Contents
MySQL8 インストール
①インストール
|
1 |
# dnf install community-mysql-server |
➁MySQLサーバーを起動
|
1 |
# systemctl start mysqld |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
# systemctl status mysqld ● mysqld.service - MySQL 8.0 database server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service; disabled; preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/service.d mq10-timeout-abort.conf, 50-keep-warm.conf Active: active (running) since Thu 2025-04-17 13:15:59 JST; 3s ago Invocation: 7c4e09bd78b84f60937297fd611e495a Process: 8437 ExecStartPre=/usr/libexec/mysql-check-socket (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 8460 ExecStartPre=/usr/libexec/mysql-prepare-db-dir mysqld.service (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 8536 (mysqld) Status: "Server is operational" Tasks: 38 (limit: 4583) Memory: 440.2M (peak: 453.8M) CPU: 2.016s CGroup: /system.slice/mysqld.service mq8536 /usr/libexec/mysqld --basedir=/usr Apr 17 13:15:55 Lepard systemd[1]: Starting mysqld.service - MySQL 8.0 database server... Apr 17 13:15:55 Lepard mysql-prepare-db-dir[8460]: Initializing MySQL database Apr 17 13:15:59 Lepard systemd[1]: Started mysqld.service - MySQL 8.0 database server. |
➂mysqlバージョン確認
|
1 2 |
# mysql -V mysql Ver 8.0.40 for Linux on x86_64 (Source distribution) |
④MySQLサーバーに接続し、rootユーザーのパスワードを変更
|
1 2 3 |
# mysql mysql>alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'password'; |
⑤基本的なポリシーを設定
「mysql_secure_installation」 コマンドを使用してrootユーザーのパスワードを設定し、いくつかの基本的なポリシーを設定します
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 |
# mysql_secure_installation Securing the MySQL server deployment. Enter password for user root: VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords and improve security. It checks the strength of password and allows the users to set only those passwords which are secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component? # パスワード品質チェックを有効にするか否か Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: y There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8 MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file # パスワード品質チェックを有効にした場合は強度を選択 Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 0 ←各自任意でよい Using existing password for root. # MySQL root パスワードを設定 Estimated strength of the password: 100 Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y New password: ← 任意のパスワード Re-enter new password: ← 再度同じパスワード # 入力したパスワードで良いかの確認 Estimated strength of the password: 100 Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. # 匿名ユーザーを削除するか否か Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. # root ユーザーのリモートログインを無効とするか否か Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. # テストデータベースを削除するか否か Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y - Dropping test database... Success. - Removing privileges on test database... Success. Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. # 特権情報をリロードするか否か Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y Success. All done! |
以降、mysqlに接続するには次のコマンドを使用する
|
1 |
# mysql -u root -p |
WordPressインストール
1. Word Press 用のデータベースを作成
例としてデータベース[wp_db] データベースユーザー[wp_user] パスワード[?W123456]とします
# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 8.0.40 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE wp_db DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
Query OK, 1 row affected, 2 warnings (0.00 sec)
mysql> CREATE USER 'wp_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '?W123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL ON wp_db.* TO 'wp_user'@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit;
Bye
2.Wordpressインストール
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # wget http://ja.wordpress.org/latest-ja.tar.gz # tar xvf latest-ja.tar.gz |
3.Wordpress設定ファイルの編集
# cd wordpress/
# cp wp-config-sample.php wp-config.php
# vi wp-config.php
<?php
/**
- The base configuration for WordPress
* - The wp-config.php creation script uses this file during the installation.
- You don't have to use the website, you can copy this file to "wp-config.php"
- and fill in the values.
* - This file contains the following configurations:
* - * Database settings
- * Secret keys
- * Database table prefix
- * ABSPATH
* - @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/wordpress/wp-config/
* - @package WordPress
*/
// ** Database settings - You can get this info from your web host ** //
/** The name of the database for WordPress */
define( 'DB_NAME', 'wp_db' );
/** Database username */
define( 'DB_USER', 'wp_user' );
/** Database password */
define( 'DB_PASSWORD', '?W123456' );
/** Database hostname */
define( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' );
/** Database charset to use in creating database tables. */
define( 'DB_CHARSET', 'utf8' );
/** The database collate type. Don't change this if in doubt. */
define( 'DB_COLLATE', '' );
/**#@+
- Authentication unique keys and salts.
* - Change these to different unique phrases! You can generate these using
- the {@link https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/ WordPress.org secret-key service}.
* - You can change these at any point in time to invalidate all existing cookies.
- This will force all users to have to log in again.
* - @since 2.6.0
*/
define( 'AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'NONCE_KEY', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
define( 'NONCE_SALT', 'put your unique phrase here' );
/*#@-/
/**
- WordPress database table prefix.
* - You can have multiple installations in one database if you give each
- a unique prefix. Only numbers, letters, and underscores please!
* - At the installation time, database tables are created with the specified prefix.
- Changing this value after WordPress is installed will make your site think
- it has not been installed.
* - @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/wordpress/wp-config/#table-prefix
*/
$table_prefix = 'wp_';
/**
- For developers: WordPress debugging mode.
* - Change this to true to enable the display of notices during development.
- It is strongly recommended that plugin and theme developers use WP_DEBUG
- in their development environments.
* - For information on other constants that can be used for debugging,
- visit the documentation.
* - @link https://developer.wordpress.org/advanced-administration/debug/debug-wordpress/
*/
define( 'WP_DEBUG', false );
/* Add any custom values between this line and the "stop editing" line. */
/* That's all, stop editing! Happy publishing. */
/** Absolute path to the WordPress directory. */
if ( ! defined( 'ABSPATH' ) ) {
define( 'ABSPATH', DIR . '/' );
}
/** Sets up WordPress vars and included files. */
require_once ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php';
また、最終行に以下の分を追加します。
これをしないと、プラグインを追加するときにFTP接続情報なるものを聞かれます。
define('FS_METHOD', 'direct');
4.ファイルの移動
①/var/www/html/[wordpress用ドメイン名]の下に展開した中身を移動
|
1 2 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # mv wordpress/* . |
移動されたことを確認後 wordpressディレクトリーとダウンロードしたlatest-ja.tar.gzを削除
|
1 2 3 |
# cd /var/www/html/[FQDN] # rm -R -f wordpress # rm latest-ja.tar.gz |
wordpressディレクトリの所有者をapacheにします
|
1 2 |
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/html/[FQDN] # systemctl restart httpd |
5.wordpress インストールの開始
ブラウザでhttp://[FQDN]/wp-admin/install.phpにアクセスし、ユーザー名、パスワード等必要事項を入力し、インストールを開始してください
「このサイトにアクセスできません」または「お使いのサーバーの PHP では WordPress に必要な MySQL 拡張を利用できないようです。」表示されたら 次をインストールしてapacheとmysqlを再起動する
|
1 2 3 |
# dnf install php-mysqlnd # systemctl restart mysqld # systemctl restart httpd |
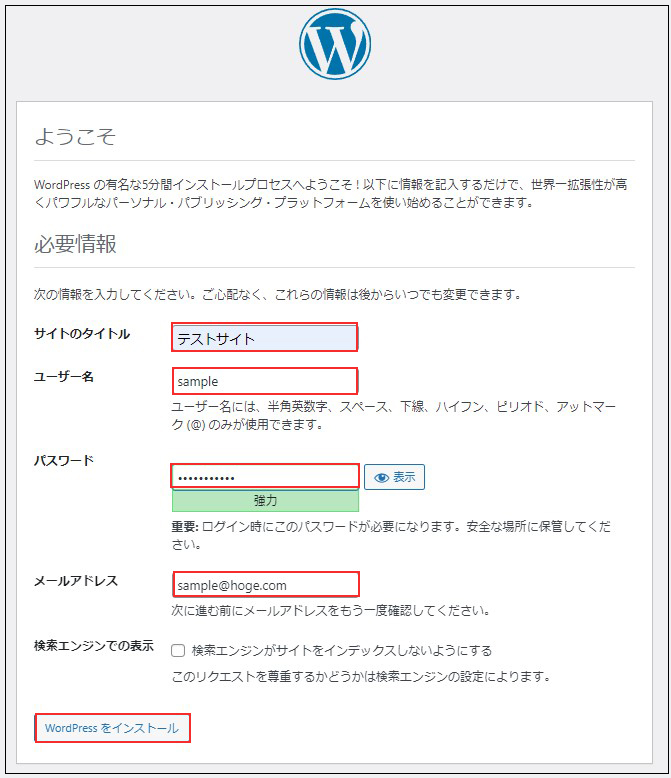
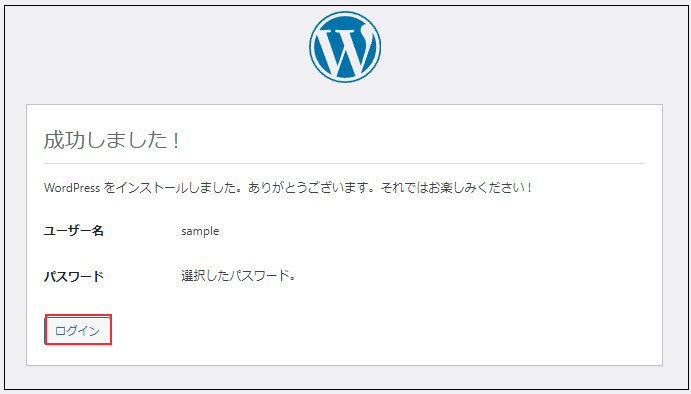
ユーザー名 : 先ほど設定したユーザー名
パスワード : 先ほど設定したユーザーのパスワード
を入力し、[ログイン]をクリック
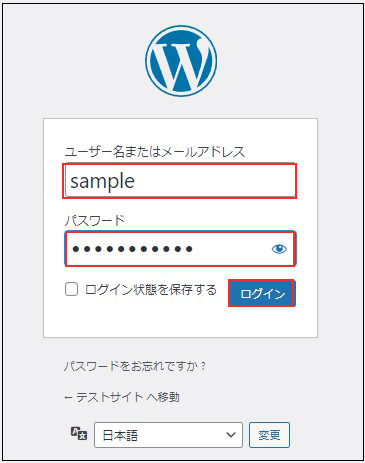
ログインに成功すると下記WordPressの管理画面にアクセスできます