con show ens160 ipv4.method: manual ipv4.dns: 192.168.11.1 ipv4.dns-search: -- ipv4.dns-options: -- ipv4.dns-priority: 0 ipv4.addresses: 192.168.11.83/24 ipv4.gateway: 192.168.11.1 ipv4.routes: -- ipv4.route-metric: -1 ipv4.route-table: 0 (unspec) ipv4.routing-rules: -- ipv4.ignore-auto-routes: no ipv4.ignore-auto-dns: no ipv4.dhcp-client-id: -- ipv4.dhcp-iaid: -- ipv4.dhcp-timeout: 0 (default) ipv4.dhcp-send-hostname: yes ipv4.dhcp-hostname: -- ipv4.dhcp-fqdn: -- ipv4.dhcp-hostname-flags: 0x0 (none) ipv4.never-default: no ipv4.may-fail: yes ipv4.required-timeout: -1 (default) ipv4.dad-timeout: -1 (default) ipv4.dhcp-vendor-class-identifier: -- ipv4.link-local: 0 (default) ipv4.dhcp-reject-servers: -- |
7.ネットワークの設定(GUIで設定の方法)
|
1 |
# nmtui |
7.1 固定IPアドレス設定
OSインストール時にデフォルトの DHCP による IP アドレス取得の設定になっている場合は、必要に応じてネットワークの設定を変更し固定IPアドレスにします。今回はネットワークインターフェースの名称「ens160」である
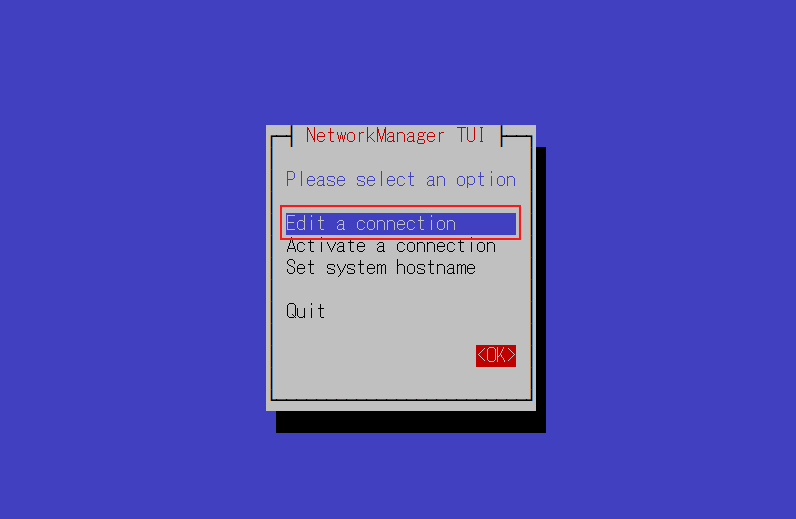
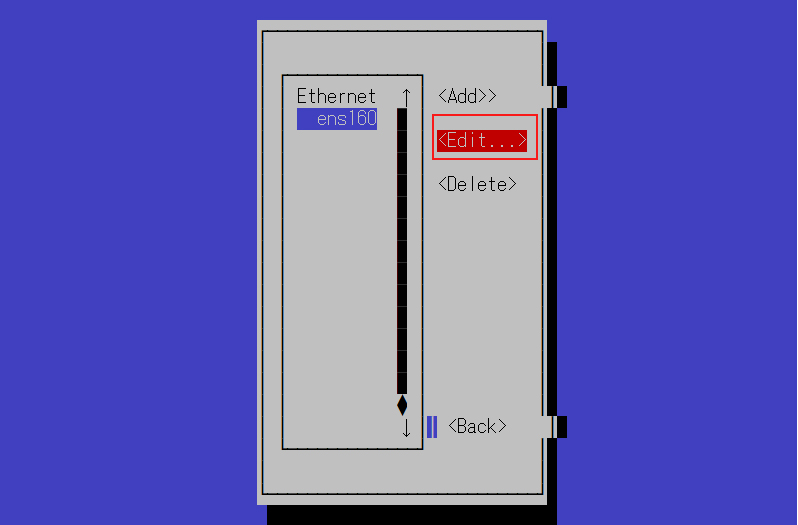
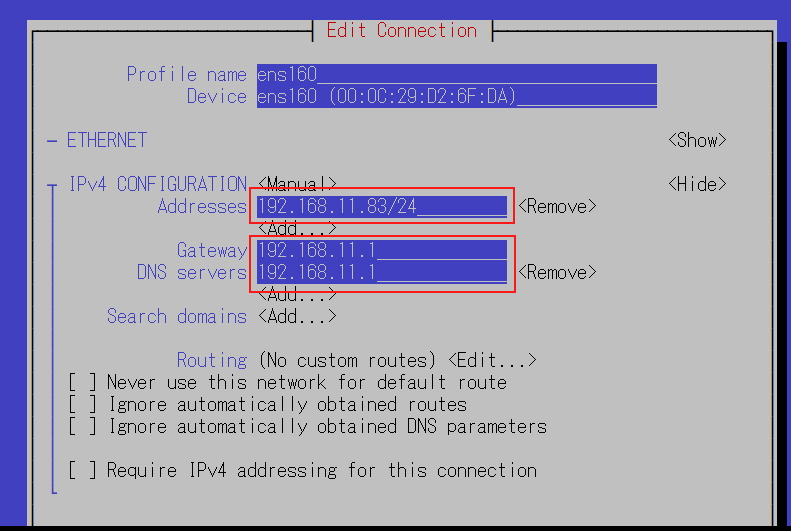
IPv4設定のアドレスを変更する
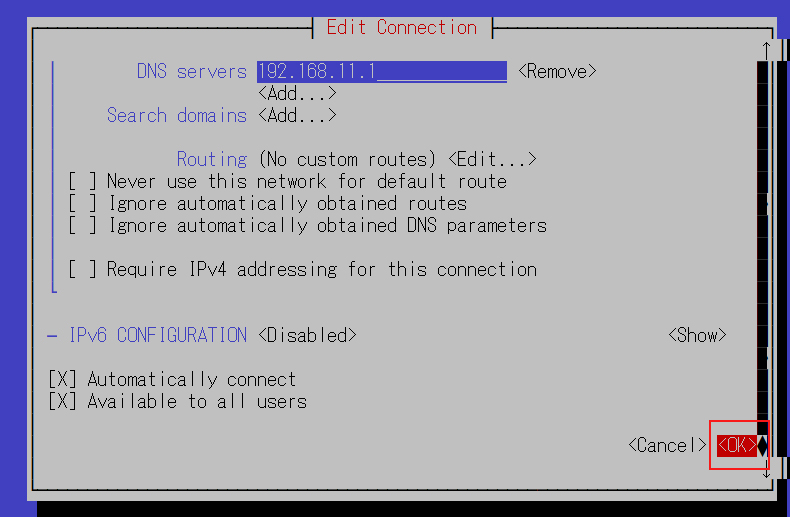
下へスクロールし、OKクリック
7.2 ホスト名の変更
試しにホスト名をLepardに変更します

8.Vimの設定
①Vim拡張機能のインストール
|
1 |
# dnf -y install vim-enhanced |
②Vimの適用と反映
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# vi ~/.bashrc # 最終行にエイリアス追記 alias vi='vim' # source ~/.bashrc |
③ユーザー固有環境として Vim の設定
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
# vi ~/.vimrc " vim の独自拡張機能を使用 (vi との互換性無し) set nocompatible " 文字コードを指定 set encoding=utf-8 " ファイルエンコードを指定 (先頭から順に成功するまで読み込む) set fileencodings=utf-8,iso-2022-jp,sjis,euc-jp " 自動認識させる改行コードを指定 set fileformats=unix,dos " バックアップを取得 set backup " バックアップを取得するディレクトリを指定 set backupdir=~/backup " 検索履歴を残す世代数 set history=50 " 検索時に大文字小文字を区別しない set ignorecase " 検索語に大文字を混ぜると検索時に大文字を区別する set smartcase " 検索語にマッチした単語をハイライト set hlsearch " インクリメンタルサーチを使用 set incsearch " 行番号を表示 set number " 改行 ( $ ) やタブ ( ^I ) を可視化 set list " 括弧入力時に対応する括弧を強調 set showmatch " ファイルの末尾に改行を入れない set binary noeol " 自動インデントを有効にする set autoindent " 構文ごとに色分け表示 syntax on " syntax on の場合のコメント文の色を変更 highlight Comment ctermfg=LightCyan " ウィンドウ幅で行を折り返す set wrap |


